目录
抽象类和接口是C#中实现抽象化和多态性的两个核心概念。本篇文章将详细阐述抽象类和接口的概念、特点、应用场景,并通过多个示例加深对这些概念的理解。
抽象类(Abstract Class)
概念
- 不能实例化:抽象类不能被实例化,它通常作为基类存在,为子类提供一套通用的接口和部分实现。
- 包含实现:抽象类可以包含具体的方法实现和抽象方法。抽象方法必须在子类中被重写。
- 单继承:一个类只能继承自一个抽象类(C#中不支持多重继承)。
应用场景
当你希望提供一个通用的基类,该基类定义了一些子类共有的方法实现,并且还有一些方法需要由子类提供具体实现时,使用抽象类是一个不错的选择。
示例
示例1:图形基类
C#namespace App07
{
// 抽象的图形基类
public abstract class Shape
{
// 抽象方法:计算面积
public abstract double Area();
// 具体实现的方法:显示形状信息
public void Display()
{
Console.WriteLine("This is a shape.");
}
}
// 圆形类,继承自Shape
public class Circle : Shape
{
public double Radius { get; set; }
// 重写抽象方法:计算圆的面积
public override double Area()
{
return Math.PI * Radius * Radius;
}
}
// 矩形类,继承自Shape
public class Rectangle : Shape
{
public double Width { get; set; }
public double Height { get; set; }
// 重写抽象方法:计算矩形的面积
public override double Area()
{
return Width * Height;
}
}
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Circle circle = new Circle();
circle.Radius = 5;
Console.WriteLine("The area of the circle is {0}.", circle.Area());
Rectangle rectangle = new Rectangle();
rectangle.Width = 4;
rectangle.Height = 6;
