目录
你是否在WPF开发中遇到过这样的困惑:为什么有时候点击子控件,父控件的事件也会被触发?为什么PreviewMouseDown总是比MouseDown先执行?如何才能优雅地处理复杂界面中的事件传播?
这些问题的答案都指向一个核心概念——路由事件。作为WPF架构的重要组成部分,路由事件不仅决定了事件的传播方式,更是构建高效用户界面的关键技术。
本文将通过3种路由策略的深入解析,帮你彻底掌握这个看似复杂但极其实用的技术点,让你的C#开发更加得心应手。
💡 路由事件:WPF中的"事件高速公路"
🔍 问题分析:为什么需要路由事件?
在传统的Windows Forms开发中,事件处理相对简单——每个控件只处理自己的事件。但在WPF的复杂UI树结构中,这种方式会带来诸多问题:
- 代码重复:为每个按钮都要写相同的事件处理逻辑
- 维护困难:修改事件逻辑需要更新多个地方
- 性能问题:大量事件处理器占用内存
- 灵活性差:无法实现统一的权限控制或日志记录
路由事件通过三种传播策略,完美解决了这些痛点。
🚀 三大路由策略实战解析
🔥 冒泡事件(Bubble):自下而上的智能传播
核心特点:事件从触发源开始,逐级向上传播到根元素
XML<Window x:Class="AppWpfEvent.MainWindow"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:AppWpfEvent"
mc:Ignorable="d"
Title="MainWindow" Height="450" Width="800">
<Grid Margin="20">
<Grid.RowDefinitions>
<RowDefinition Height="Auto"/>
<RowDefinition Height="*"/>
<RowDefinition Height="Auto"/>
</Grid.RowDefinitions>
<!-- 标题 -->
<TextBlock Grid.Row="0" Text="WPF 按钮事件统一处理示例"
FontSize="18" FontWeight="Bold"
HorizontalAlignment="Center" Margin="0,0,0,20"/>
<!-- 按钮区域 -->
<StackPanel Grid.Row="1" Orientation="Vertical"
HorizontalAlignment="Center" VerticalAlignment="Center">
<Button x:Name="SaveButton" Content="保存数据"
Width="120" Height="35" Margin="5"/>
<Button x:Name="DeleteButton" Content="删除数据"
Width="120" Height="35" Margin="5"/>
<Button x:Name="RefreshButton" Content="刷新数据"
Width="120" Height="35" Margin="5"/>
<Button x:Name="CancelButton" Content="取消操作"
Width="120" Height="35" Margin="5"/>
<!-- 测试按钮 - 没有在 switch 中定义,会走 default 分支 -->
<Button x:Name="TestButton" Content="测试按钮"
Width="120" Height="35" Margin="5"/>
</StackPanel>
<!-- 状态栏 -->
<StatusBar Grid.Row="2">
<StatusBarItem>
<TextBlock x:Name="StatusLabel" Text="就绪"/>
</StatusBarItem>
</StatusBar>
</Grid>
</Window>
C#using System.Text;
using System.Windows;
using System.Windows.Controls;
using System.Windows.Data;
using System.Windows.Documents;
using System.Windows.Input;
using System.Windows.Media;
using System.Windows.Media.Imaging;
using System.Windows.Navigation;
using System.Windows.Shapes;
namespace AppWpfEvent
{
/// <summary>
/// Interaction logic for MainWindow.xaml
/// </summary>
public partial class MainWindow : Window
{
public MainWindow()
{
InitializeComponent();
// 🎯 关键技巧:在父容器统一处理所有子按钮事件
// 使用 AddHandler 注册路由事件,即使 e.Handled=true 也能捕获
this.AddHandler(Button.ClickEvent, new RoutedEventHandler(AnyButtonClicked));
}
private void AnyButtonClicked(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
Button clickedButton = e.Source as Button;
if (clickedButton == null) return;
// 💡 实战技巧:通过按钮名称实现不同逻辑
switch (clickedButton.Name)
{
case "SaveButton":
SaveData();
break;
case "DeleteButton":
DeleteData();
break;
case "CancelButton":
CancelOperation();
break;
case "RefreshButton":
RefreshData();
break;
default:
