目录
在本篇文章中,我们将深入探讨C#中构造函数与析构函数的概念、应用特点和使用场景。通过丰富的示例和详细的注释,阐述如何在实际编程中有效地使用它们,确保程序的健壮性和可靠性。
构造函数(Constructor)
什么是构造函数
构造函数是一种特殊的方法,用于在创建对象时初始化对象的状态。它在对象创建时被自动调用,可以有参数,也可以进行重载。
构造函数的特点
- 名称与类名相同:构造函数的名称必须与类名完全一致。
- 无返回类型:构造函数不需要也不能指定返回类型。
- 自动调用:在创建对象时,构造函数会被自动调用,无需手动调用。
- 可以重载:可以定义多个构造函数,只要它们的参数列表不同。
构造函数的用途
- 初始化对象的状态:为对象的字段赋初始值。
- 分配资源:如打开文件、建立数据库连接等。
示例:定义和使用构造函数
示例1:定义一个简单的类并使用默认构造函数
C#using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace AppConstructor
{
public class Book
{
public string Title { get; set; }
public string Author { get; set; }
// 默认构造函数
public Book()
{
Title = "未知";
Author = "未知";
}
}
}
C#namespace AppConstructor
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
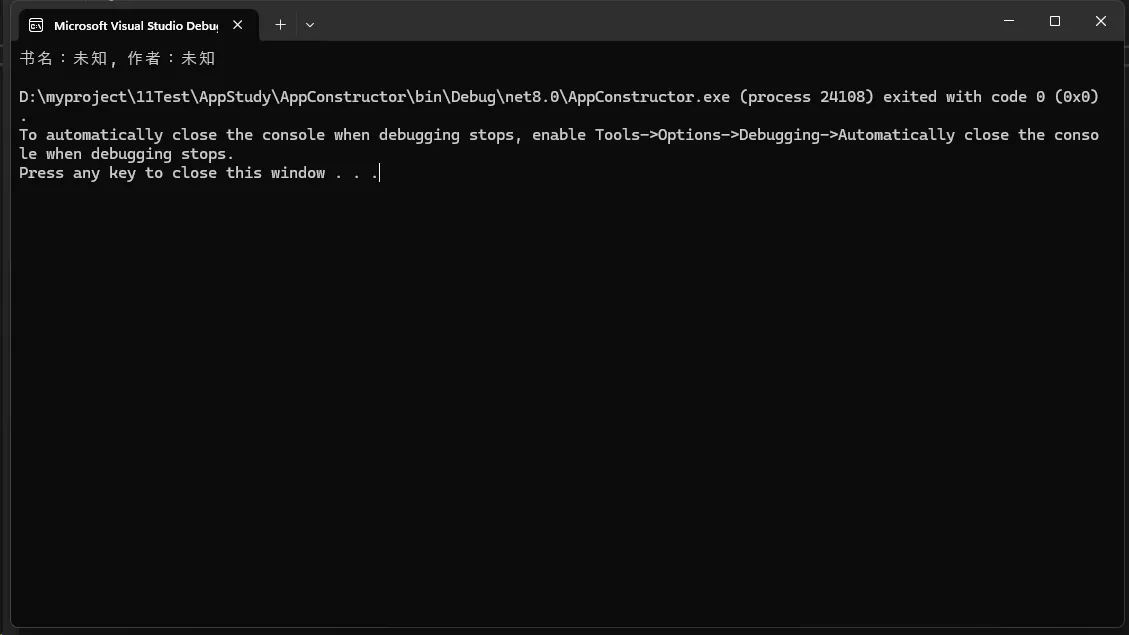
// 使用默认构造函数创建对象
Book defaultBook = new Book();
Console.WriteLine($"书名:{defaultBook.Title}, 作者:{defaultBook.Author}");
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
示例2:带参数的构造函数
C#using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace AppConstructor
{
public class Book
{
public string Title { get; set; }
public string Author { get; set; }
// 带参数的构造函数