Console.WriteLine("The area of the rectangle is {0}.", rectangle.Area());
}
}
}
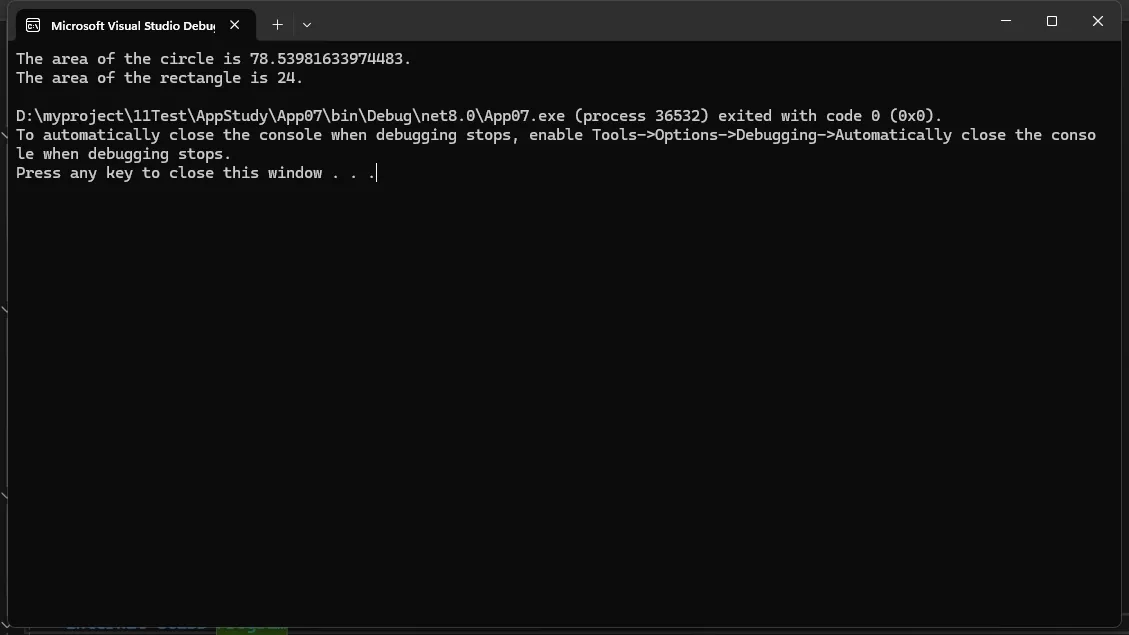
说明:
Shape类是一个抽象类,包含一个抽象方法Area()和一个具体方法Display()。Circle和Rectangle类继承自Shape,并实现了Area()方法。
示例2:动物基类
C#namespace App07
{
// 抽象的动物基类
public abstract class Animal
{
// 抽象方法:发出叫声
public abstract void MakeSound();
// 具体方法:共同的行为
public void Sleep()
{
Console.WriteLine("The animal is sleeping.");
}
}
// 狗类,继承自Animal
public class Dog : Animal
{
public override void MakeSound()
{
Console.WriteLine("Dog barks: Woof!");
}
}
// 猫类,继承自Animal
public class Cat : Animal
{
public override void MakeSound()
{
Console.WriteLine("Cat meows: Meow!");
}
}
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 创建Dog对象
Dog dog = new Dog();
// 调用Dog的共同行为
dog.Sleep();
// 调用Dog的叫声
dog.MakeSound();
// 创建Cat对象
Cat cat = new Cat();
// 调用Cat的共同行为
cat.Sleep();
// 调用Cat的叫声
cat.MakeSound();
}
}
}
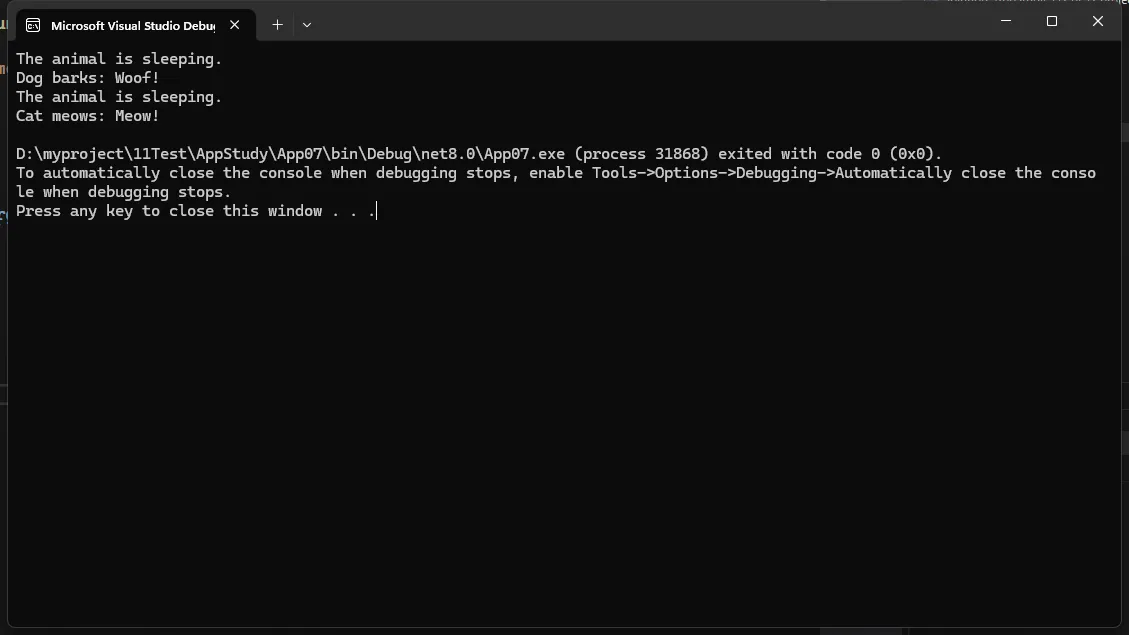
说明:
Animal类定义了共有的行为Sleep(),并要求子类实现MakeSound()方法。
接口(Interface)
概念
- 完全抽象:接口只能包含方法、属性、事件、索引器的声明,不能包含任何实现。
- 多实现:一个类可以实现多个接口,实现接口即需要实现其所有成员。
- 成员默认是公共的:接口成员默认是公共的,不能包含访问修饰符。
应用场景
当你希望定义一组不相关类之间的通用行为契约,并且不涉及实现细节时,接口是最好的选择。
示例
示例1:可绘制和可变形
