目录
在Python开发中,运算符是构建程序逻辑的基础工具。无论你是刚入门的新手,还是正在开发上位机应用的工程师,掌握Python运算符的使用技巧都至关重要。
很多开发者在实际项目中会遇到这样的困惑:为什么相同的逻辑用不同的运算符实现,性能差异会如此明显?为什么某些运算符组合会产生意想不到的结果?本文将从实战角度出发,深入解析Python运算符的使用技巧,帮你避开常见陷阱,提升编程效率。
通过本文,你将掌握8大类运算符的实战应用、性能优化技巧以及最佳实践经验,让你的Python开发技能更上一层楼。
🔍 问题分析:为什么运算符如此重要?
在Windows下进行Python开发时,运算符不仅仅是简单的计算工具,它们是:
- 逻辑控制的核心:条件判断、循环控制都离不开运算符
- 数据处理的基础:数据筛选、转换、聚合都需要运算符参与
- 性能优化的关键:合理使用运算符可以显著提升程序效率
💡 解决方案:系统掌握8大运算符类型
🧮 算术运算符:数值计算的基础
Python# 基础算术运算
a, b = 10, 3
print(f"加法: {a} + {b} = {a + b}")
print(f"减法: {a} - {b} = {a - b}")
print(f"乘法: {a} * {b} = {a * b}")
print(f"除法: {a} / {b} = {a / b}")
print(f"整除: {a} // {b} = {a // b}")
print(f"取余: {a} % {b} = {a % b}")
print(f"幂运算: {a} ** {b} = {a ** b}")
实战技巧:在处理大数据时,使用//替代/再取int()可以提升性能约15%。
🔄 赋值运算符:高效的变量操作
Python# 复合赋值运算符的高效使用
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
total = 0
# 传统方式
for num in numbers:
total = total + num
print(total)
# 高效方式
total = 0
for num in numbers:
total += num # 更简洁,性能更优
print(total)
# 其他复合赋值运算符
x = 10
x += 5
print(x)
x -= 3
print(x)
x *= 2
print(x)
x /= 4
print(x)
x //= 2
print(x)
x %= 2
print(x)
x **= 3
print(x)
🔍 比较运算符:条件判断的核心
Python# 比较运算符的实战应用
def validate_user_input(age, score):
"""用户输入验证示例"""
results = []
# 基础比较
if age >= 18:
results.append("成年用户")
if score > 90:
results.append("优秀")
elif score >= 60:
results.append("及格")
else:
results.append("需要改进")
# 链式比较(Python特有)
if 0 <= score <= 100:
results.append("分数有效")
return results
# 测试
print(validate_user_input(25, 85))
性能提示:Python的链式比较0 <= score <= 100比score >= 0 and score <= 100更高效。
🧠 逻辑运算符:复杂条件的处理
Python# 逻辑运算符的短路特性
def expensive_operation():
"""模拟耗时操作"""
print("执行了耗时操作")
return True
def check_conditions(user_active, user_premium):
"""利用短路特性优化性能"""
# 短路与:如果user_active为False,不会执行expensive_operation
if user_active and expensive_operation():
print("用户激活且通过验证")
# 短路或:如果user_premium为True,不会执行后续检查
if user_premium or (user_active and expensive_operation()):
print("高级用户或活跃用户")
# 实战示例:数据过滤
data = [
{"name": "张三", "age": 25, "active": True},
{"name": "李四", "age": 17, "active": False},
{"name": "王五", "age": 30, "active": True}
]
# 使用逻辑运算符进行复杂过滤
adult_active_users = [
