目录
在C#中,与Windows系统API进行交互时,结构体(struct)和联合体(union)是非常重要的数据类型,用于表示和操作复杂的数据结构。本文将介绍在C#中如何定义和使用结构体和联合体,并提供多个例子进行演示。
结构体(Struct)
在C#中,结构体通常用于表示各种系统数据结构,如窗口信息、消息参数、文件属性等。结构体的定义和使用非常常见,下面是一个简单的例子:
定义与使用结构体
C#using System;
public struct RECT
{
public int left;
public int top;
public int right;
public int bottom;
}
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
RECT rc = new RECT { left = 10, top = 20, right = 100, bottom = 200 };
// 使用rc表示一个矩形区域,进行相应的操作
}
}
在上面的例子中,我们定义了一个名为RECT的结构体,用于表示矩形区域的坐标。在Main方法中,我们创建了一个RECT类型的实例rc,并设置其left、top、right和bottom字段的值,然后可以使用rc表示一个矩形区域进行相应的操作。
结构体中的布局属性(StructLayout)
在C#中,可以使用System.Runtime.InteropServices命名空间中的StructLayout特性来指定结构体的布局方式,以便与C或C++编写的库进行交互。
C#using System;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
[StructLayout(LayoutKind.Sequential)]
public struct POINT
{
public int x;
public int y;
}
class Program
{
[DllImport("user32.dll")]
public static extern bool GetCursorPos(out POINT lpPoint);
static void Main()
{
while (true)
{
POINT point;
GetCursorPos(out point);
Console.WriteLine($"Cursor position: ({point.x}, {point.y})");
System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(100);
}
}
}
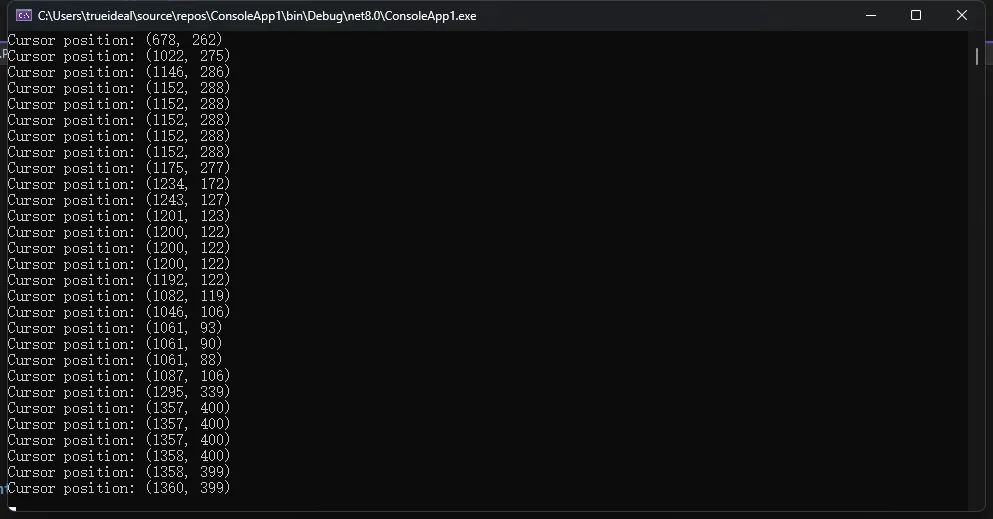
在上面的例子中,我们定义了一个名为POINT的结构体,用于表示屏幕上的点的坐标。我们使用StructLayout特性指定了POINT结构体的布局方式为按顺序排列。然后,在Main方法中,我们调用GetCursorPos函数获取鼠标的位置,并输出结果。
联合体(Union)
在C#中,联合体通常用于表示多个字段共享相同的内存位置的情况,例如处理不同类型的数据。下面是一个简单的例子:
结构体示例
C#[StructLayout(LayoutKind.Sequential)]
public struct WIN32_FIND_DATA
{
public FileAttributes dwFileAttributes;
public System.Runtime.InteropServices.ComTypes.FILETIME ftCreationTime;
public System.Runtime.InteropServices.ComTypes.FILETIME ftLastAccessTime;
public System.Runtime.InteropServices.ComTypes.FILETIME ftLastWriteTime;
public int nFileSizeHigh;
public int nFileSizeLow;
public int dwReserved0;
public int dwReserved1;
[MarshalAs(UnmanagedType.ByValTStr, SizeConst = 260)]
public string cFileName;
[MarshalAs(UnmanagedType.ByValTStr, SizeConst = 14)]
public string cAlternateFileName;
}
联合体示例
C#[StructLayout(LayoutKind.Explicit)]
public struct MyUnion
{
[FieldOffset(0)]
public int intValue;
[FieldOffset(0)]
public float floatValue;
[FieldOffset(0)]
public byte byteValue;
}
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
MyUnion u = new MyUnion();
u.intValue = 10;
Console.WriteLine($"Int value: {u.intValue}, Float value: {u.floatValue}, Byte value: {u.byteValue}");
}
}
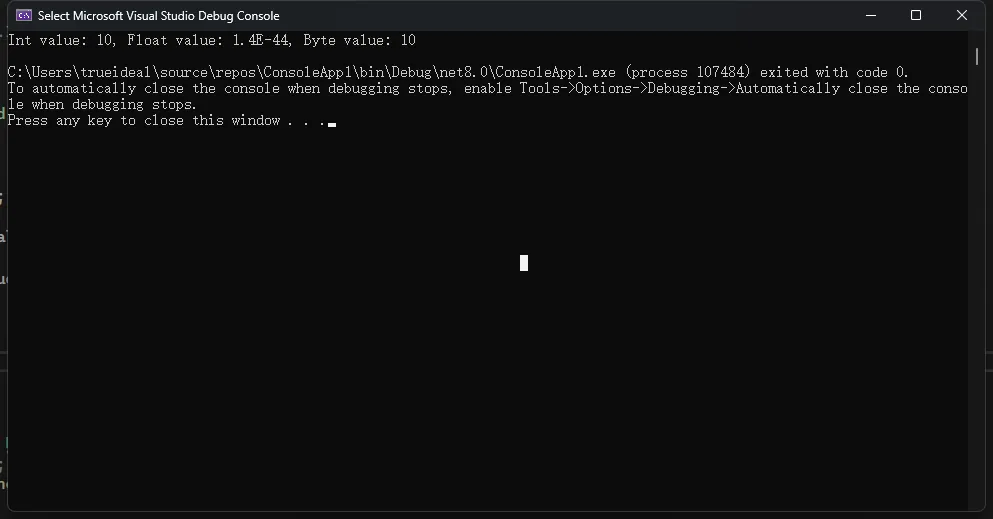
在这些例子中,我们展示了更多关于结构体和联合体在C#中的使用方法,以及它们在实际编程中的应用场景。
结构体和联合体在C#中与Windows系统API进行交互时扮演着重要的角色,它们可以帮助我们更好地处理复杂的数据结构。希望本文能够帮助您更好地理解和使用结构体和联合体在C#与Windows系统API编程中的应用。
本文作者:技术老小子
本文链接:
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!