public Book(string title, string author)
{
Title = title;
Author = author;
}
}
}
C#namespace AppConstructor
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
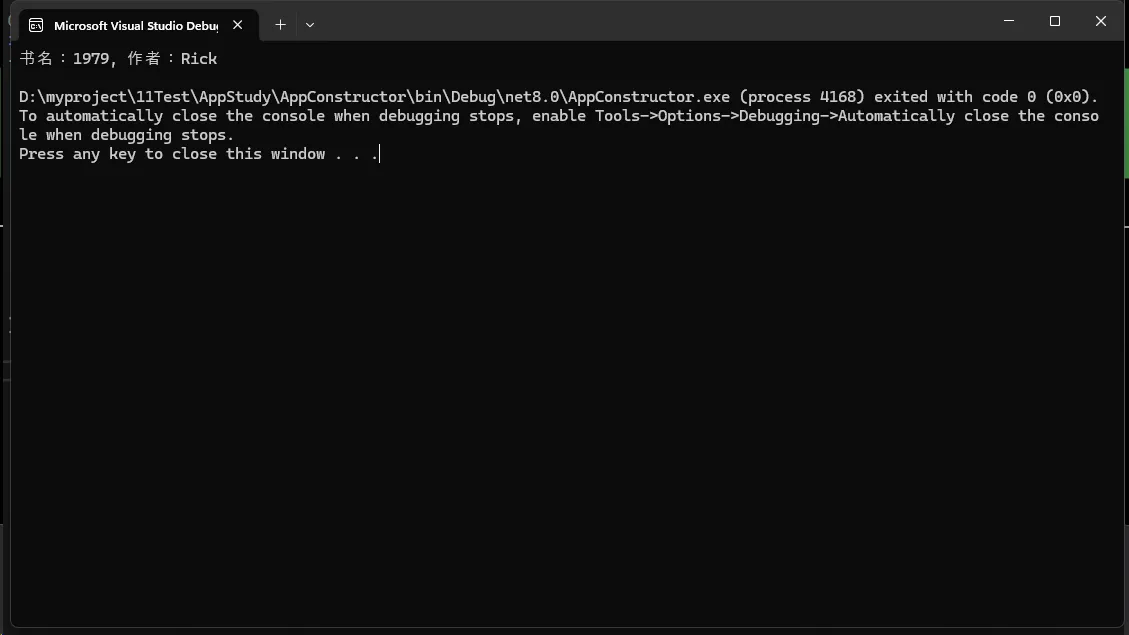
// 使用带参数的构造函数创建对象
Book specificBook = new Book("1979", "Rick");
Console.WriteLine($"书名:{specificBook.Title}, 作者:{specificBook.Author}");
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
示例3:构造函数的重载
C#namespace AppConstructor
{
public class Rectangle
{
public double Width { get; set; }
public double Height { get; set; }
// 默认构造函数
public Rectangle()
{
Width = 1.0;
Height = 1.0;
}
// 带一个参数的构造函数
public Rectangle(double side)
{
Width = side;
Height = side;
}
// 带两个参数的构造函数
public Rectangle(double width, double height)
{
Width = width;
Height = height;
}
}
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
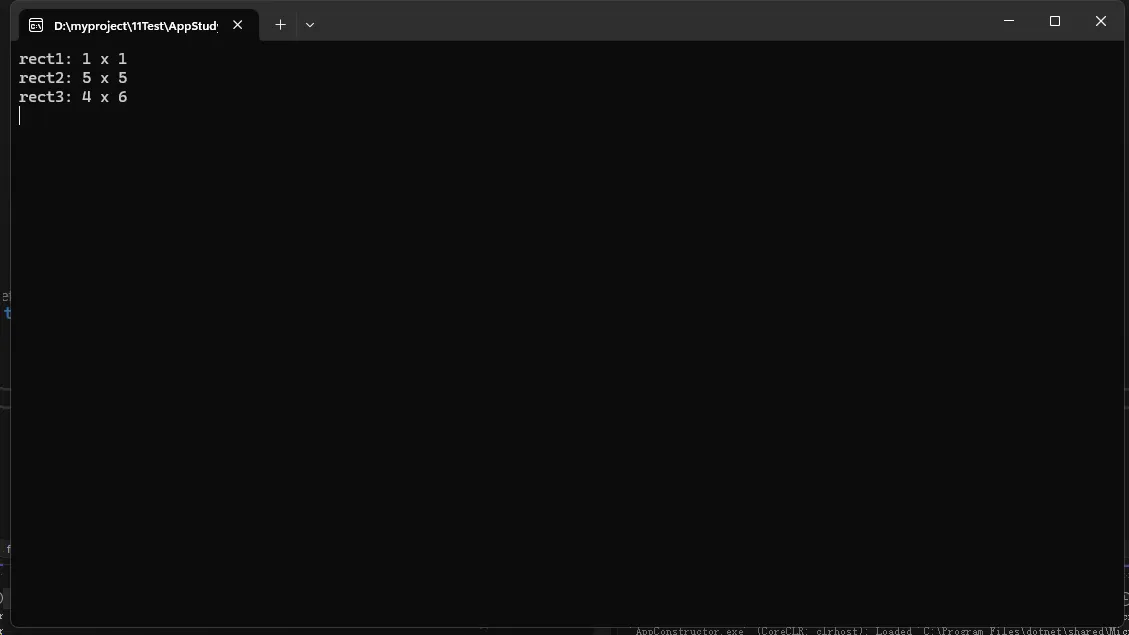
// 使用不同的构造函数
Rectangle rect1 = new Rectangle();
Rectangle rect2 = new Rectangle(5.0);
Rectangle rect3 = new Rectangle(4.0, 6.0);
Console.WriteLine($"rect1: {rect1.Width} x {rect1.Height}");
Console.WriteLine($"rect2: {rect2.Width} x {rect2.Height}");
