目录
在日常的Python开发中,处理CSV(逗号分隔值)文件是一个非常常见的需求。无论是数据分析、报表生成,还是系统间数据交换,CSV格式都扮演着重要角色。很多开发者可能会选择pandas等第三方库,但其实Python内置的csv模块就能满足大部分需求,而且更加轻量、高效。
本文将从实战角度出发,详细介绍如何使用Python内置的csv模块来处理各种CSV文件操作场景,包括读取、写入、处理特殊字符等常见问题,让你轻松掌握这个实用的数据处理工具。
🔍 问题分析
在Windows环境下的Python开发中,CSV文件处理主要面临以下几个挑战:
编码问题
- Windows系统默认使用GBK编码
- CSV文件可能包含中文字符
- 不同来源的文件编码格式不统一
数据格式问题
- 字段中包含逗号、换行符等特殊字符
- 数字和字符串类型的混合处理
- 空值和缺失数据的处理
性能考虑
- 大文件的分批处理
- 内存占用优化
- 读写效率提升
💡 解决方案
Python的csv模块提供了reader、writer、DictReader、DictWriter等核心类,能够完美解决上述问题。
核心优势
- 原生支持:无需安装第三方库
- 编码友好:配合open()函数轻松处理编码
- 内存高效:逐行处理,适合大文件
- 格式灵活:支持自定义分隔符和引用符
💻 代码实战
🚀 基础读取操作
Pythonimport csv
def read_csv_basic(filename):
"""基础CSV文件读取"""
try:
with open(filename, 'r', encoding='utf-8', newline='') as file:
csv_reader = csv.reader(file)
# 读取标题行
headers = next(csv_reader)
print(f"表头: {headers}")
# 读取数据行
for row_num, row in enumerate(csv_reader, 1):
print(f"第{row_num}行: {row}")
except FileNotFoundError:
print(f"文件 {filename} 不存在")
except UnicodeDecodeError:
print("编码错误,尝试使用GBK编码")
# 自动尝试GBK编码
with open(filename, 'r', encoding='gbk', newline='') as file:
csv_reader = csv.reader(file)
for row in csv_reader:
print(row)
# 使用示例
read_csv_basic('振动数据.csv')
🎯 字典模式读取(推荐)
Pythonimport csv
def read_csv_dict(filename):
"""使用DictReader读取CSV,更直观易用"""
try:
with open(filename, 'r', encoding='utf-8', newline='') as file:
csv_reader = csv.DictReader(file)
print(f"字段名: {csv_reader.fieldnames}")
for row_num, row in enumerate(csv_reader, 1):
print(f"第{row_num}行数据:")
for key, value in row.items():
print(f" {key}: {value}")
print("-" * 30)
except Exception as e:
print(f"读取文件时发生错误: {e}")
# 实际应用示例:处理员工数据
def process_employee_data(filename):
"""处理员工数据CSV文件"""
employees = []
with open(filename, 'r', encoding='utf-8', newline='') as file:
reader = csv.DictReader(file)
for row in reader:
# 数据清洗和类型转换
employee = {
'name': row['姓名'].strip(),
'age': int(row['年龄']) if row['年龄'].isdigit() else 0,
'salary': float(row['工资']) if row['工资'] else 0.0,
'department': row['部门'].strip()
}
employees.append(employee)
return employees
✍️ CSV文件写入操作
Pythonimport csv
def write_csv_basic(filename, data):
"""基础CSV写入操作"""
with open(filename, 'w', encoding='utf-8', newline='') as file:
csv_writer = csv.writer(file)
# 写入表头
csv_writer.writerow(['姓名', '年龄', '城市'])
# 写入数据
for row in data:
csv_writer.writerow(row)
# 使用示例
sample_data = [
['张三', 25, '北京'],
['李四', 30, '上海'],
['王五', 28, '深圳']
]
write_csv_basic('output.csv', sample_data)
🎨 字典模式写入(推荐)
Pythonimport csv
def write_csv_dict(filename, data, fieldnames):
"""使用DictWriter写入CSV"""
with open(filename, 'w', encoding='utf-8', newline='') as file:
writer = csv.DictWriter(file, fieldnames=fieldnames)
# 写入表头
writer.writeheader()
# 写入数据
writer.writerows(data)
# 实际应用:生成销售报表
def generate_sales_report():
"""生成销售报表示例"""
sales_data = [
{'产品名称': 'iPhone 14', '销量': 150, '单价': 6999, '总金额': 1049850},
{'产品名称': 'MacBook Pro', '销量': 80, '单价': 19999, '总金额': 1599920},
{'产品名称': 'iPad Air', '销量': 200, '单价': 4399, '总金额': 879800}
]
fieldnames = ['产品名称', '销量', '单价', '总金额']
write_csv_dict('sales_report.csv', sales_data, fieldnames)
print("销售报表生成完成!")
