目录
在C#中,我们可以使用系统的Windows API来进行文件操作,例如创建、读取、写入、删除文件等。下面将介绍如何使用C#调用系统的Windows API来实现文件操作,并提供一些示例代码来说明具体的用法。
创建文件
我们可以使用CreateFile函数来创建一个新的文件。下面是一个示例代码:
CreateFile 是 Windows API 中用于创建或打开文件或 I/O 设备的函数。它的具体参数说明如下:
C#[DllImport("kernel32.dll", SetLastError = true)]
static extern IntPtr CreateFile(string lpFileName, uint dwDesiredAccess, uint dwShareMode, IntPtr lpSecurityAttributes, uint dwCreationDisposition, uint dwFlagsAndAttributes, IntPtr hTemplateFile);
lpFileName:要创建或打开的文件或设备的名称。这可以是一个文件的路径和名称,也可以是一个 I/O 设备的名称,例如\\.\COM1。dwDesiredAccess:指定对文件或设备的访问权限。可以使用常量来指定权限,例如GENERIC_READ或GENERIC_WRITE。dwShareMode:指定其他进程可以如何访问文件。可以使用常量来指定共享模式,例如FILE_SHARE_READ或FILE_SHARE_WRITE。lpSecurityAttributes:指向SECURITY_ATTRIBUTES结构的指针,用于指定文件或设备的安全描述符。可以将其设置为IntPtr.Zero,表示不使用安全描述符。dwCreationDisposition:指定操作系统如何创建或打开文件。可以使用常量来指定创建或打开的方式,例如CREATE_NEW或OPEN_EXISTING。dwFlagsAndAttributes:指定文件或设备的属性和标志。可以使用常量来指定属性和标志,例如FILE_ATTRIBUTE_NORMAL。hTemplateFile:对于文件句柄的模板文件的句柄。对于一般文件操作,可以将其设置为IntPtr.Zero。
C#internal class Program
{
[DllImport("kernel32.dll", SetLastError = true)]
static extern IntPtr CreateFile(string lpFileName, uint dwDesiredAccess, uint dwShareMode, IntPtr lpSecurityAttributes, uint dwCreationDisposition, uint dwFlagsAndAttributes, IntPtr hTemplateFile);
public const uint GENERIC_WRITE = 0x40000000;
public const uint CREATE_NEW = 1;
[DllImport("kernel32.dll", SetLastError = true)]