LogButtonClick(clickedButton.Name);
break;
}
// ⚠️ 重要:阻止事件继续向上冒泡(可选)
e.Handled = true;
}
#region 业务逻辑方法
private void SaveData()
{
try
{
// 模拟保存操作
MessageBox.Show("数据保存成功!", "提示", MessageBoxButton.OK, MessageBoxImage.Information);
LogButtonClick("SaveButton - 执行成功");
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
MessageBox.Show($"保存失败:{ex.Message}", "错误", MessageBoxButton.OK, MessageBoxImage.Error);
}
}
private void DeleteData()
{
var result = MessageBox.Show("确定要删除数据吗?", "确认",
MessageBoxButton.YesNo, MessageBoxImage.Question);
if (result == MessageBoxResult.Yes)
{
// 执行删除操作
MessageBox.Show("数据删除成功!", "提示", MessageBoxButton.OK, MessageBoxImage.Information);
LogButtonClick("DeleteButton - 执行成功");
}
}
private void CancelOperation()
{
// 取消当前操作
MessageBox.Show("操作已取消", "提示", MessageBoxButton.OK, MessageBoxImage.Information);
LogButtonClick("CancelButton - 操作取消");
}
private void RefreshData()
{
// 刷新数据
MessageBox.Show("数据刷新完成!", "提示", MessageBoxButton.OK, MessageBoxImage.Information);
LogButtonClick("RefreshButton - 刷新完成");
}
private void LogButtonClick(string buttonName)
{
string logMessage = $"[{DateTime.Now:yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss}] 按钮点击: {buttonName}";
// 这里可以写入日志文件、数据库或控制台
Console.WriteLine(logMessage);
// 或者显示在状态栏
// StatusLabel.Content = logMessage;
}
#endregion
}
}

🎯 实际应用场景:
- 数据网格操作:统一处理编辑、删除、查看按钮
- 工具栏管理:集中处理所有工具按钮的权限和状态
- 动态UI:为运行时创建的控件提供统一事件处理
⚠️ 常见坑点提醒:
- 忘记设置
e.Handled = true导致事件过度传播 - 混淆
e.Source和sender的区别(Source是事件真正来源)
🏃 隧道事件(Tunnel):自上而下的预处理机制
核心特点:事件从根元素开始向下传播,通常用于预处理
C#using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows;
using System.Windows.Controls;
using System.Windows.Data;
using System.Windows.Documents;
using System.Windows.Input;
using System.Windows.Media;
using System.Windows.Media.Imaging;
using System.Windows.Navigation;
using System.Windows.Shapes;
namespace AppWpfEvent
{
/// <summary>
/// Interaction logic for SecurePanel.xaml
/// </summary>
public partial class SecurePanel : UserControl
{
private readonly IPermissionService _permissionService;
private readonly ILoggingService _loggingService;
private readonly Dictionary<string, UserRole> _controlPermissions;
public SecurePanel()
{
InitializeComponent();
// 依赖注入初始化
_permissionService = new PermissionService();
_loggingService = new LoggingService();
// 控件权限映射
_controlPermissions = new Dictionary<string, UserRole>
{
["DeleteButton"] = UserRole.Admin,
["SaveButton"] = UserRole.Editor,
["ViewButton"] = UserRole.Guest
};
InitializeSecurityEvents();
}
private void InitializeSecurityEvents()
{
// 🔒 隧道事件:在子控件处理前进行预处理
this.PreviewMouseDown += SecurePanel_PreviewMouseDown;
this.PreviewKeyDown += SecurePanel_PreviewKeyDown;
this.PreviewTextInput += SecurePanel_PreviewTextInput;
// 📊 冒泡事件:记录最终执行的操作