generate_sales_report()
🔧 处理特殊字符和格式
Pythonimport csv
def handle_special_csv():
"""处理包含特殊字符的CSV文件"""
# 自定义CSV格式
class CustomDialect(csv.Dialect):
delimiter = ';' # 使用分号作为分隔符
quotechar = '"'
quoting = csv.QUOTE_MINIMAL
lineterminator = '\n'
escapechar = '\\' # 设置转义字符
# 注册自定义方言
csv.register_dialect('custom', CustomDialect)
# 写入包含特殊字符的数据
special_data = [
['商品描述', '价格', '备注'],
['苹果,红色,甜', '5.5', '产地:新疆\n品质优良'],
['香蕉;黄色', '3.2', '含有"维生素"丰富']
]
with open('special_data.csv', 'w', encoding='utf-8', newline='') as file:
writer = csv.writer(file, dialect='custom')
for row in special_data:
writer.writerow(row)
# 读取包含特殊字符的数据
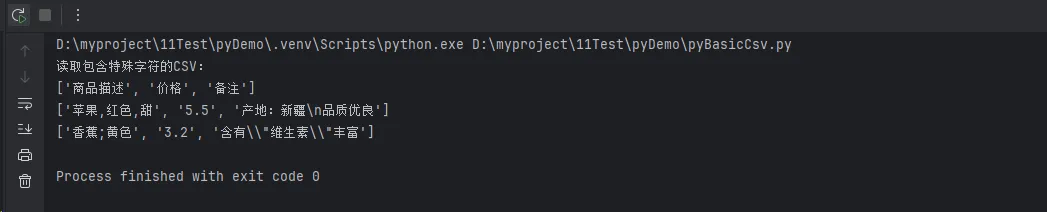
print("读取包含特殊字符的CSV:")
with open('special_data.csv', 'r', encoding='utf-8', newline='') as file:
reader = csv.reader(file, delimiter=';')
for row in reader:
print(row)
handle_special_csv()
📊 大文件处理优化
Pythonimport csv
def process_large_csv(filename, batch_size=1000):
"""分批处理大型CSV文件"""
def process_batch(batch_data):
"""处理一批数据"""
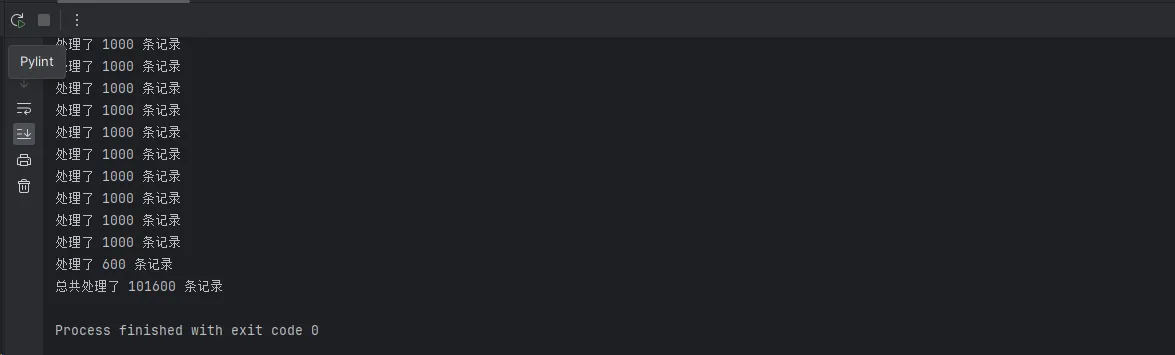
# 这里可以进行数据处理、计算、存储等操作
print(f"处理了 {len(batch_data)} 条记录")
return len(batch_data)
total_processed = 0
batch_data = []
try:
with open(filename, 'r', encoding='utf-8', newline='') as file:
reader = csv.DictReader(file)
for row in reader:
batch_data.append(row)
# 达到批次大小时处理数据
if len(batch_data) >= batch_size:
total_processed += process_batch(batch_data)
batch_data = [] # 清空批次数据
# 处理最后一批数据
if batch_data:
total_processed += process_batch(batch_data)
print(f"总共处理了 {total_processed} 条记录")
except MemoryError:
print("内存不足,建议减小batch_size")
except Exception as e:
print(f"处理文件时发生错误: {e}")
process_large_csv("振动数据.csv")
🛠️ 实用工具函数
Pythonimport csv