[return: MarshalAs(UnmanagedType.Bool)]
static extern bool CloseHandle(IntPtr hObject);
static void Main()
{
string fileName = "./test.txt";
IntPtr handle = CreateFile(fileName, GENERIC_WRITE, 0, IntPtr.Zero, CREATE_NEW, 0, IntPtr.Zero);
if (handle != IntPtr.Zero)
{
Console.WriteLine("File created successfully!");
CloseHandle(handle);
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Failed to create file!");
}
}
}
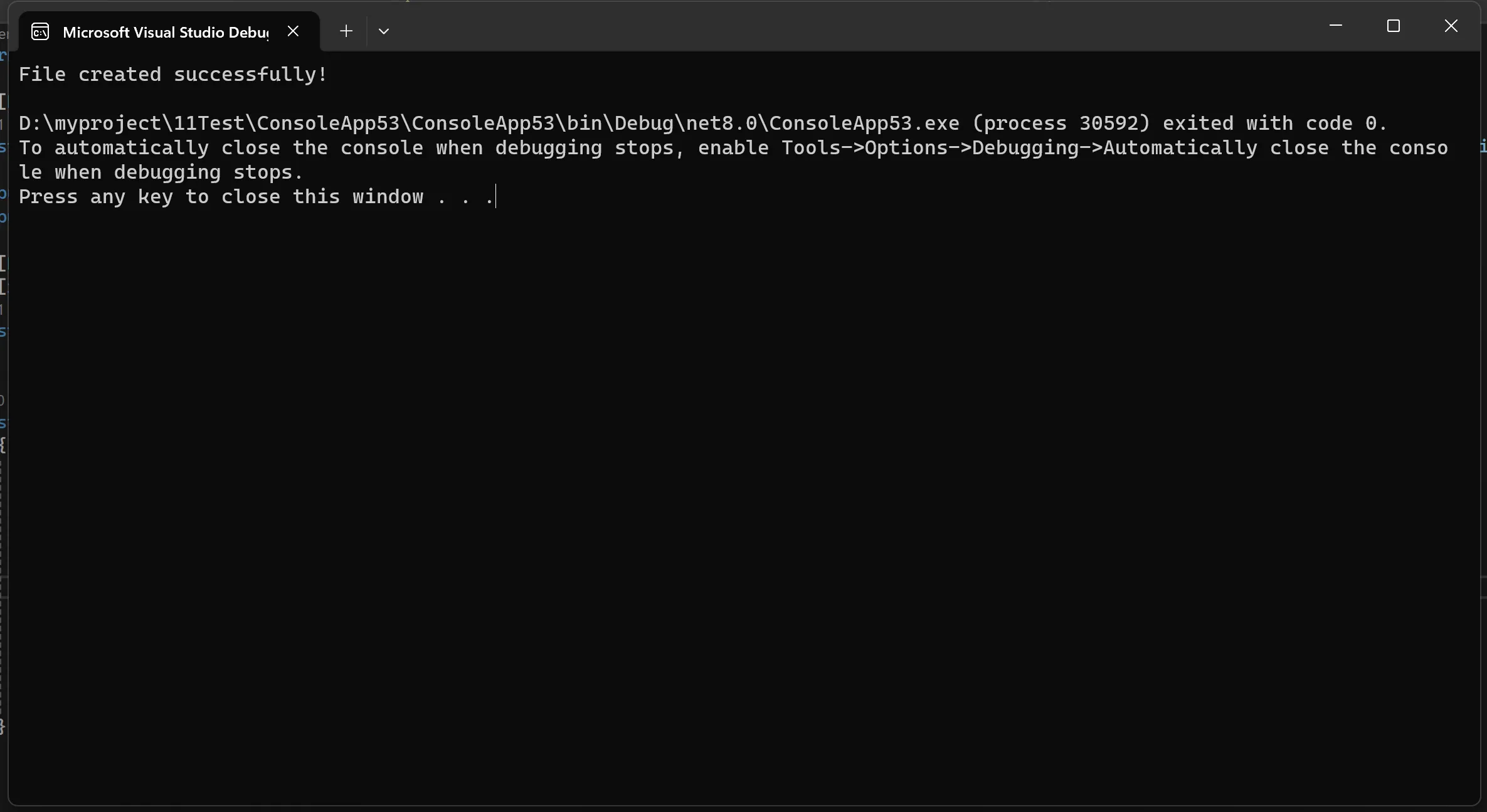
在上面的示例中,我们使用CreateFile函数创建了一个名为test.txt的新文件,并指定了文件的访问权限和创建方式。如果文件创建成功,将输出File created successfully!,否则将输出Failed to create file!。
读取文件
我们可以使用ReadFile函数来读取文件的内容。下面是一个示例代码:
C#internal class Program
{
[DllImport("kernel32.dll", SetLastError = true)]
static extern IntPtr CreateFile(string lpFileName, uint dwDesiredAccess, uint dwShareMode, IntPtr lpSecurityAttributes, uint dwCreationDisposition, uint dwFlagsAnd
public const uint GENERIC_WRITE = 0x40000000;
public const uint CREATE_NEW = 1;
public const uint GENERIC_READ = 0x80000000;
public const int OPEN_EXISTING = 3;
[DllImport("kernel32.dll", SetLastError = true)]
[return: MarshalAs(UnmanagedType.Bool)]
static extern bool CloseHandle(IntPtr hObject);
[DllImport("kernel32.dll", SetLastError = true)]
static extern bool ReadFile(IntPtr hFile, byte[] lpBuffer, uint nNumberOfBytesToRead, out uint lpNumberOfBytesRead, IntPtr lpOverlapped);
static void Main()
{