C#namespace App07
{
// 可绘制的接口
public interface IDrawable
{
void Draw();
}
// 可变形的接口
public interface ITransformable
{
void Rotate(double angle);
void Scale(double factor);
}
// 实现了IDrawable和ITransformable的形状类
public class TransformableShape : IDrawable, ITransformable
{
public void Draw()
{
Console.WriteLine("Drawing the shape.");
}
public void Rotate(double angle)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Rotating the shape by {angle} degrees.");
}
public void Scale(double factor)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Scaling the shape by a factor of {factor}.");
}
}
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
TransformableShape shape = new TransformableShape();
shape.Draw();
shape.Rotate(45);
shape.Scale(2.0);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
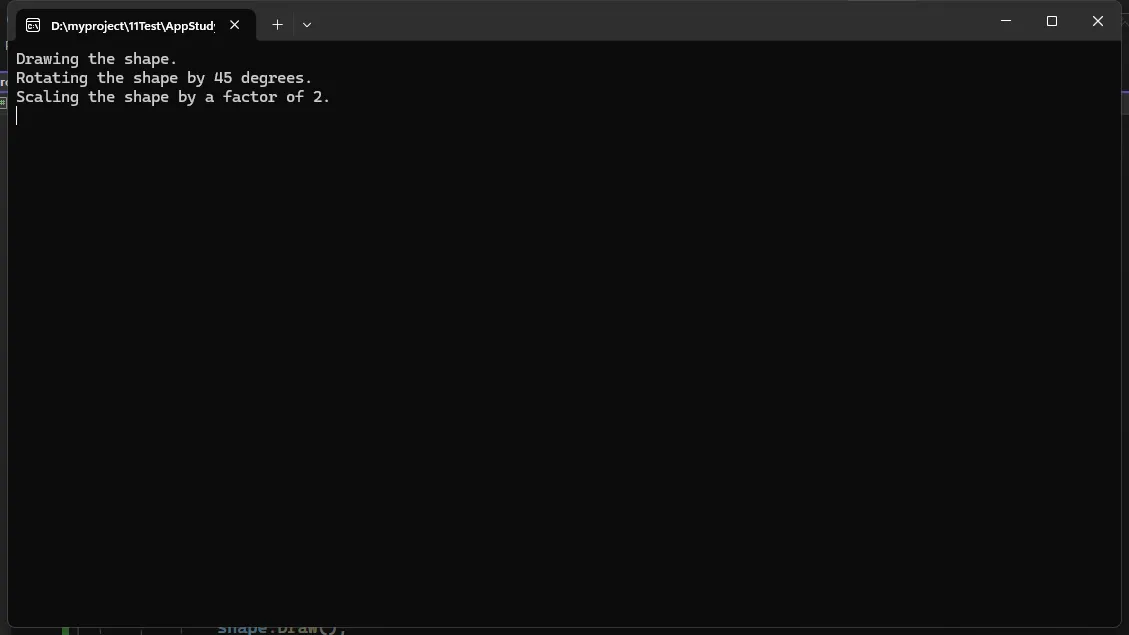
说明:
IDrawable和ITransformable是两个接口,定义了绘制和变形的行为。TransformableShape类实现了这两个接口,必须提供所有方法的实现。
示例2:数据存储接口
C#namespace App07
{
// 数据存储接口
public interface IDataStore
{
void Save(string data);
string Load();
}
// 本地文件存储类
public class FileDataStore : IDataStore
{
public void Save(string data)
{