Console.WriteLine($"rect3: {rect3.Width} x {rect3.Height}");
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
构造函数的链式调用
示例4:构造函数的链式调用
C#namespace AppConstructor
{
public class Point
{
public int X { get; set; }
public int Y { get; set; }
// 默认构造函数,调用带参数的构造函数
public Point() : this(0, 0)
{
}
// 带一个参数的构造函数,调用带两个参数的构造函数
public Point(int value) : this(value, value)
{
}
// 带两个参数的构造函数
public Point(int x, int y)
{
X = x;
Y = y;
}
}
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
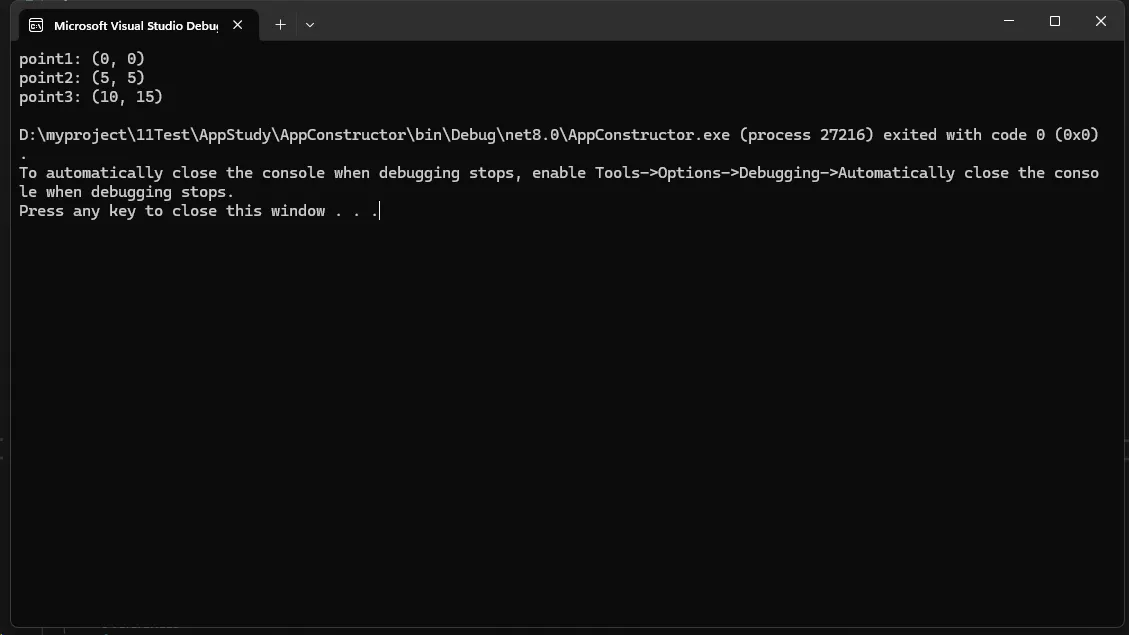
// 使用构造函数创建对象
Point point1 = new Point();
Point point2 = new Point(5);
Point point3 = new Point(10, 15);
Console.WriteLine($"point1: ({point1.X}, {point1.Y})");
Console.WriteLine($"point2: ({point2.X}, {point2.Y})");
Console.WriteLine($"point3: ({point3.X}, {point3.Y})");
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
析构函数(Destructor)
什么是析构函数
析构函数是一种特殊的方法,用于在对象被销毁前执行清理操作。它在对象被垃圾回收器回收之前自动调用,用于释放非托管资源,如文件句柄、数据库连接等。
注意:在 .NET 5这后的,Net版本中 中析构函数 ~FileManager() 不会被调用的问题,这个只能用于.Net Framework,在Net中推荐的方式是实现 IDisposable 接口。
析构函数的特点
- 名称为类名前加波浪号:如