string fileName = "./test.txt";
IntPtr handle = CreateFile(fileName, GENERIC_READ, 0, IntPtr.Zero, OPEN_EXISTING, 0, IntPtr.Zero);
if (handle != IntPtr.Zero)
{
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
uint bytesRead;
if (ReadFile(handle, buffer, (uint)buffer.Length, out bytesRead, IntPtr.Zero))
{
string content = Encoding.Default.GetString(buffer, 0, (int)bytesRead);
Console.WriteLine("File content: " + content);
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Failed to read file!");
}
// Close the file handle
CloseHandle(handle);
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Failed to open file!");
}
}
}
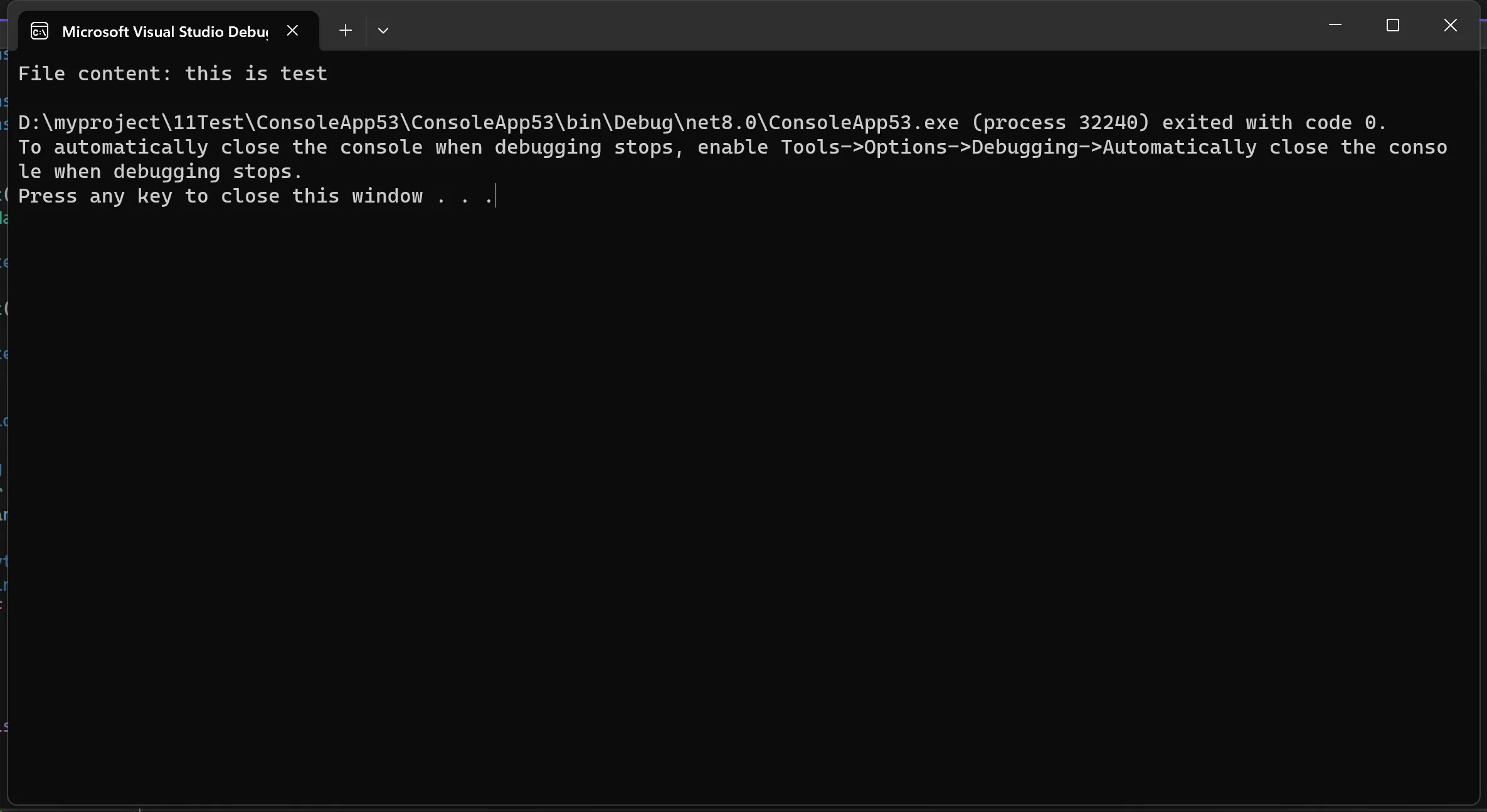
在上面的示例中,我们使用ReadFile函数读取了名为test.txt的文件的内容,并将结果输出到控制台。
写入文件
我们可以使用WriteFile函数来向文件中写入内容。下面是一个示例代码:
C#class Program
{
[DllImport("kernel32.dll", SetLastError = true)]
static extern IntPtr CreateFile(string lpFileName, uint dwDesiredAccess, uint dwShareMode, IntPtr lpSecurityAttributes, uint dwCreationDisposition, uint dwFlagsAndAttributes, IntPtr hTemplateFile);
[DllImport("kernel32.dll", SetLastError = true)]
static extern bool WriteFile(IntPtr hFile, byte[] lpBuffer, uint nNumberOfBytesToWrite, out uint lpNumberOfBytesWritten, IntPtr lpOverlapped);
public const int OPEN_EXISTING = 3;
public const uint GENERIC_WRITE = 0x40000000;
[DllImport("kernel32.dll", SetLastError = true)]
[return: MarshalAs(UnmanagedType.Bool)]
