目录
在这篇文章中,我们将探讨如何使用C#通过Windows API来读取和修改其他应用程序的内存。这种技术常用于游戏外挂开发、程序调试和系统监控等场景。
基础知识
在开始之前,我们需要了解以下几个关键的Windows API函数:
- OpenProcess:获取目标进程的句柄
- ReadProcessMemory:读取目标进程的内存
- WriteProcessMemory:写入目标进程的内存
- VirtualAllocEx:在目标进程中分配内存
- VirtualFreeEx:释放目标进程中的内存
被修改的示例程序
首先,我们创建一个简单的Windows窗体应用程序,它包含一个数值会随时间变化的计数器:
C#public partial class Form1 : Form
{
private int counter = 100;
private Thread counterThread;
private bool isRunning = false;
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void StartCounter()
{
if (isRunning) return; // 防止多次点击启动按钮
isRunning = true;
counterThread = new Thread(() =>
{
while (isRunning)
{
this.Invoke((MethodInvoker)delegate
{
unsafe
{
fixed (int* ptr = &counter)
{
// 显示计数值和其内存地址
lblCounter.Text = $"{counter}";
txtAddress.Text = $"0x{(IntPtr)ptr:X}";
}
}
});
Thread.Sleep(1000);
counter++;
}
});
counterThread.IsBackground = true;
counterThread.Start();
}
private void StopCounter()
{
isRunning = false;
if (counterThread != null && counterThread.IsAlive)
{
// 等待线程完成
counterThread.Join(1000);
}
}
private void btnStart_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
StartCounter();
btnStart.Enabled = false;
btnStop.Enabled = true;
}
private void btnStop_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
StopCounter();
btnStart.Enabled = true;
btnStop.Enabled = false;
}
// 确保在窗体关闭时停止线程
protected override void OnFormClosing(FormClosingEventArgs e)
{
StopCounter();
base.OnFormClosing(e);
}
}
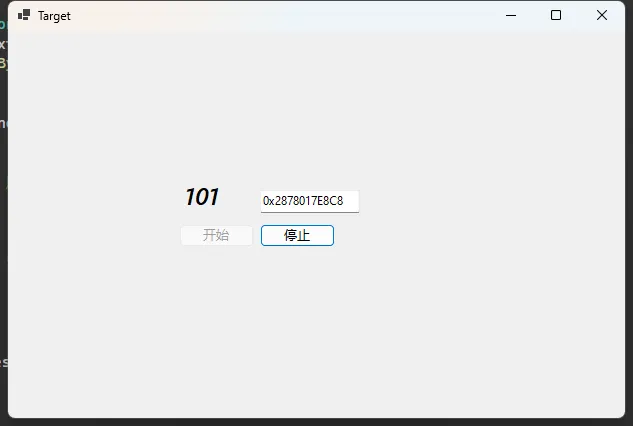
内存修改器程序
下面是一个完整的内存修改器程序,可以读取和修改上面示例程序的计数器值
C#public partial class Form1 : Form
{
[DllImport("kernel32.dll")]
public static extern IntPtr OpenProcess(int dwDesiredAccess, bool bInheritHandle, int dwProcessId);
[DllImport("kernel32.dll")]
public static extern bool ReadProcessMemory(IntPtr hProcess, IntPtr lpBaseAddress, byte[] lpBuffer, int dwSize, ref int lpNumberOfBytesRead);
[DllImport("kernel32.dll")]
public static extern bool WriteProcessMemory(IntPtr hProcess, IntPtr lpBaseAddress, byte[] lpBuffer, int dwSize, ref int lpNumberOfBytesWritten);