this.AddHandler(Button.ClickEvent, new RoutedEventHandler(LogButtonAction));
}
#region 隧道事件处理(预处理)
private void SecurePanel_PreviewMouseDown(object sender, MouseButtonEventArgs e)
{
var targetElement = e.Source as FrameworkElement;
if (targetElement == null) return;
// 📋 权限检查
if (!CheckControlPermission(targetElement))
{
e.Handled = true;
ShowPermissionDeniedMessage(targetElement.Name);
return;
}
// 📊 操作日志
_loggingService.LogUserAction($"鼠标点击: {targetElement.GetType().Name} - {targetElement.Name}");
// 🎯 输入验证
if (!ValidateInput(targetElement, e))
{
e.Handled = true;
return;
}
// 🚨 安全检查
if (!PassSecurityCheck(targetElement, "MouseClick"))
{
e.Handled = true;
_loggingService.LogSecurityViolation($"安全检查失败: {targetElement.Name}");
return;
}
}
private void SecurePanel_PreviewKeyDown(object sender, KeyEventArgs e)
{
var targetElement = e.Source as FrameworkElement;
// 🚫 危险快捷键控制
if (IsDangerousKey(e.Key))
{
if (!_permissionService.HasPermission(UserRole.Admin))
{
e.Handled = true;
ShowKeyboardRestrictionMessage(e.Key);
return;
}
}
// 📝 特殊输入控制
if (targetElement is TextBox textBox)
{
if (!ValidateKeyInput(textBox, e.Key))
{
e.Handled = true;
ShowInputValidationError($"不允许的输入: {e.Key}");
return;
}
}
_loggingService.LogUserAction($"键盘输入: {e.Key} 在 {targetElement?.Name ?? "Unknown"}");
}
private void SecurePanel_PreviewTextInput(object sender, TextCompositionEventArgs e)
{
var textBox = e.Source as TextBox;
if (textBox == null) return;
// 🔤 字符级别验证
if (!ValidateTextInput(textBox, e.Text))
{
e.Handled = true;
ShowInputValidationError($"不允许的字符: {e.Text}");
_loggingService.LogSecurityViolation($"非法字符输入尝试: {e.Text}");
}
}
#endregion
#region 权限验证方法
private bool CheckControlPermission(FrameworkElement element)
{
if (element?.Name == null) return true;
// 检查控件特定权限
if (_controlPermissions.TryGetValue(element.Name, out UserRole requiredRole))
{
var hasPermission = _permissionService.HasPermission(requiredRole);
if (!hasPermission)
{
_loggingService.LogSecurityViolation(
$"权限不足: 用户尝试访问 {element.Name},需要 {requiredRole} 权限");
}
return hasPermission;
}
return true; // 未配置权限的控件默认允许
}
private bool ValidateInput(FrameworkElement element, MouseButtonEventArgs e)
{
// 🎯 特定控件的输入验证
switch (element)
{
case TextBox textBox when string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(textBox.Text):
ShowInputValidationError("文本框不能为空");
return false;
case Button button when button.IsEnabled == false:
ShowInputValidationError("按钮当前不可用");
return false;
default:
return true;
}
}
private bool PassSecurityCheck(FrameworkElement element, string actionType)
{
// 🛡️ 安全规则检查
var securityContext = new SecurityContext
{
ElementName = element.Name,
ActionType = actionType,
Timestamp = DateTime.Now,
UserRole = _permissionService.GetCurrentUserRole()