static extern bool CloseHandle(IntPtr hObject);
static void Main()
{
string fileName = "test.txt";
IntPtr handle = CreateFile(fileName, GENERIC_WRITE, 0, IntPtr.Zero, OPEN_EXISTING, 0, IntPtr.Zero);
if (handle != IntPtr.Zero)
{
string content = "Hello, world!";
byte[] buffer = Encoding.Default.GetBytes(content);
uint bytesWritten;
if (WriteFile(handle, buffer, (uint)buffer.Length, out bytesWritten, IntPtr.Zero))
{
Console.WriteLine("File written successfully!");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Failed to write file!");
}
// Close the file handle
CloseHandle(handle);
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Failed to open file!");
}
}
}
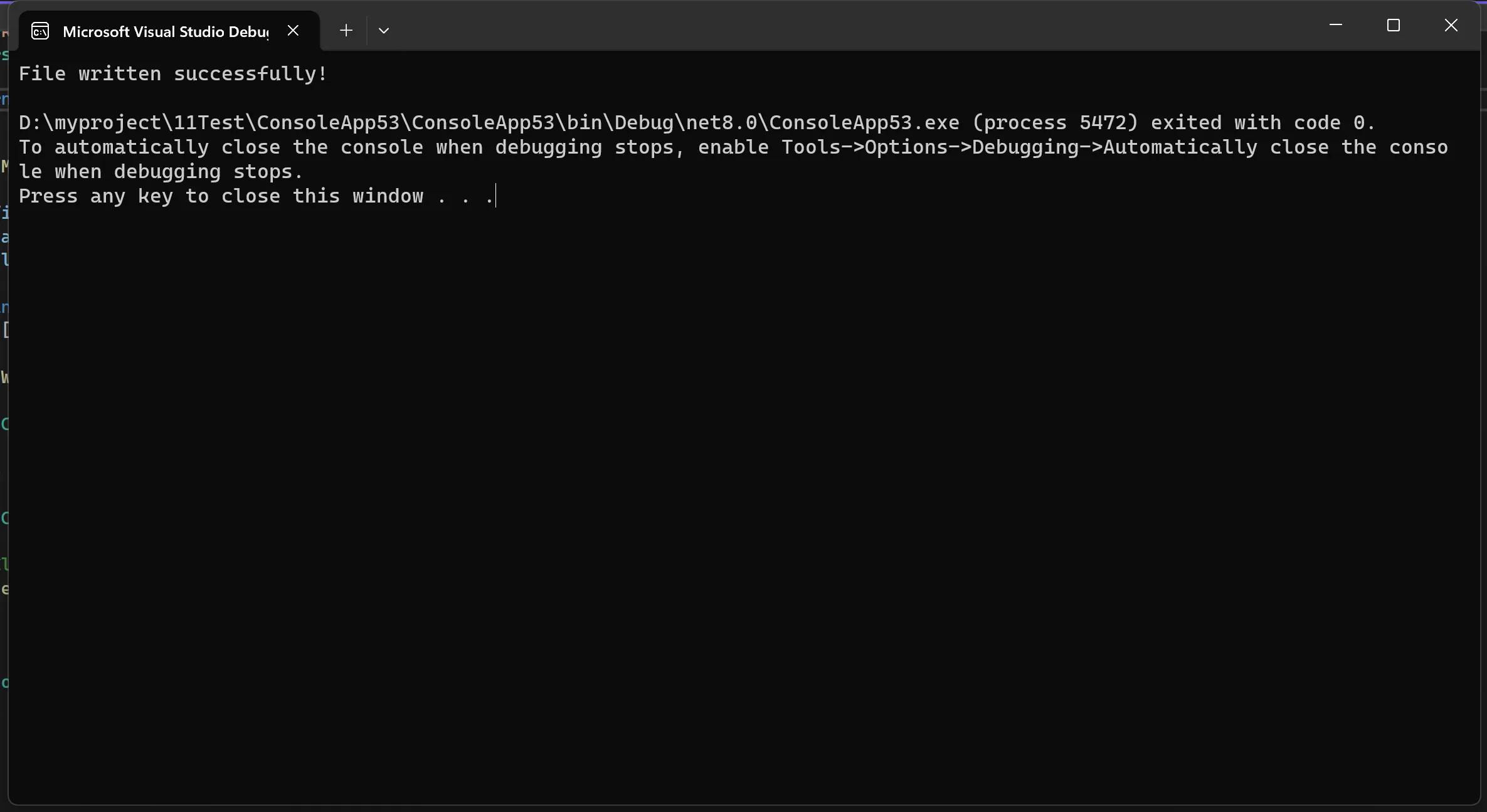
在上面的示例中,我们使用WriteFile函数向名为test.txt的文件中写入了内容,并根据操作结果输出了相应的信息。
删除文件
我们可以使用DeleteFile函数来删除一个文件。下面是一个示例代码:
C#class Program
{
[DllImport("kernel32.dll", SetLastError = true)]
static extern bool DeleteFile(string lpFileName);
static void Main()
{
string fileName = "./test.txt";
if (DeleteFile(fileName))
{
Console.WriteLine("File deleted successfully!");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Failed to delete file!");
}
}
}
在上面的示例中,我们使用DeleteFile函数删除了名为test.txt的文件,并根据操作结果输出了相应的信息。
通过上面的示例代码,我们可以看到如何使用C#调用系统的Windows API来实现文件操作,包括创建文件、读取文件、写入文件和删除文件等操作。这些操作可以帮助我们更灵活地处理文件,满足不同的需求。
本文作者:技术老小子
本文链接:
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!