Console.WriteLine("Saving data to file.");
// 实际的文件保存逻辑
}
public string Load()
{
Console.WriteLine("Loading data from file.");
// 实际的文件加载逻辑
return "Data from file";
}
}
// 云端存储类
public class CloudDataStore : IDataStore
{
public void Save(string data)
{
Console.WriteLine("Saving data to cloud.");
// 实际的云保存逻辑
}
public string Load()
{
Console.WriteLine("Loading data from cloud.");
// 实际的云加载逻辑
return "Data from cloud";
}
}
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 选择存储方式
IDataStore dataStore = new FileDataStore();
// 保存数据
dataStore.Save("Some data");
// 加载数据
string loadedData = dataStore.Load();
Console.WriteLine("Loaded data: " + loadedData);
}
}
}
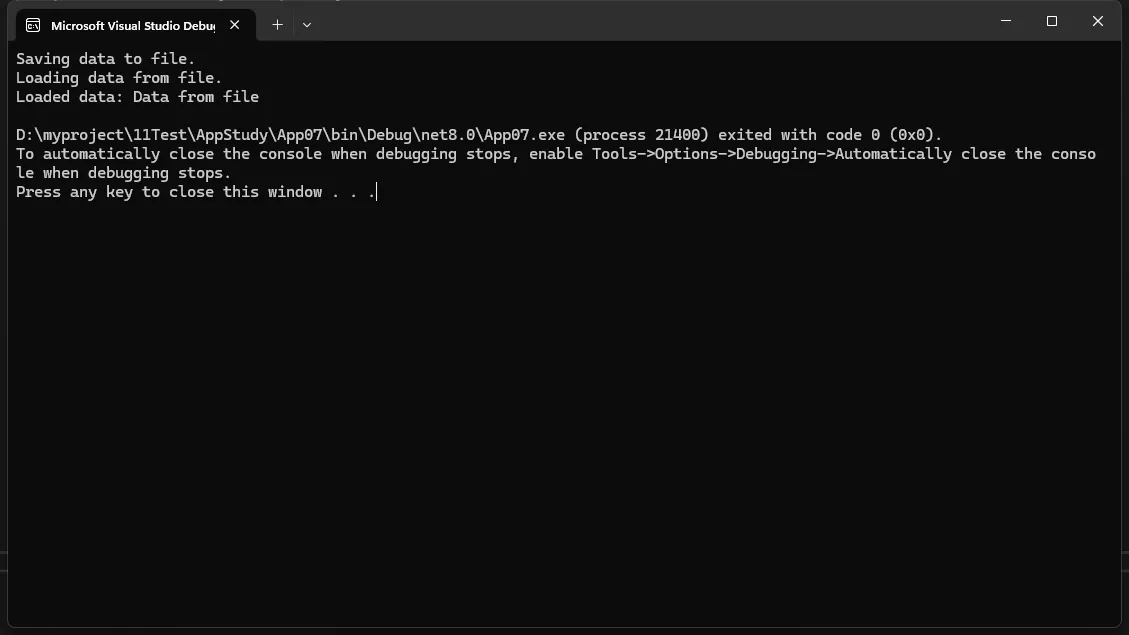
说明:
IDataStore接口定义了数据存储的行为。FileDataStore和CloudDataStore类分别实现了本地文件存储和云端存储。
抽象类与接口的组合使用
有时,我们可以将抽象类和接口结合起来使用,以充分利用它们的优势。
示例:动物行为
C#namespace App07
{
// 抽象的动物类
public abstract class Animal
{
public abstract void Eat();
public void Breathe()
{
Console.WriteLine("Animal breathes.");
}
}
// 可移动的接口
public interface IMovable
{
void Move();
}
// 可飞行的接口
public interface IFlyable
{
void Fly();
}
// 狗类,继承自Animal并实现IMovable接口
public class Dog : Animal, IMovable
