目录
在Windows窗体应用程序开发中,数据绑定是一项核心技术,能够有效地将用户界面与底层数据源连接起来。本文将详细介绍如何在C# Windows Forms应用中实现复杂数据绑定,特别是使用DataGridView控件展示和管理数据。无论你是C#初学者还是希望提升数据处理能力的开发者,本教程都能帮助你掌握这一重要技能。
什么是数据绑定?
数据绑定是指将UI控件与数据源建立连接,使得数据能够自动在两者之间流动。在Windows Forms中,这意味着当数据源发生变化时,UI控件会自动更新;同样,当用户通过UI修改数据时,这些更改也会反映到底层数据源中。
BindingSource类的作用
BindingSource是实现复杂数据绑定的关键组件,它充当UI控件与数据源之间的中介,提供以下优势:
- 简化数据源与控件之间的连接
- 支持数据筛选和排序
- 提供内置的导航功能
- 处理数据变更通知
- 简化多控件共享同一数据源的实现
实战案例:员工管理系统
下面,我们将通过一个员工管理系统的案例,展示如何实现复杂数据绑定。
第一步:定义数据模型
首先,我们需要创建一个代表员工的数据模型类:
C#// 员工数据模型
public class Employee
{
public int Id { get; set; } // 员工ID
public string Name { get; set; } // 姓名
public string Department { get; set; } // 所属部门
public decimal Salary { get; set; } // 薪资
public DateTime HireDate { get; set; } // 入职日期
public bool IsActive { get; set; } // 在职状态
}
第二步:初始化数据源
接下来,我们需要创建一个数据源,在实际应用中这通常来自数据库,但在本例中我们使用模拟数据:
C#// 初始化员工数据
private void InitializeDataSource()
{
// 模拟数据库数据
employeeList = new List<Employee>
{
new Employee {
Id = 1,
Name = "张三",
Department = "技术部",
Salary = 8000,
HireDate = DateTime.Now.AddYears(-3),
IsActive = true
},
new Employee {
Id = 2,
Name = "李四",
Department = "市场部",
Salary = 7000,
HireDate = DateTime.Now.AddYears(-2),
IsActive = true
},
new Employee {
Id = 3,
Name = "王五",
Department = "人事部",
Salary = 6000,
HireDate = DateTime.Now.AddYears(-1),
IsActive = false
}
};
}
第三步:配置DataGridView并绑定数据
最后,我们将数据源与DataGridView控件绑定,并自定义显示效果:
C#// 配置DataGridView并绑定数据
private void SetupDataGridView()
{
// 创建绑定源作为UI与数据之间的桥梁
bindingSource = new BindingSource();
bindingSource.DataSource = employeeList;
// 将绑定源关联到DataGridView
dataGridView1.DataSource = bindingSource;
// 自定义列显示
dataGridView1.Columns["Id"].Visible = false; // 隐藏ID列
dataGridView1.Columns["Name"].HeaderText = "姓名";
dataGridView1.Columns["Department"].HeaderText = "部门";
dataGridView1.Columns["Salary"].HeaderText = "薪资";
dataGridView1.Columns["HireDate"].HeaderText = "入职日期";
dataGridView1.Columns["IsActive"].HeaderText = "在职状态";
}
完整代码示例
下面是实现这一功能的完整代码:
C#using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace AppDataGrid
{
public partial class Form2 : Form
{
// 数据源集合
private List<Employee> employeeList;
// 绑定源
private BindingSource bindingSource;
public Form2()
{
InitializeComponent();
InitializeDataSource();
InitializeDataGridView();
SetupDataGridView();
}
// 代码初始化方式
private void InitializeDataGridView()
{
// 设置一些常用属性
dataGridView1.AllowUserToAddRows = false; // 不允许用户添加行
dataGridView1.AllowUserToDeleteRows = false; // 不允许用户删除行
dataGridView1.ReadOnly = true; // 禁用编辑功能
dataGridView1.AutoSizeColumnsMode = DataGridViewAutoSizeColumnsMode.Fill; // 自动调整列宽度以填充整个DataGridView
dataGridView1.SelectionMode = DataGridViewSelectionMode.FullRowSelect; // 选择整行
}
// 配置DataGridView并绑定数据
private void SetupDataGridView()
{
// 创建绑定源作为UI与数据之间的桥梁
bindingSource = new BindingSource();
bindingSource.DataSource = employeeList;
// 将绑定源关联到DataGridView
dataGridView1.DataSource = bindingSource;
// 自定义列显示
dataGridView1.Columns["Id"].Visible = false; // 隐藏ID列
dataGridView1.Columns["Name"].HeaderText = "姓名";
dataGridView1.Columns["Department"].HeaderText = "部门";
dataGridView1.Columns["Salary"].HeaderText = "薪资";
dataGridView1.Columns["HireDate"].HeaderText = "入职日期";
dataGridView1.Columns["IsActive"].HeaderText = "在职状态";
}
// 初始化员工数据
