目录
在Python开发过程中,输入输出函数是每个程序员都必须掌握的基础技能。无论是制作简单的控制台程序,还是开发复杂的上位机应用,输入输出操作都扮演着至关重要的角色。
很多初学者在使用input()和print()函数时,往往只停留在基础应用层面,却不知道这些函数还藏着许多实用的高级技巧。本文将从问题分析、解决方案到代码实战,带你全面掌握Python输入输出函数的核心要点,让你的编程技巧更上一层楼。
🔍 问题分析
📊 常见的输入输出难题
在实际Python开发中,我们经常遇到以下问题:
- 数据类型转换混乱:用户输入的都是字符串,如何正确转换为需要的数据类型?
- 输出格式不规范:如何让输出结果更加美观、易读?
- 异常处理缺失:用户输入错误数据时程序崩溃怎么办?
- 批量数据处理:如何高效处理多个输入输出操作?
这些问题在上位机开发和日常编程中频繁出现,掌握解决方案至关重要。
💡 解决方案
🎪 Python输入函数深度解析
input()函数的核心机制
input()函数的工作原理非常简单,但细节决定成败:
Python# 基础语法
user_input = input("提示信息:")
关键特点:
- 总是返回字符串类型
- 程序会暂停等待用户输入
- 按回车键确认输入
🔄 智能类型转换技巧
Python# 方法一:直接转换(风险较高)
age = int(input("请输入年龄:"))
# 方法二:安全转换(推荐)
def safe_input(prompt, data_type=str):
while True:
try:
user_input = input(prompt)
if data_type == int:
return int(user_input)
elif data_type == float:
return float(user_input)
else:
return user_input
except ValueError:
print(f"输入格式错误,请输入{data_type.__name__}类型的数据")
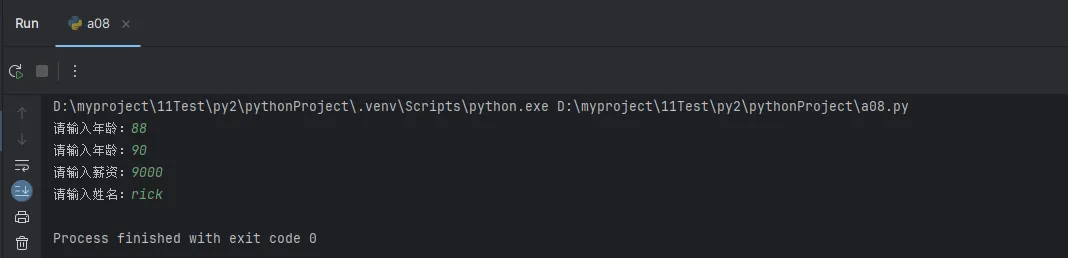
# 使用示例
age = safe_input("请输入年龄:", int)
salary = safe_input("请输入薪资:", float)
name = safe_input("请输入姓名:")
🎨 Python输出函数高级技巧
print()函数的强大参数
Python# 基础用法
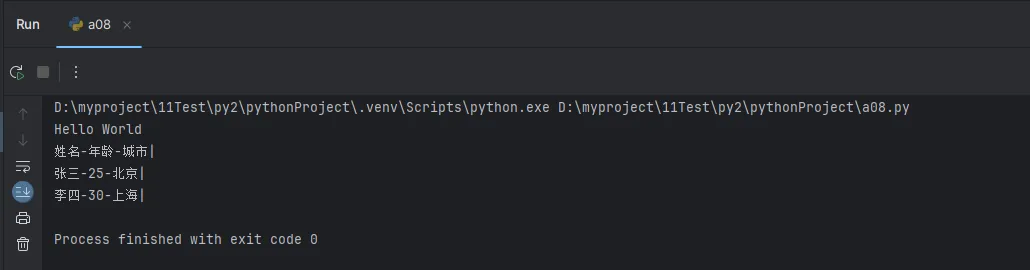