};
return _permissionService.ValidateSecurityContext(securityContext);
}
#endregion
#region 输入验证方法
private bool IsDangerousKey(Key key)
{
var dangerousKeys = new[] { Key.Delete, Key.F12, Key.System };
return dangerousKeys.Contains(key);
}
private bool ValidateKeyInput(TextBox textBox, Key key)
{
// 根据文本框名称应用不同验证规则
switch (textBox.Name)
{
case "NumericTextBox":
return key >= Key.D0 && key <= Key.D9 ||
key >= Key.NumPad0 && key <= Key.NumPad9 ||
key == Key.Back || key == Key.Delete || key == Key.Tab;
case "AlphaTextBox":
return (key >= Key.A && key <= Key.Z) ||
key == Key.Back || key == Key.Delete || key == Key.Tab;
default:
return true;
}
}
private bool ValidateTextInput(TextBox textBox, string input)
{
// 危险字符检查
var dangerousChars = new[] { "<", ">", "&", "\"", "'", "script" };
foreach (var dangerousChar in dangerousChars)
{
if (input.Contains(dangerousChar))
{
return false;
}
}
// 长度检查
if (textBox.Text.Length + input.Length > textBox.MaxLength && textBox.MaxLength > 0)
{
return false;
}
return true;
}
#endregion
#region 冒泡事件处理(后处理)
private void LogButtonAction(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
if (e.Source is Button button)
{
_loggingService.LogUserAction($"按钮执行完成: {button.Name} - {button.Content}");
// 执行成功后的额外处理
OnActionCompleted(button.Name);
}
}
private void OnActionCompleted(string actionName)
{
// 🎉 操作完成后的业务逻辑
switch (actionName)
{
case "SaveButton":
ShowSuccessMessage("数据保存成功!");
break;
case "DeleteButton":
ShowSuccessMessage("数据删除成功!");
break;
}
}
#endregion
#region 消息显示方法
private void ShowPermissionDeniedMessage(string elementName)
{
var requiredRole = _controlPermissions.TryGetValue(elementName, out UserRole role)
? role.ToString()
: "未知";
MessageBox.Show($"权限不足!访问 {elementName} 需要 {requiredRole} 权限。",
"权限错误", MessageBoxButton.OK, MessageBoxImage.Warning);
}
private void ShowKeyboardRestrictionMessage(Key key)
{
MessageBox.Show($"快捷键 {key} 被限制使用,需要管理员权限。",
"操作限制", MessageBoxButton.OK, MessageBoxImage.Information);
}
private void ShowInputValidationError(string message)
{
MessageBox.Show($"输入验证失败:{message}",
"输入错误", MessageBoxButton.OK, MessageBoxImage.Error);
}
private void ShowSuccessMessage(string message)
{
MessageBox.Show(message, "操作成功",
MessageBoxButton.OK, MessageBoxImage.Information);
}
#endregion
}
#region 服务接口和实现
// 💡 权限服务接口
public interface IPermissionService
{
bool HasPermission(UserRole role);
UserRole GetCurrentUserRole();
bool ValidateSecurityContext(SecurityContext context);
}
public class PermissionService : IPermissionService
{
private readonly UserRole _currentUserRole = UserRole.Editor; // 模拟当前用户角色
public bool HasPermission(UserRole requiredRole)
{
// 权限级别:Admin > Editor > Guest
return _currentUserRole >= requiredRole;
}