~ClassName()。 - 无参数:析构函数不能带有参数,也不能进行重载。
- 无需显式调用:由垃圾回收器自动调用。
析构函数的用途
- 释放非托管资源:清理如文件、数据库连接等非托管资源。
- 执行必要的清理工作:确保资源被正确释放,避免资源泄漏。
示例:定义和使用析构函数
示例5:管理文件资源的类
C#using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.IO;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace AppDestructor
{
public class FileManager
{
private FileStream fileStream;
// 构造函数,打开文件
public FileManager(string filePath)
{
fileStream = new FileStream(filePath, FileMode.OpenOrCreate);
Console.WriteLine("文件已打开。");
}
// 析构函数,关闭文件
~FileManager()
{
if (fileStream != null)
{
fileStream.Close();
fileStream = null;
Console.WriteLine("文件已关闭。");
}
}
}
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 使用FileManager
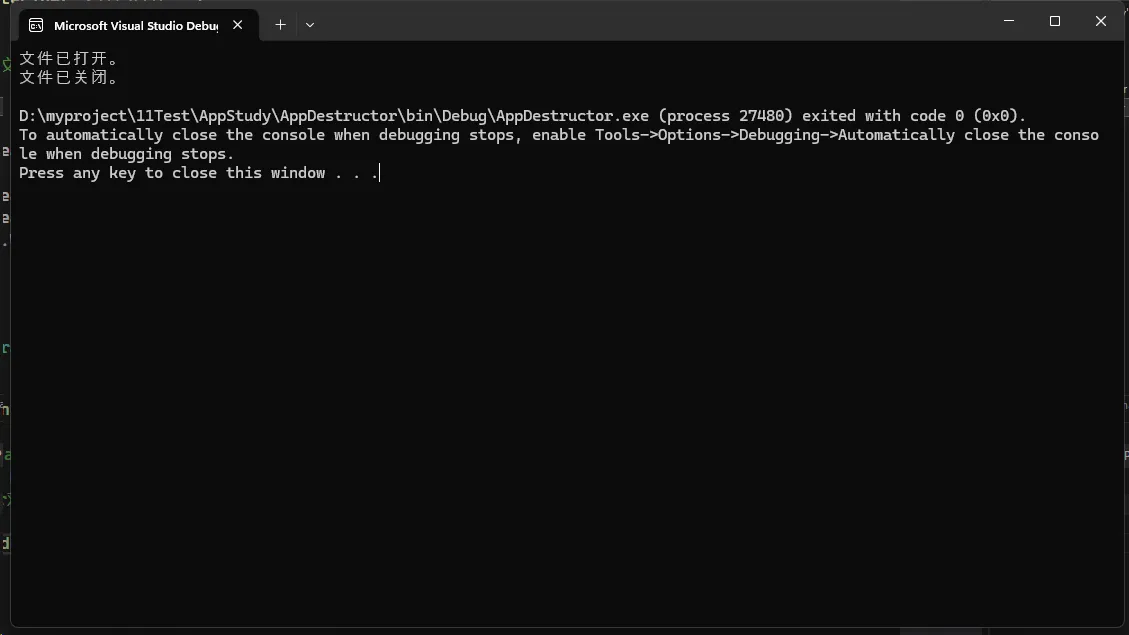
FileManager manager = new FileManager("example.txt");
// 当manager对象被垃圾回收时,析构函数将被调用
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
注意:
- 垃圾回收器的调用时机不确定,因此析构函数的执行时间也是不确定的。
- 最好使用
IDisposable接口和using语句来确保资源及时释放。
使用IDisposable接口和using语句
由于析构函数的调用时机不确定,推荐实现IDisposable接口,并使用using语句。
这里其实可以不写析构函数
示例6:改进的资源管理
C#namespace AppDestructorNet
{
public class FileManager : IDisposable
{