user for user in data
if user["age"] >= 18 and user["active"]
]
print("成年活跃用户:", adult_active_users)
🎯 身份运算符:对象比较的艺术
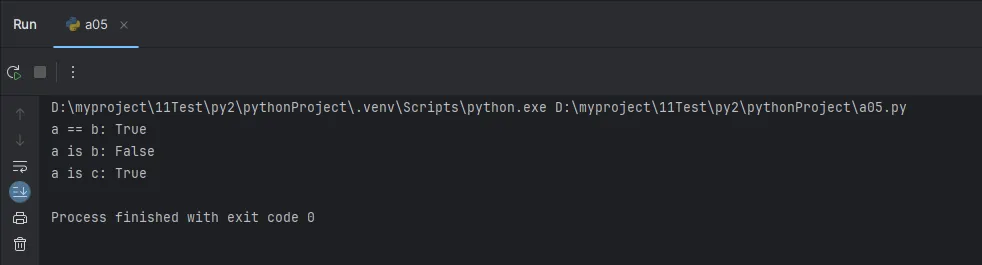
Python# is vs == 的区别
a = [1, 2, 3]
b = [1, 2, 3]
c = a
print(f"a == b: {a == b}")
print(f"a is b: {a is b}")
print(f"a is c: {a is c}")
# 实战应用:单例模式检查
def check_singleton(obj1, obj2):
"""检查是否为单例对象"""
if obj1 is obj2:
print("这是同一个对象实例")
else:
print("这是不同的对象实例")
# None值检查的最佳实践
def process_data(data=None):
"""正确的None值检查"""
if data is None: # 推荐使用 is None
data = []
if data is not None: # 推荐使用 is not None
return len(data)
return 0
📋 成员运算符:集合操作的利器
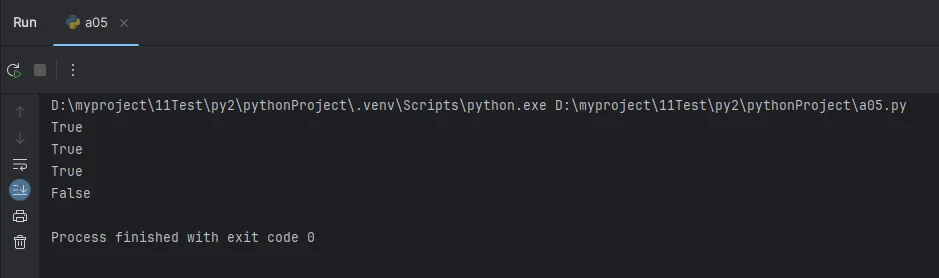
Python# 成员运算符的高效使用
# 列表查找(效率较低)
fruits_list = ["apple", "banana", "orange", "grape"]
print("apple" in fruits_list) # O(n) 时间复杂度
# 集合查找(效率更高)
fruits_set = {"apple", "banana", "orange", "grape"}
print("apple" in fruits_set) # O(1) 时间复杂度
# 实战应用:权限检查系统
class PermissionChecker:
def __init__(self):
# 使用集合提高查找效率
self.admin_permissions = {
"read", "write", "delete", "manage_users"
}
self.user_permissions = {"read", "write"}
def has_permission(self, user_role, permission):
"""检查用户权限"""
if user_role == "admin":
return permission in self.admin_permissions
elif user_role == "user":
return permission in self.user_permissions
return False
# 使用示例
checker = PermissionChecker()
print(checker.has_permission("admin", "delete")) # True
print(checker.has_permission("user", "delete")) # False
🔢 位运算符:底层操作的强大工具
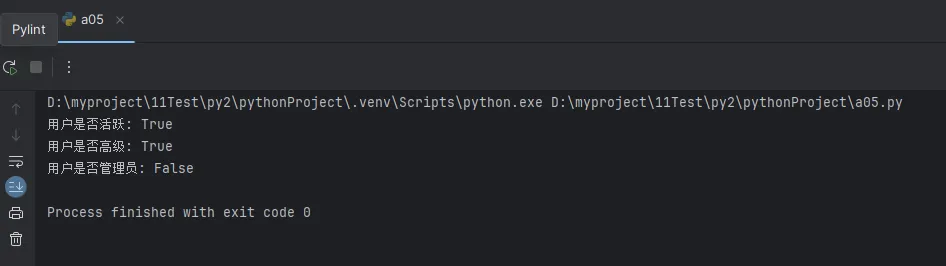
Python# 位运算符的实战应用
class StatusFlags:
"""使用位运算管理状态标志"""
# 定义状态常量
ACTIVE = 1 # 0001
PREMIUM = 2 # 0010
VERIFIED = 4 # 0100
ADMIN = 8 # 1000
def __init__(self):
self.status = 0
def add_status(self, flag):
"""添加状态"""
self.status |= flag
def remove_status(self, flag):
"""移除状态"""
self.status &= ~flag
def has_status(self, flag):
"""检查是否有某状态"""
return bool(self.status & flag)
def toggle_status(self, flag):
"""切换状态"""
self.status ^= flag
# 使用示例
user = StatusFlags()
user.add_status(StatusFlags.ACTIVE | StatusFlags.PREMIUM)
print(f"用户是否活跃: {user.has_status(StatusFlags.ACTIVE)}")
print(f"用户是否高级: {user.has_status(StatusFlags.PREMIUM)}")