class CSVHelper:
"""CSV处理工具类"""
@staticmethod
def detect_encoding(filename):
"""检测CSV文件编码"""
import chardet
with open(filename, 'rb') as file:
raw_data = file.read(10000) # 读取前10KB
result = chardet.detect(raw_data)
return result['encoding']
@staticmethod
def csv_to_dict_list(filename, encoding='utf-8'):
"""将CSV文件转换为字典列表"""
data = []
try:
with open(filename, 'r', encoding=encoding, newline='') as file:
reader = csv.DictReader(file)
for row in reader:
data.append(dict(row))
except UnicodeDecodeError:
# 尝试其他编码
encoding = CSVHelper.detect_encoding(filename)
return CSVHelper.csv_to_dict_list(filename, encoding)
return data
@staticmethod
def filter_csv(input_file, output_file, filter_func):
"""根据条件过滤CSV数据"""
with open(input_file, 'r', encoding='utf-8', newline='') as infile, \
open(output_file, 'w', encoding='utf-8', newline='') as outfile:
reader = csv.DictReader(infile)
writer = csv.DictWriter(outfile, fieldnames=reader.fieldnames)
writer.writeheader()
for row in reader:
if filter_func(row):
writer.writerow(row)
# 使用示例
def salary_filter(row):
"""筛选工资大于5000的员工"""
try:
return float(row.get('工资', 0)) > 5000
except ValueError:
return False
CSVHelper.filter_csv('employee.csv', 'high_salary.csv', salary_filter)
🎯 总结
通过本文的详细介绍,我们掌握了Python内置csv模块的核心用法。总结一下三个关键要点:
- 编码处理是关键:在Windows环境下,正确处理UTF-8和GBK编码能避免90%的乱码问题,记住使用
encoding参数和newline=''。 - 字典模式更实用:DictReader和DictWriter让代码更易读易维护,特别适合处理有明确字段含义的数据文件。
- 大文件要分批处理:合理使用批处理和生成器,能够高效处理大型CSV文件而不会造成内存溢出。
掌握这些技巧后,你就能在Python开发中游刃有余地处理各种CSV文件操作需求了。无论是数据导入导出、报表生成,还是系统集成,csv模块都能为你提供可靠的解决方案。继续深入学习Python数据处理,可以进一步了解pandas、openpyxl等更强大的数据处理库。
本文作者:技术老小子
本文链接:
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!
目录