private FileStream fileStream;
// 构造函数,打开文件
public FileManager(string filePath)
{
fileStream = new FileStream(filePath, FileMode.OpenOrCreate);
Console.WriteLine("文件已打开。");
}
// 实现IDisposable接口
public void Dispose()
{
if (fileStream != null)
{
fileStream.Close();
fileStream = null;
Console.WriteLine("文件已关闭。");
}
GC.SuppressFinalize(this);
}
// 析构函数
~FileManager()
{
Dispose();
}
}
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
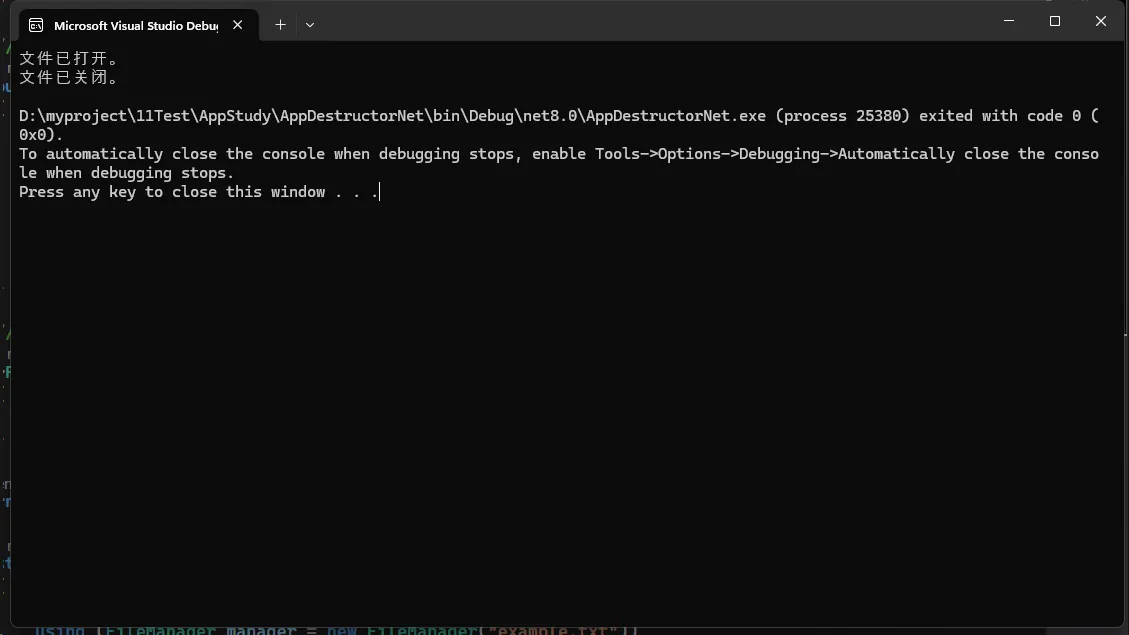
// 使用using语句
using (FileManager manager = new FileManager("example.txt"))
{
// 进行文件操作
}
// 离开using块后,Dispose方法会被自动调用,资源被及时释放
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
总结
在本文中,我们详细了解了C#中构造函数与析构函数的概念、特点和使用场景。通过多个示例,展示了如何定义和使用它们,以及如何通过实现IDisposable接口和使用using语句来更好地管理资源。
- 构造函数用于初始化对象的状态,是对象正确创建的关键。
- 析构函数用于在对象销毁前执行清理操作,但由于调用时机不确定,推荐使用
IDisposable接口和using语句来确保资源的及时释放。
注意事项:
- 优先使用IDisposable接口和using语句:确保资源被及时释放,避免资源泄漏。
- 避免在析构函数中编写复杂逻辑:析构函数的执行时间不确定,过多的逻辑可能导致性能问题。
- 谨慎管理非托管资源:确保非托管资源被正确释放,避免内存泄漏。
通过合理使用构造函数和析构函数,可以有效地管理对象的生命周期,提高程序的健壮性和可靠性。
本文作者:技术老小子
本文链接:
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!
目录