print("Hello World")
# 高级参数详解
print("姓名", "年龄", "城市", sep="-", end="|\n")
print("张三", 25, "北京", sep="-", end="|\n")
print("李四", 30, "上海", sep="-", end="|\n")
# 输出结果:
# 姓名-年龄-城市|
# 张三-25-北京|
# 李四-30-上海|
 核心参数说明:
核心参数说明:
sep:多个值之间的分隔符end:输出结束后的字符(默认是换行符)file:输出目标(默认是控制台)flush:是否立即刷新输出缓冲区
🎯 格式化输出的三种方法
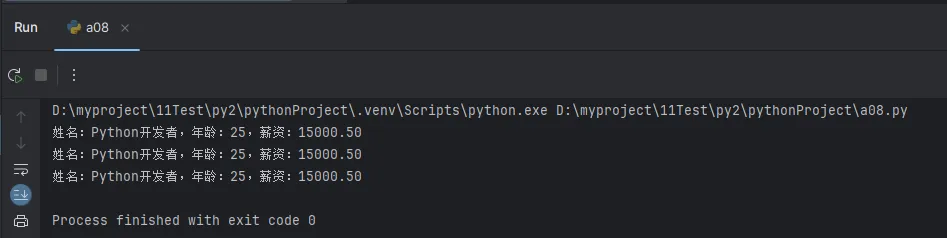
Pythonname = "Python开发者"
age = 25
salary = 15000.5
# 方法一:f-string(Python 3.6+,推荐)
print(f"姓名:{name},年龄:{age},薪资:{salary:.2f}")
# 方法二:format()方法
print("姓名:{},年龄:{},薪资:{:.2f}".format(name, age, salary))
# 方法三:%格式化(传统方法)
print("姓名:%s,年龄:%d,薪资:%.2f" % (name, age, salary))
🛠️ 代码实战
🚀 实战项目一:智能计算器
Pythonclass SmartCalculator:
def __init__(self):
self.history = []
def get_number(self, prompt):
"""安全获取数字输入"""
while True:
try:
return float(input(prompt))
except ValueError:
print("❌ 请输入有效的数字!")
def get_operator(self):
"""获取运算符"""
operators = ['+', '-', '*', '/']
while True:
op = input("请输入运算符(+, -, *, /):")
if op in operators:
return op
print("❌ 请输入有效的运算符!")
def calculate(self):
"""执行计算"""
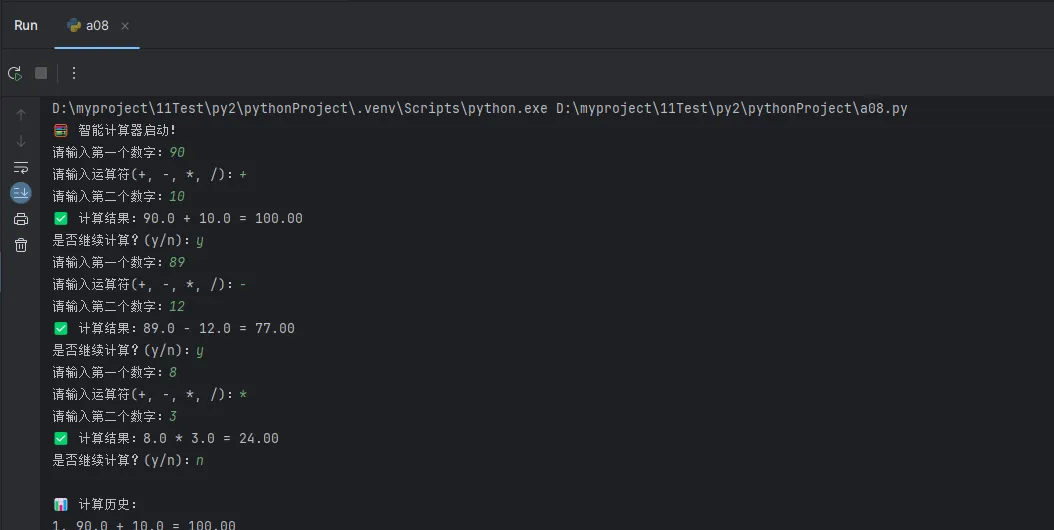
print("🧮 智能计算器启动!")