private void InitializeDataSource()
{
// 模拟数据库数据
employeeList = new List<Employee>
{
new Employee {
Id = 1,
Name = "张三",
Department = "技术部",
Salary = 8000,
HireDate = DateTime.Now.AddYears(-3),
IsActive = true
},
new Employee {
Id = 2,
Name = "李四",
Department = "市场部",
Salary = 7000,
HireDate = DateTime.Now.AddYears(-2),
IsActive = true
},
new Employee {
Id = 3,
Name = "王五",
Department = "人事部",
Salary = 6000,
HireDate = DateTime.Now.AddYears(-1),
IsActive = false
}
};
}
}
}

扩展功能
在实际应用中,我们可以为这个简单示例添加更多功能:
添加员工信息
C#private void btnAdd_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// 创建新员工
Employee newEmployee = new Employee
{
Id = employeeList.Count + 1,
Name = "新员工",
Department = "待分配",
Salary = 5000,
HireDate = DateTime.Now,
IsActive = true
};
// 添加到集合
employeeList.Add(newEmployee);
// 刷新数据源
bindingSource.ResetBindings(false);
}
删除员工信息
C#private void btnDelete_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (dataGridView1.SelectedRows.Count > 0)
{
// 获取选中的员工
Employee selectedEmployee = dataGridView1.SelectedRows[0].DataBoundItem as Employee;
// 从集合中移除
employeeList.Remove(selectedEmployee);
// 刷新数据源
bindingSource.ResetBindings(false);
}
}
实现数据筛选
因为这上面绑定的是List,所以用以下方法
C#private List<Employee> filteredEmployeeList; // 存储过滤后数据
private void txtSearch_TextChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
string filterText = txtSearch.Text.Trim();
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(filterText))
{
// 还原为原始数据
bindingSource.DataSource = employeeList;
}
else
{
// 使用LINQ过滤
filteredEmployeeList = employeeList
.Where(emp => emp.Name.Contains(filterText, StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase))
.ToList();
// 重新设置数据源
bindingSource.DataSource = null;
bindingSource.DataSource = filteredEmployeeList;
}
// 确保DataGridView更新显示
dataGridView1.Refresh();
}

绑定如果是DataTable(推荐这个)
C#using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace AppDataGrid
{
public partial class Form2 : Form
{
// 数据源
private DataTable employeeTable;
// 数据视图
private DataView employeeView;
public Form2()
{
InitializeComponent();
InitializeDataSource();
InitializeDataGridView();
SetupDataGridView();
}
// 代码初始化方式
private void InitializeDataGridView()
{
// 设置一些常用属性
dataGridView1.AllowUserToAddRows = false; // 不允许用户添加行
dataGridView1.AllowUserToDeleteRows = false; // 不允许用户删除行
dataGridView1.ReadOnly = true; // 禁用编辑功能
dataGridView1.AutoSizeColumnsMode = DataGridViewAutoSizeColumnsMode.Fill; // 自动调整列宽度以填充整个DataGridView
dataGridView1.SelectionMode = DataGridViewSelectionMode.FullRowSelect; // 选择整行
}
// 配置DataGridView并绑定数据
private void SetupDataGridView()
{
// 创建DataView作为数据源
employeeView = new DataView(employeeTable);
// 将DataView绑定到DataGridView
dataGridView1.DataSource = employeeView;
// 自定义列显示
dataGridView1.Columns["Id"].Visible = false; // 隐藏ID列
dataGridView1.Columns["Name"].HeaderText = "姓名";
dataGridView1.Columns["Department"].HeaderText = "部门";
dataGridView1.Columns["Salary"].HeaderText = "薪资";
dataGridView1.Columns["HireDate"].HeaderText = "入职日期";
dataGridView1.Columns["IsActive"].HeaderText = "在职状态";
}
// 初始化员工数据
private void InitializeDataSource()
{
// 创建DataTable
employeeTable = new DataTable("Employees");
// 定义DataTable结构
employeeTable.Columns.Add("Id", typeof(int));
employeeTable.Columns.Add("Name", typeof(string));