public UserRole GetCurrentUserRole()
{
return _currentUserRole;
}
public bool ValidateSecurityContext(SecurityContext context)
{
// 🛡️ 复杂的安全验证逻辑
// 时间窗口检查(防止重放攻击)
if ((DateTime.Now - context.Timestamp).TotalSeconds > 30)
{
return false;
}
// 权限上下文检查
if (context.ActionType == "MouseClick" && context.UserRole < UserRole.Editor)
{
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
// 📊 日志服务接口
public interface ILoggingService
{
void LogUserAction(string action);
void LogSecurityViolation(string violation);
}
public class LoggingService : ILoggingService
{
public void LogUserAction(string action)
{
Console.WriteLine($"[{DateTime.Now:yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss}] ACTION: {action}");
// 实际项目中写入日志文件或数据库
}
public void LogSecurityViolation(string violation)
{
Console.WriteLine($"[{DateTime.Now:yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss}] SECURITY: {violation}");
// 发送安全警报或写入安全日志
}
}
#endregion
#region 数据模型
public enum UserRole
{
Guest = 1,
Editor = 2,
Admin = 3
}
public class SecurityContext
{
public string ElementName { get; set; }
public string ActionType { get; set; }
public DateTime Timestamp { get; set; }
public UserRole UserRole { get; set; }
}
#endregion
}
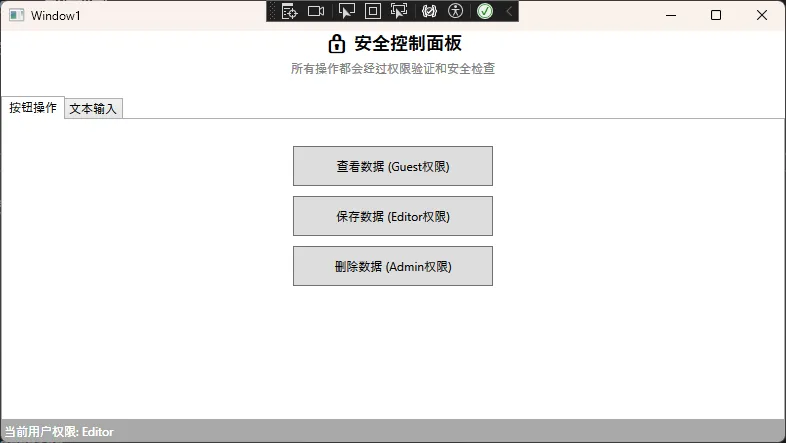 🎯 实际应用场景:
🎯 实际应用场景:
- 安全控制:在用户操作前进行权限验证
- 输入过滤:阻止不合法的输入或操作
- 全局监控:记录用户行为和系统日志
⭐ 直接事件(Direct):精准控制的专用通道
核心特点:事件只在定义它的对象上触发,不进行任何传播
C#using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Controls;
using System.Windows.Media;
using System.Windows.Threading;
using System.Windows;
namespace AppWpfEvent
{
public class SmartButton : Button
{
// 🎯 定义直接路由事件
public static readonly RoutedEvent ValidationCompletedEvent =
EventManager.RegisterRoutedEvent(
"ValidationCompleted",
RoutingStrategy.Direct, // 关键:只在当前对象触发,不传播
typeof(RoutedEventHandler),
typeof(SmartButton));
// 📝 .NET标准事件访问器
public event RoutedEventHandler ValidationCompleted
{
add { AddHandler(ValidationCompletedEvent, value); }
remove { RemoveHandler(ValidationCompletedEvent, value); }
}
// 🔒 验证状态
private bool _isValidating = false;
private string _originalContent;
protected override async void OnClick()
{
if (_isValidating) return;
try
{
_isValidating = true;
_originalContent = this.Content?.ToString();
// 🎨 开始验证状态
this.IsEnabled = false;
this.Background = Brushes.Orange;
this.Content = "验证中...";
// 🌐 异步验证(模拟2秒网络请求)
await Task.Delay(2000);
bool isValid = new Random().Next(0, 2) == 1; // 随机结果
// 🔔 触发直接事件(重点:只在这个按钮上触发)
var args = new ValidationEventArgs(ValidationCompletedEvent, this)
{
IsValid = isValid,
Message = isValid ? "验证成功" : "验证失败"
};
RaiseEvent(args);
// ✅ 更新UI状态
this.Background = isValid ? Brushes.LightGreen : Brushes.LightCoral;
this.Content = args.Message;
// 只有验证成功才执行原始点击逻辑
if (isValid)
{