while True:
try:
num1 = self.get_number("请输入第一个数字:")
operator = self.get_operator()
num2 = self.get_number("请输入第二个数字:")
if operator == '+':
result = num1 + num2
elif operator == '-':
result = num1 - num2
elif operator == '*':
result = num1 * num2
elif operator == '/':
if num2 == 0:
print("❌ 除数不能为零!")
continue
result = num1 / num2
# 格式化输出结果
expression = f"{num1} {operator} {num2} = {result:.2f}"
print(f"✅ 计算结果:{expression}")
# 保存历史记录
self.history.append(expression)
# 询问是否继续
if input("是否继续计算?(y/n):").lower() != 'y':
break
except Exception as e:
print(f"❌ 发生错误:{e}")
# 显示历史记录
if self.history:
print("\n📊 计算历史:")
for i, record in enumerate(self.history, 1):
print(f"{i}. {record}")
# 运行计算器
if __name__ == "__main__":
calculator = SmartCalculator()
calculator.calculate()
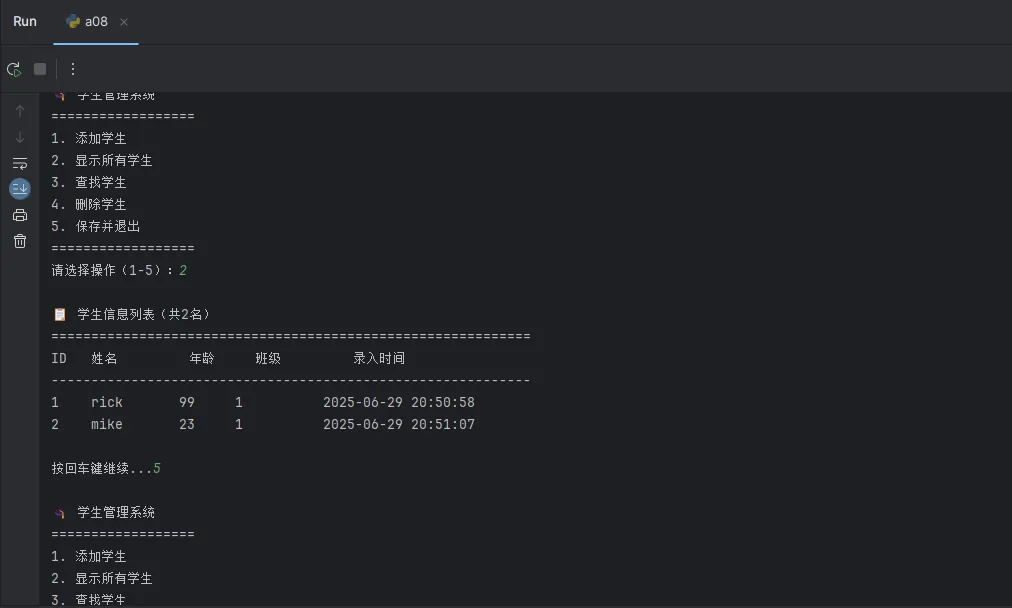
🎪 实战项目二:学生管理系统
Pythonimport json
from datetime import datetime
class StudentManager:
def __init__(self):
self.students = []
self.load_data()
def display_menu(self):
"""显示主菜单"""
menu = """
🎓 学生管理系统
==================
1. 添加学生
2. 显示所有学生
3. 查找学生
4. 删除学生
5. 保存并退出
=================="""
print(menu)
def add_student(self):
"""添加学生信息"""
print("\n➕ 添加新学生")
print("-" * 20)
name = input("姓名:").strip()
if not name:
print("❌ 姓名不能为空!")
return
while True:
try:
age = int(input("年龄:"))
if age <= 0 or age > 100:
print("❌ 请输入合理的年龄!")
continue
break
except ValueError:
print("❌ 请输入有效的年龄!")
grade = input("班级:").strip()
# 创建学生信息字典
student = {
'id': len(self.students) + 1,
'name': name,
'age': age,
'grade': grade,
'create_time': datetime.now().strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")
}
self.students.append(student)
print(f"✅ 学生 {name} 添加成功!")