employeeTable.Columns.Add("Department", typeof(string));
employeeTable.Columns.Add("Salary", typeof(decimal));
employeeTable.Columns.Add("HireDate", typeof(DateTime));
employeeTable.Columns.Add("IsActive", typeof(bool));
// 设置主键
employeeTable.PrimaryKey = new DataColumn[] { employeeTable.Columns["Id"] };
// 添加初始数据
employeeTable.Rows.Add(1, "张三", "技术部", 8000, DateTime.Now.AddYears(-3), true);
employeeTable.Rows.Add(2, "李四", "市场部", 7000, DateTime.Now.AddYears(-2), true);
employeeTable.Rows.Add(3, "王五", "人事部", 6000, DateTime.Now.AddYears(-1), false);
}
private void btnAdd_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// 获取新ID
int newId = 1;
if (employeeTable.Rows.Count > 0)
{
newId = employeeTable.AsEnumerable()
.Max(row => row.Field<int>("Id")) + 1;
}
// 创建新行
DataRow newRow = employeeTable.NewRow();
newRow["Id"] = newId;
newRow["Name"] = "新员工";
newRow["Department"] = "待分配";
newRow["Salary"] = 5000;
newRow["HireDate"] = DateTime.Now;
newRow["IsActive"] = true;
// 添加到DataTable
employeeTable.Rows.Add(newRow);
// DataView会自动更新,不需要额外刷新
}
private void btnDelete_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (dataGridView1.SelectedRows.Count > 0)
{
// 获取选中行的索引
int rowIndex = dataGridView1.SelectedRows[0].Index;
// 获取DataView中的DataRowView
DataRowView rowView = employeeView[rowIndex];
// 删除底层DataTable中的行
rowView.Row.Delete();
// 接受更改
employeeTable.AcceptChanges();
}
}
private void txtSearch_TextChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// 根据姓名筛选
string filterText = txtSearch.Text.Trim();
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(filterText))
{
employeeView.RowFilter = string.Empty; // 清除筛选
}
else
{
// 设置筛选条件 - 使用DataView的RowFilter属性
employeeView.RowFilter = $"Name LIKE '%{filterText}%'";
}
}
}
}
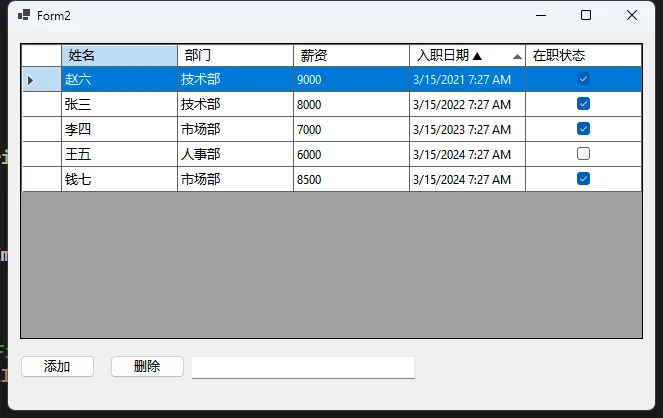
实现数据排序
C#using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace AppDataGrid
{
public partial class Form2 : Form
{
// 数据源
private DataTable employeeTable;
// 数据视图
private DataView employeeView;
// 排序状态跟踪
private string currentSortColumn = string.Empty;
private ListSortDirection currentSortDirection = ListSortDirection.Ascending;
public Form2()
{
InitializeComponent();
InitializeDataSource();
InitializeDataGridView();
SetupDataGridView();
}
// 代码初始化方式
private void InitializeDataGridView()
{
// 设置一些常用属性
dataGridView1.AllowUserToAddRows = false; // 不允许用户添加行
dataGridView1.AllowUserToDeleteRows = false; // 不允许用户删除行
dataGridView1.ReadOnly = true; // 禁用编辑功能
dataGridView1.AutoSizeColumnsMode = DataGridViewAutoSizeColumnsMode.Fill; // 自动调整列宽度以填充整个DataGridView
dataGridView1.SelectionMode = DataGridViewSelectionMode.FullRowSelect; // 选择整行
// 添加列标题点击事件处理
dataGridView1.ColumnHeaderMouseClick += DataGridView1_ColumnHeaderMouseClick;
}
// 处理列标题点击事件 - 实现排序功能
private void DataGridView1_ColumnHeaderMouseClick(object sender, DataGridViewCellMouseEventArgs e)
{
// 获取点击的列
DataGridViewColumn clickedColumn = dataGridView1.Columns[e.ColumnIndex];
string columnName = clickedColumn.DataPropertyName;
// 如果是隐藏列或不支持排序的列,则返回
if (columnName == "Id" || string.IsNullOrEmpty(columnName))
return;
// 确定排序方向
ListSortDirection direction;
// 如果点击的是当前排序列,则切换排序方向
if (columnName == currentSortColumn)
{
direction = currentSortDirection == ListSortDirection.Ascending ?