await Task.Delay(1000);
base.OnClick(); // 触发正常的Button点击事件
}
}
finally
{
// 🔄 2秒后恢复原始状态
await Task.Delay(2000);
_isValidating = false;
this.IsEnabled = true;
this.Content = _originalContent;
this.Background = SystemColors.ControlBrush;
}
}
}
// 🎯 自定义事件参数
public class ValidationEventArgs : RoutedEventArgs
{
public bool IsValid { get; set; }
public string Message { get; set; }
public ValidationEventArgs(RoutedEvent routedEvent, object source)
: base(routedEvent, source) { }
}
}
C#<Window x:Class="AppWpfEvent.Window2"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:AppWpfEvent"
mc:Ignorable="d"
Title="Window2" Height="450" Width="800">
<Grid Margin="30">
<Grid.RowDefinitions>
<RowDefinition Height="Auto"/>
<RowDefinition Height="Auto"/>
<RowDefinition Height="*"/>
</Grid.RowDefinitions>
<!-- 标题 -->
<TextBlock Grid.Row="0" Text="🎯 SmartButton 直接路由事件演示"
FontSize="18" FontWeight="Bold"
HorizontalAlignment="Center" Margin="0,0,0,30"/>
<!-- 按钮区域 -->
<StackPanel x:Name="ButtonPanel" Grid.Row="1"
Orientation="Horizontal" HorizontalAlignment="Center">
<!-- 这些按钮会在代码中动态创建 -->
</StackPanel>
<!-- 日志显示 -->
<Border Grid.Row="2" BorderBrush="Gray" BorderThickness="1"
Margin="0,30,0,0" Padding="10">
<ScrollViewer>
<TextBlock x:Name="LogTextBlock" FontFamily="Consolas"
FontSize="12" TextWrapping="Wrap"/>
</ScrollViewer>
</Border>
</Grid>
</Window>
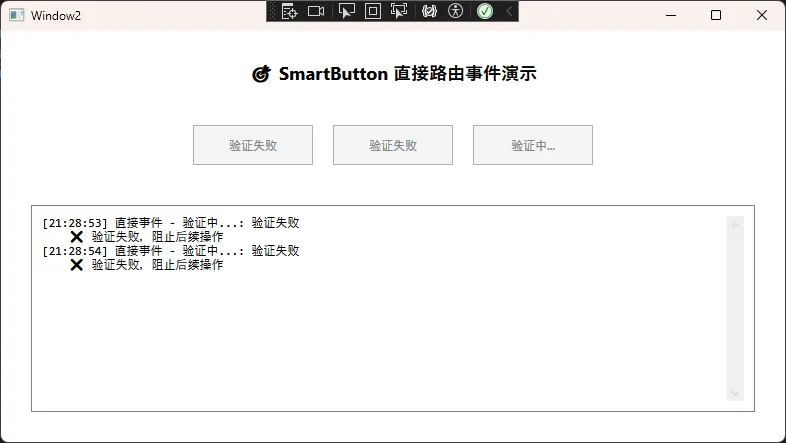
🎯 实际应用场景:
- 自定义控件:内部状态变化通知
- 业务逻辑事件:特定的业务操作完成通知
- 性能优化:避免不必要的事件传播开销
🛠️ 最佳实践与性能优化
💎 选择合适的路由策略
C#// ✅ 推荐做法:根据场景选择路由策略
public class EventStrategyGuide
{
public void DemonstrateProperUsage()
{
// 🔥 冒泡事件:适合统一处理多个子控件
panel.AddHandler(Button.ClickEvent, HandleAllButtons);
// 🏃 隧道事件:适合预处理和验证
panel.PreviewTextInput += ValidateInput;
// ⭐ 直接事件:适合自定义控件的特殊通知
customControl.SpecialEvent += HandleSpecialCase;
}
}
⚡ 性能优化技巧
C#public class PerformanceOptimizedEventHandler
{
// 💡 技巧1:合理使用事件处理器标记
private void OptimizedEventHandler(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
// 尽早判断并标记处理完成
if (ShouldIgnoreEvent(e.Source))
{
e.Handled = true;
return;
}
// 实际处理逻辑
ProcessEvent(e);
e.Handled = true; // 防止不必要的传播
}
// 💡 技巧2:使用弱引用避免内存泄漏
private void AttachWeakEventHandler()
{
WeakEventManager<Button, RoutedEventArgs>
.AddHandler(button, "Click", WeakEventHandler);
}
}
🎉 总结:掌握路由事件的三个关键要点
通过本文的深入解析,我们掌握了路由事件的核心知识:
- 🔥 冒泡事件是处理大量相似控件的最佳选择,能够显著减少代码重复并提高维护性
- 🏃 隧道事件是实现权限控制、输入验证等预处理逻辑的利器,为应用程序提供了强大的安全保障
- ⭐ 直接事件则是构建高性能自定义控件的必备技能,能够精确控制事件传播范围
掌握这三种路由策略,你就能够:
- 编写更加优雅和高效的事件处理代码
- 构建具有良好架构的WPF应用程序
- 解决复杂UI交互中的各种挑战
💭 思考题:在你的项目中,是否遇到过需要为大量相似控件编写重复事件处理代码的情况?你觉得哪种路由策略最适合解决这个问题?
🤝 互动邀请:如果你在使用路由事件过程中遇到了其他问题,或者有更好的实践经验,欢迎在评论区分享讨论!
觉得这篇文章对你的C#开发有帮助吗?请转发给更多的.NET同行,让我们一起提升技术水平!关注我,获取更多实用的C#开发技巧和最佳实践。
本文作者:技术老小子
本文链接:
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!
目录