def display_students(self):
"""显示所有学生"""
if not self.students:
print("\n📭 暂无学生信息")
return
print(f"\n📋 学生信息列表(共{len(self.students)}名)")
print("=" * 60)
print(f"{'ID':<4} {'姓名':<10} {'年龄':<6} {'班级':<10} {'录入时间':<20}")
print("-" * 60)
for student in self.students:
print(f"{student['id']:<4} {student['name']:<10} "
f"{student['age']:<6} {student['grade']:<10} "
f"{student['create_time']:<20}")
def search_student(self):
"""查找学生"""
if not self.students:
print("\n📭 暂无学生信息")
return
keyword = input("\n🔍 请输入学生姓名或班级:").strip()
found_students = []
for student in self.students:
if keyword in student['name'] or keyword in student['grade']:
found_students.append(student)
if found_students:
print(f"\n🎯 找到 {len(found_students)} 名学生:")
print("-" * 40)
for student in found_students:
print(f"ID: {student['id']}, 姓名: {student['name']}, "
f"年龄: {student['age']}, 班级: {student['grade']}")
else:
print("❌ 未找到匹配的学生")
def save_data(self):
"""保存数据到文件"""
try:
with open('students.json', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
json.dump(self.students, f, ensure_ascii=False, indent=2)
print("💾 数据保存成功!")
except Exception as e:
print(f"❌ 保存失败:{e}")
def load_data(self):
"""从文件加载数据"""
try:
with open('students.json', 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
self.students = json.load(f)
print("📂 数据加载成功!")
except FileNotFoundError:
print("📁 未找到数据文件,将创建新文件")
except Exception as e:
print(f"❌ 加载数据失败:{e}")
def run(self):
"""运行主程序"""
print("🎓 欢迎使用学生管理系统!")
while True:
self.display_menu()
choice = input("请选择操作(1-5):").strip()
if choice == '1':
self.add_student()
elif choice == '2':
self.display_students()
elif choice == '3':
self.search_student()
elif choice == '4':
# 删除功能的实现留给读者练习
print("🚧 删除功能开发中...")
elif choice == '5':
self.save_data()
print("👋 感谢使用,再见!")
break
else:
print("❌ 无效选择,请重新输入!")
input("\n按回车键继续...")
# 运行程序
if __name__ == "__main__":
manager = StudentManager()
manager.run()
🔧 高级输入输出技巧
Pythonimport sys
import os
from inputimeout import inputimeout, TimeoutOccurred
class AdvancedIO:
@staticmethod
def colored_print(text, color='white'):
"""彩色输出"""
colors = {
'red': '\033[91m',
'green': '\033[92m',
'yellow': '\033[93m',
'blue': '\033[94m',
'purple': '\033[95m',
'cyan': '\033[96m',