{
public override void Eat()
{
Console.WriteLine("Dog eats.");
}
public void Move()
{
Console.WriteLine("Dog runs.");
}
}
// 鸟类,继承自Animal并实现IMovable和IFlyable接口
public class Bird : Animal, IMovable, IFlyable
{
public override void Eat()
{
Console.WriteLine("Bird eats.");
}
public void Move()
{
Console.WriteLine("Bird walks.");
}
public void Fly()
{
Console.WriteLine("Bird flies.");
}
}
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 创建Dog对象并调用方法
Dog dog = new Dog();
dog.Eat();
dog.Breathe();
dog.Move();
// 创建Bird对象并调用方法
Bird bird = new Bird();
bird.Eat();
bird.Breathe();
bird.Move();
bird.Fly();
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
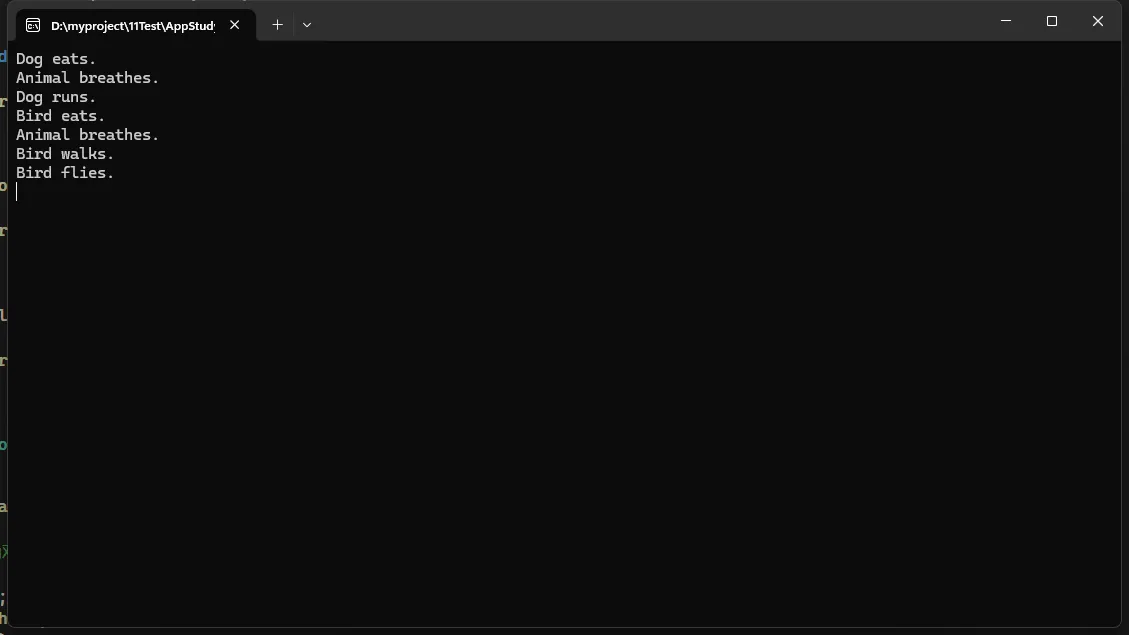
说明:
Animal是一个抽象类,定义了所有动物的共有行为。IMovable和IFlyable是接口,定义了可移动和可飞行的行为。Dog类继承自Animal并实现了IMovable接口。Bird类继承自Animal并实现了IMovable和IFlyable接口。
总结
抽象类和接口是C#中实现代码抽象化和多态的两个重要工具。它们各自有不同的适用场景:
- 抽象类:适用于具有共同特征的类,需要共享代码实现,提供默认行为。
- 接口:适用于不相关的类之间共享行为契约,不涉及实现,只关注功能的定义。
在实际开发中,可以根据需求选择使用抽象类或接口,甚至结合使用,以实现最佳的设计和代码复用。希望通过本文的详细讲解和丰富的示例,你能够更好地理解和应用抽象类和接口来构建灵活且强大的C#应用程序。
本文作者:技术老小子
本文链接:
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!
目录