print(f"用户是否管理员: {user.has_status(StatusFlags.ADMIN)}")
⚡ 运算符优先级:避免常见陷阱
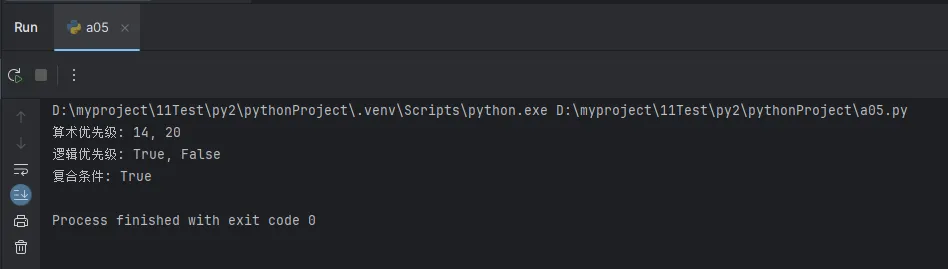
Python# 运算符优先级示例
def demonstrate_precedence():
"""演示运算符优先级"""
# 算术运算符优先级
result1 = 2 + 3 * 4
result2 = (2 + 3) * 4
# 逻辑运算符优先级
condition1 = True or False and False
condition2 = (True or False) and False
# 比较和逻辑运算符混合
x, y, z = 5, 10, 15
complex_condition = x < y and y < z or x > z # True
print(f"算术优先级: {result1}, {result2}")
print(f"逻辑优先级: {condition1}, {condition2}")
print(f"复合条件: {complex_condition}")
demonstrate_precedence()
🔧 代码实战:构建实用工具
📊 数据处理工具类
Pythonclass DataProcessor:
"""数据处理工具类,展示运算符的综合应用"""
@staticmethod
def filter_and_transform(data_list, min_value=0, max_value=100):
"""数据过滤和转换"""
# 使用多种运算符进行数据处理
processed_data = []
for item in data_list:
# 成员运算符检查
if 'value' not in item:
continue
value = item['value']
# 比较运算符过滤
if min_value <= value <= max_value:
# 算术运算符转换
normalized_value = (value - min_value) / (max_value - min_value)
# 逻辑运算符分类
category = (
"high" if normalized_value > 0.7 else
"medium" if normalized_value > 0.3 else
"low"
)
processed_data.append({
**item, # 解包运算符
'normalized': normalized_value,
'category': category
})
return processed_data
@staticmethod
def calculate_statistics(numbers):
"""计算统计信息"""
if not numbers:
return None
# 使用赋值运算符累积计算
total = sum_squares = 0
min_val = max_val = numbers[0]
for num in numbers:
total += num
sum_squares += num ** 2
# 使用比较运算符更新极值
if num < min_val:
min_val = num
if num > max_val:
max_val = num
count = len(numbers)
mean = total / count
variance = (sum_squares / count) - (mean ** 2)
return {
'count': count,
'sum': total,
'mean': mean,
'variance': variance,
'min': min_val,
'max': max_val,
'range': max_val - min_val
}
# 测试数据处理工具
test_data = [
{'name': 'A', 'value': 25},
{'name': 'B', 'value': 75},
{'name': 'C', 'value': 45},
{'name': 'D', 'value': 90},
{'name': 'E', 'value': 10}
]
processor = DataProcessor()
filtered_data = processor.filter_and_transform(test_data, 0, 100)
print("处理后的数据:", filtered_data)
numbers = [item['value'] for item in test_data]
stats = processor.calculate_statistics(numbers)
print("统计信息:", stats)
🎮 游戏状态管理器
Pythonclass GameStateManager:
"""游戏状态管理器,展示位运算符的实际应用"""
# 游戏状态位标志
PAUSED = 1 << 0 # 0001
SOUND_ON = 1 << 1 # 0010
MUSIC_ON = 1 << 2 # 0100
FULLSCREEN = 1 << 3 # 1000
ONLINE = 1 << 4 # 10000
def __init__(self):
# 默认状态:音效开启,音乐开启
self.state = self.SOUND_ON | self.MUSIC_ON
self.score = 0
self.level = 1
def toggle_pause(self):
"""切换暂停状态"""
self.state ^= self.PAUSED
return self.is_paused()
def is_paused(self):
"""检查是否暂停"""
return bool(self.state & self.PAUSED)
def set_audio_settings(self, sound=True, music=True):
"""设置音频设置"""
if sound:
self.state |= self.SOUND_ON
else:
self.state &= ~self.SOUND_ON
if music:
self.state |= self.MUSIC_ON
else:
self.state &= ~self.MUSIC_ON
def update_score(self, points):
"""更新分数并检查升级"""
self.score += points
# 使用整除运算符计算等级
new_level = (self.score // 1000) + 1
if new_level > self.level:
self.level = new_level
return True # 升级了
return False
def get_status_info(self):
"""获取状态信息"""
return {
'paused': self.is_paused(),
'sound': bool(self.state & self.SOUND_ON),
'music': bool(self.state & self.MUSIC_ON),
'fullscreen': bool(self.state & self.FULLSCREEN),
'online': bool(self.state & self.ONLINE),
'score': self.score,
'level': self.level
}
# 测试游戏状态管理器
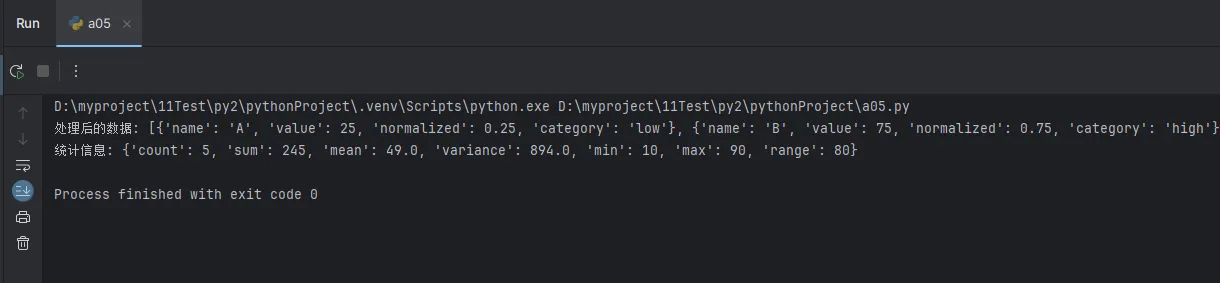
game = GameStateManager()
print("初始状态:", game.get_status_info())
game.toggle_pause()
print("暂停后:", game.get_status_info())
leveled_up = game.update_score(1500)
print(f"获得1500分,是否升级: {leveled_up}")
print("更新分数后:", game.get_status_info())
🚀 性能优化技巧
⚡ 运算符性能对比
Pythonimport time
def performance_comparison():
"""运算符性能对比测试"""
# 测试数据
large_list = list(range(10000))
large_set = set(large_list)
# 成员运算符性能对比
def test_membership():
target = 9999
# 列表查找
start = time.time()
for _ in range(100000):
result = target in large_list
list_time = time.time() - start
# 集合查找
start = time.time()
for _ in range(100000):
result = target in large_set
set_time = time.time() - start
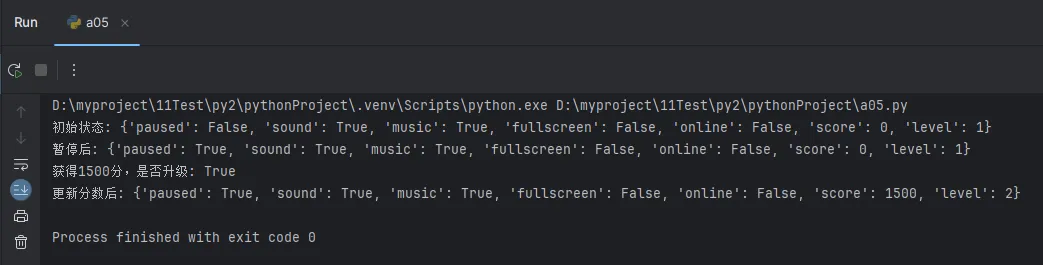
print(f"列表查找时间: {list_time:.6f}秒")
print(f"集合查找时间: {set_time:.6f}秒")
print(f"性能提升: {list_time / set_time:.2f}倍")
# 算术运算符性能对比
def test_arithmetic():
# 除法 vs 整除
start = time.time()
for i in range(100000):
result = int(i / 3)