ListSortDirection.Descending : ListSortDirection.Ascending;
}
else
{
// 新列,默认升序
direction = ListSortDirection.Ascending;
}
// 更新排序状态
currentSortColumn = columnName;
currentSortDirection = direction;
// 应用排序
employeeView.Sort = columnName + (direction == ListSortDirection.Ascending ? " ASC" : " DESC");
// 更新列标题显示(可选)- 添加排序指示符
UpdateColumnHeaderSortIndicator();
}
// 更新列标题显示排序指示符(可选)
private void UpdateColumnHeaderSortIndicator()
{
// 清除所有列的排序箭头指示
foreach (DataGridViewColumn column in dataGridView1.Columns)
{
column.HeaderText = column.HeaderText.Replace(" ▲", "").Replace(" ▼", "");
}
// 给当前排序列添加排序指示符
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(currentSortColumn))
{
DataGridViewColumn sortColumn = dataGridView1.Columns[currentSortColumn];
if (sortColumn != null)
{
sortColumn.HeaderText += currentSortDirection == ListSortDirection.Ascending ? " ▲" : " ▼";
}
}
}
// 配置DataGridView并绑定数据
private void SetupDataGridView()
{
// 创建DataView作为数据源
employeeView = new DataView(employeeTable);
// 将DataView绑定到DataGridView
dataGridView1.DataSource = employeeView;
// 自定义列显示
dataGridView1.Columns["Id"].Visible = false; // 隐藏ID列
dataGridView1.Columns["Name"].HeaderText = "姓名";
dataGridView1.Columns["Department"].HeaderText = "部门";
dataGridView1.Columns["Salary"].HeaderText = "薪资";
dataGridView1.Columns["HireDate"].HeaderText = "入职日期";
dataGridView1.Columns["IsActive"].HeaderText = "在职状态";
// 确保DataPropertyName与实际列名一致(用于排序)
foreach (DataGridViewColumn column in dataGridView1.Columns)
{
column.DataPropertyName = column.Name;
}
}
// 初始化员工数据
private void InitializeDataSource()
{
// 创建DataTable
employeeTable = new DataTable("Employees");
// 定义DataTable结构
employeeTable.Columns.Add("Id", typeof(int));
employeeTable.Columns.Add("Name", typeof(string));
employeeTable.Columns.Add("Department", typeof(string));
employeeTable.Columns.Add("Salary", typeof(decimal));
employeeTable.Columns.Add("HireDate", typeof(DateTime));
employeeTable.Columns.Add("IsActive", typeof(bool));
// 设置主键
employeeTable.PrimaryKey = new DataColumn[] { employeeTable.Columns["Id"] };
// 添加初始数据
employeeTable.Rows.Add(1, "张三", "技术部", 8000, DateTime.Now.AddYears(-3), true);
employeeTable.Rows.Add(2, "李四", "市场部", 7000, DateTime.Now.AddYears(-2), true);
employeeTable.Rows.Add(3, "王五", "人事部", 6000, DateTime.Now.AddYears(-1), false);
employeeTable.Rows.Add(4, "赵六", "技术部", 9000, DateTime.Now.AddYears(-4), true);
employeeTable.Rows.Add(5, "钱七", "市场部", 8500, DateTime.Now.AddYears(-1), true);
}
private void btnAdd_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// 获取新ID
int newId = 1;
if (employeeTable.Rows.Count > 0)
{
newId = employeeTable.AsEnumerable()
.Max(row => row.Field<int>("Id")) + 1;
}
// 创建新行
DataRow newRow = employeeTable.NewRow();
newRow["Id"] = newId;
newRow["Name"] = "新员工";
newRow["Department"] = "待分配";
newRow["Salary"] = 5000;
newRow["HireDate"] = DateTime.Now;
newRow["IsActive"] = true;
// 添加到DataTable
employeeTable.Rows.Add(newRow);