'white': '\033[97m',
'end': '\033[0m'
}
print(f"{colors.get(color, colors['white'])}{text}{colors['end']}")
@staticmethod
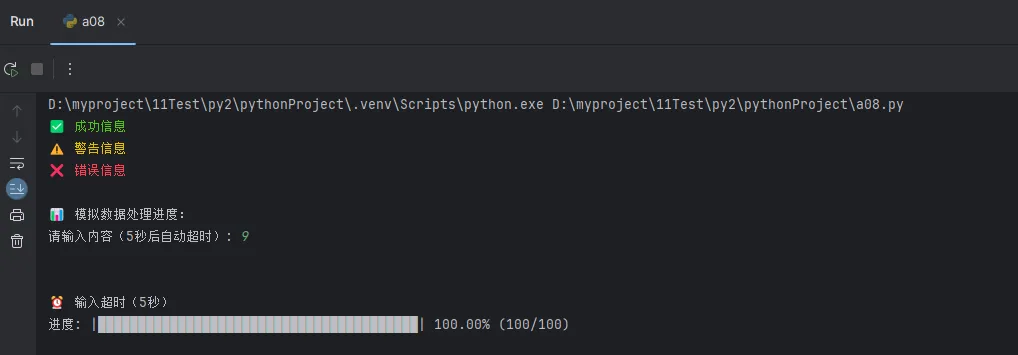
def progress_bar(current, total, bar_length=40):
"""进度条显示"""
percent = current / total
filled_length = int(bar_length * percent)
bar = '█' * filled_length + '-' * (bar_length - filled_length)
print(f'\r进度: |{bar}| {percent:.2%} ({current}/{total})', end='')
if current == total:
print() # 完成时换行
@staticmethod
def input_with_timeout_win(prompt, timeout=10):
try:
result = inputimeout(prompt=prompt, timeout=timeout)
return result
except TimeoutOccurred:
print(f"\n⏰ 输入超时({timeout}秒)")
return None
# 使用示例
if __name__ == "__main__":
io = AdvancedIO()
# 彩色输出示例
io.colored_print("✅ 成功信息", 'green')
io.colored_print("⚠️ 警告信息", 'yellow')
io.colored_print("❌ 错误信息", 'red')
# 进度条示例
print("\n📊 模拟数据处理进度:")
import time
result = io.input_with_timeout_win("请输入内容(5秒后自动超时): ", timeout=5)
for i in range(101):
io.progress_bar(i, 100)
time.sleep(0.02) # 模拟处理时间
🎯 性能优化建议
- 批量输出优化:使用列表收集输出内容,最后一次性输出
- 避免频繁类型转换:在合适的时机进行数据类型转换
- 使用缓冲区:合理设置输出缓冲区提高性能
🛡️ 安全编程实践
Python# 输入验证和异常处理的最佳实践
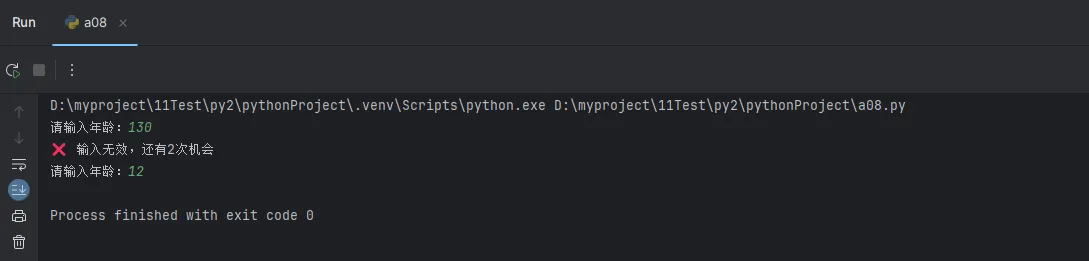
def secure_input(prompt, input_type=str, validator=None):
"""安全的输入函数"""
max_attempts = 3
attempts = 0
while attempts < max_attempts:
try:
user_input = input(prompt).strip()
# 类型转换
if input_type != str:
user_input = input_type(user_input)
# 自定义验证
if validator and not validator(user_input):
raise ValueError("验证失败")
return user_input
except (ValueError, TypeError) as e:
attempts += 1
remaining = max_attempts - attempts
if remaining > 0:
print(f"❌ 输入无效,还有{remaining}次机会")
else:
print("❌ 超过最大尝试次数")
return None
return None
# 使用示例
age = secure_input(
"请输入年龄:",
int,
lambda x: 0 < x < 120
)
🎯 结尾呼应
通过本文的深入讲解,我们全面掌握了Python输入输出函数的核心技能。让我们回顾三个关键要点:
第一,类型安全是基础。在实际的Python开发中,始终要记住input()返回的是字符串,合理的类型转换和异常处理能让程序更加健壮。无论是开发上位机应用还是数据处理脚本,这都是必备的编程技巧。
第二,格式化输出提升体验。掌握f-string和print()函数的高级参数,能够让你的程序输出更加专业美观。特别是在制作用户交互界面时,良好的输出格式能显著提升用户体验。
第三,实战项目巩固技能。文中的计算器和学生管理系统两个项目,展示了输入输出函数在实际开发中的应用。这些代码模板可以直接应用到你的项目中,助你快速提升Python开发效率。
输入输出虽然基础,但精通这些技能将为你后续的Python开发之路打下坚实基础。继续实践,不断精进,相信你一定能成为更优秀的Python开发者!
本文作者:技术老小子
本文链接:
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!
目录