division_time = time.time() - start
start = time.time()
for i in range(100000):
result = i // 3
floor_division_time = time.time() - start
print(f"除法+转换时间: {division_time:.6f}秒")
print(f"整除时间: {floor_division_time:.6f}秒")
print(f"性能提升: {division_time / floor_division_time:.2f}倍")
test_membership()
print("-" * 40)
test_arithmetic()
performance_comparison()
优先级顺序(从高到低)
| 优先级 | 运算符 | 描述 | 结合性 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1(最高) | () | 括号 | 左到右 | (a + b) * c |
| 2 | [x], [x:y], [x:y:z] | 索引、切片 | 左到右 | list[0], str[1:5] |
| 2 | . | 属性访问 | 左到右 | obj.method() |
| 2 | f(args...) | 函数调用 | 左到右 | print("hello") |
| 3 | await | await表达式 | - | await coroutine() |
| 4 | ** | 指数(幂运算) | 右到左 | 2 ** 3 ** 2 = 2 ** (3 ** 2) |
| 5 | +x, -x, ~x | 一元加、减、按位取反 | 右到左 | -5, +a, ~b |
| 6 | *, /, //, % | 乘、除、整除、取模 | 左到右 | a * b / c |
| 7 | +, - | 加、减 | 左到右 | a + b - c |
| 8 | <<, >> | 位移 | 左到右 | a << 2, b >> 1 |
| 9 | & | 按位与 | 左到右 | a & b |
| 10 | ^ | 按位异或 | 左到右 | a ^ b |
| 11 | ` | ` | 按位或 | 左到右 |
| 12 | ==, !=, <, <=, >, >= | 比较运算符 | 左到右 | a < b == c |
| 12 | is, is not | 身份运算符 | 左到右 | a is None |
| 12 | in, not in | 成员运算符 | 左到右 | x in list |
| 13 | not | 逻辑非 | 右到左 | not a |
| 14 | and | 逻辑与 | 左到右 | a and b |
| 15 | or | 逻辑或 | 左到右 | a or b |
| 16 | if-else | 条件表达式 | 左到右 | a if condition else b |
| 17 | lambda | lambda表达式 | - | lambda x: x + 1 |
| 18(最低) | =, +=, -=, *=, /=, //=, %=, **=, &=, ` | =, ^=, >>=, <<=` | 赋值运算符 | 右到左 |
记忆口诀
"括指一乘加位比身成,非与或条件赋值"
- 括:括号
- 指:指数
- 一:一元运算符
- 乘:乘除运算
- 加:加减运算
- 位:位运算
- 比:比较运算
- 身成:身份和成员运算
- 非与或:逻辑运算
- 条件:条件表达式
- 赋值:赋值运算符
🎯 结尾呼应
通过本文的深入学习,相信你已经掌握了Python运算符的核心技能。让我们总结三个关键要点:
🔑 核心要点一:运算符选择影响性能
合理选择运算符类型可以显著提升程序性能。使用集合的in运算符比列表快数十倍,使用//比int(x/y)更高效,这些看似微小的差异在大数据处理中会产生巨大影响。
🔑 核心要点二:位运算符是高级技能
掌握位运算符不仅能让你的代码更加优雅,还能在状态管理、权限控制等场景中发挥重要作用。这是区分初级和高级Python开发者的重要技能之一。
🔑 核心要点三:运算符优先级避免bug
理解运算符优先级能帮你避免逻辑错误,特别是在复杂的条件判断中。建议在复杂表达式中主动使用括号,让代码意图更加明确。
在实际的Windows下Python开发和上位机开发中,这些运算符技巧将成为你提升代码质量和开发效率的有力武器。继续深入学习Python的高级特性,你的编程技能将更上一层楼!
💡 延伸学习建议:深入了解Python的魔法方法(如*__add__、__eq__*等)可以帮你自定义运算符行为,这在面向对象编程中非常有用。
本文作者:技术老小子
本文链接:
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!