// DataView会自动更新,不需要额外刷新
// 但如果有排序,新记录可能会根据当前排序规则调整位置
}
private void btnDelete_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (dataGridView1.SelectedRows.Count > 0)
{
// 获取选中行的索引
int rowIndex = dataGridView1.SelectedRows[0].Index;
// 获取DataView中的DataRowView
DataRowView rowView = employeeView[rowIndex];
// 删除底层DataTable中的行
rowView.Row.Delete();
// 接受更改
employeeTable.AcceptChanges();
}
}
private void txtSearch_TextChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// 根据姓名筛选
string filterText = txtSearch.Text.Trim();
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(filterText))
{
employeeView.RowFilter = string.Empty; // 清除筛选
}
else
{
// 设置筛选条件 - 使用DataView的RowFilter属性
employeeView.RowFilter = $"Name LIKE '%{filterText}%'";
}
// 保持原有排序
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(currentSortColumn))
{
employeeView.Sort = currentSortColumn +
(currentSortDirection == ListSortDirection.Ascending ? " ASC" : " DESC");
}
}
}
}
数据导出与持久化
C#private void btnExport_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
using (SaveFileDialog saveDialog = new SaveFileDialog())
{
saveDialog.Filter = "CSV文件(*.csv)|*.csv";
saveDialog.Title = "导出CSV文件";
saveDialog.DefaultExt = "csv";
saveDialog.FileName = "员工数据_" + DateTime.Now.ToString("yyyyMMdd");
if (saveDialog.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK)
{
try
{
// 使用UTF-8编码并添加BOM标记,以便Excel正确识别中文
using (StreamWriter writer = new StreamWriter(saveDialog.FileName, false, new UTF8Encoding(true)))
{
// 写入标题行
List<string> headers = new List<string>();
List<string> columnNames = new List<string>();
foreach (DataGridViewColumn column in dataGridView1.Columns)
{
if (column.Visible) // 只导出可见列
{
headers.Add(column.HeaderText);
columnNames.Add(column.DataPropertyName);
}
}
writer.WriteLine(string.Join(",", headers));
// 写入数据行
foreach (DataRowView rowView in employeeView)
{
List<string> fields = new List<string>();
foreach (string columnName in columnNames)
{
object value = rowView[columnName];
string fieldValue = value?.ToString() ?? "";
fields.Add(fieldValue);
}
writer.WriteLine(string.Join(",", fields));
}
}
MessageBox.Show("数据已成功导出到CSV文件!", "导出成功",
MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Information);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
MessageBox.Show($"导出CSV时发生错误:{ex.Message}", "导出错误",
MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Error);
}
}
}
}
数据绑定的最佳实践
在使用数据绑定时,有一些最佳实践值得遵循:
- 使用正确的模型结构:确保数据模型实现了
INotifyPropertyChanged接口,以便UI能够响应数据变化。 - 考虑性能问题:当数据量较大时,考虑使用分页或虚拟化技术,避免一次加载过多数据。
- 错误处理:实现适当的错误处理机制,特别是在数据验证和转换期间。
- UI与业务逻辑分离:尽量将数据处理逻辑与UI代码分离,采用MVVM或MVC等设计模式。
- 提供视觉反馈:当数据正在加载或处理时,提供适当的视觉反馈给用户。
总结
通过本文,我们学习了如何在C# Windows Forms应用程序中实现复杂数据绑定。从创建数据模型、初始化数据源到配置DataGridView控件,每一步都详细展示了数据绑定的核心概念和实现技巧。
使用BindingSource作为数据源与UI控件之间的中介,不仅简化了代码结构,还提供了额外的功能,如数据导航、筛选和排序。这种方法特别适合构建需要频繁与数据交互的企业应用程序。
希望这篇教程能够帮助你更好地理解和应用C#中的数据绑定技术,为你的Windows Forms应用开发带来便利。
本文作者:技术老小子
本文链接:
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!