private const int PROCESS_ALL_ACCESS = 0x1F0FFF;
private IntPtr processHandle;
private Process targetProcess;
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void btnRead_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
try
{
targetProcess = Process.GetProcessesByName(txtProcessName.Text)[0];
processHandle = OpenProcess(PROCESS_ALL_ACCESS, false, targetProcess.Id);
IntPtr memoryAddress = (IntPtr)Convert.ToInt64(txtMemoryAddress.Text, 16);
byte[] buffer = new byte[4];
int bytesRead = 0;
if (ReadProcessMemory(processHandle, memoryAddress, buffer, buffer.Length, ref bytesRead))
{
int value = BitConverter.ToInt32(buffer, 0);
lblCurrentValue.Text = value.ToString();
}
else
{
MessageBox.Show("读取内存失败!");
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
MessageBox.Show($"发生错误:{ex.Message}");
}
}
private void btnWrite_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
try
{
if (processHandle == IntPtr.Zero)
{
MessageBox.Show("请先读取内存!");
return;
}
IntPtr memoryAddress = (IntPtr)Convert.ToInt64(txtMemoryAddress.Text, 16);
int newValue = Convert.ToInt32(txtNewValue.Text);
byte[] buffer = BitConverter.GetBytes(newValue);
int bytesWritten = 0;
if (WriteProcessMemory(processHandle, memoryAddress, buffer, buffer.Length, ref bytesWritten))
{
MessageBox.Show("写入成功!");
btnRead_Click(sender, e); // 刷新显示
}
else
{
MessageBox.Show("写入内存失败!");
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
MessageBox.Show($"发生错误:{ex.Message}");
}
}
}
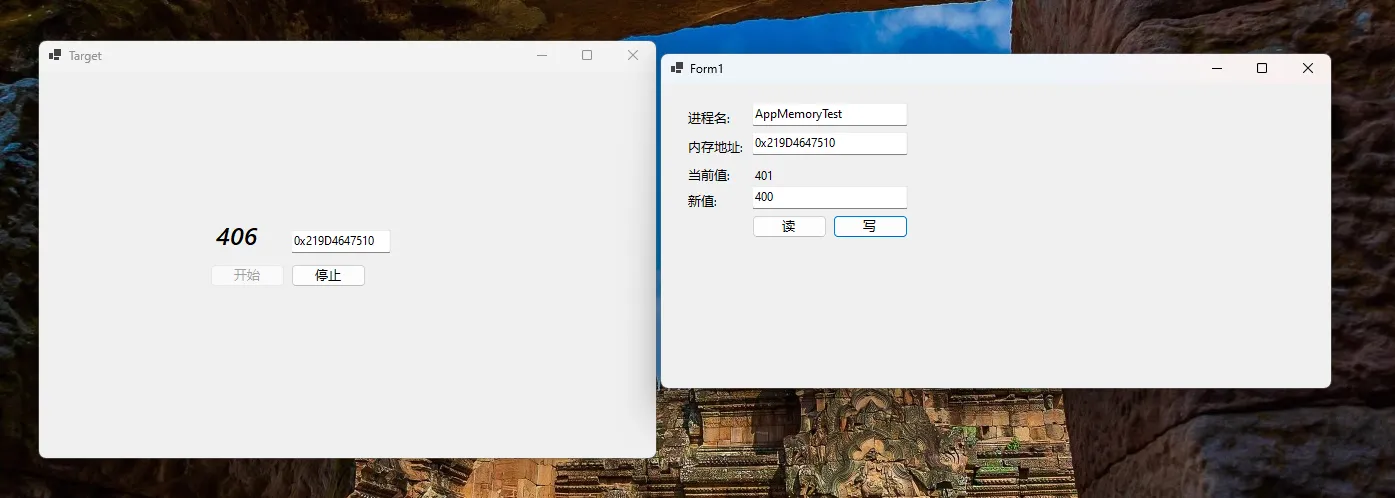
使用说明
- 首先运行目标程序(TargetApplication)
- 运行内存修改器(MemoryEditor)
- 使用工具如Cheat Engine找到目标程序中counter变量的内存地址,在这里我直接IntPtr取得了变量地址
- 在内存修改器中输入进程名和内存地址
- 点击"读取"按钮查看当前值
- 输入新值并点击"写入"按钮修改内存
注意事项
- 在实际使用时需要注意:
- 确保具有足够的系统权限
- 考虑目标程序的保护机制
- 注意内存地址的动态变化
- 在64位系统上运行时,需要注意:
- 进程权限问题
- 地址空间的差异
- 可能需要调整数据类型的大小
这个示例展示了C#中如何使用Windows API进行内存读写操作的基本方法。在实际应用中,可能需要根据具体需求进行更多的优化和安全性处理,在具体实例中,需要考虑偏移时的计算。
本文作者:技术老小子
本文链接:
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!
目录