目录
LINQ (Language Integrated Query) 是C#中最强大的特性之一,它让开发者能够以一种统一、直观的方式查询各种数据源。本文将深入探讨LINQ的进阶应用技巧,通过丰富的示例带您掌握LINQ的高级用法。
查询表达式与方法语法的灵活切换
LINQ提供两种语法形式:查询表达式和方法语法。掌握这两种语法的优势,并能根据场景灵活切换是LINQ进阶的关键。
基于复杂条件的分组查询
C#namespace AppLinq
{
internal class Program
{
public class Student
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public int Age { get; set; }
public string Major { get; set; }
public int Score { get; set; }
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 创建一个学生列表
var students = new List<Student>()
{
new Student { Name = "张三", Age = 20, Major = "计算机科学", Score = 89 },
new Student { Name = "李四", Age = 21, Major = "计算机科学", Score = 92 },
new Student { Name = "王五", Age = 19, Major = "数学", Score = 78 },
new Student { Name = "赵六", Age = 22, Major = "物理", Score = 95 },
new Student { Name = "钱七", Age = 20, Major = "数学", Score = 85 },
new Student { Name = "孙八", Age = 21, Major = "物理", Score = 82 }
};
// 查询表达式:按专业分组,计算每个专业的平均分
var queryExpression = from student in students
group student by student.Major into majorGroup
select new
{
Major = majorGroup.Key,
AverageScore = majorGroup.Average(s => s.Score),
StudentCount = majorGroup.Count()
};
// 方法语法:实现相同功能
var methodSyntax = students
.GroupBy(s => s.Major)
.Select(g => new
{
Major = g.Key,
AverageScore = g.Average(s => s.Score),
StudentCount = g.Count()
});
// 混合使用:先用查询表达式过滤,再用方法语法进行复杂处理
var hybridQuery = (from student in students
where student.Score >= 80
select student)
.OrderByDescending(s => s.Score)
.Take(3);
// 输出结果
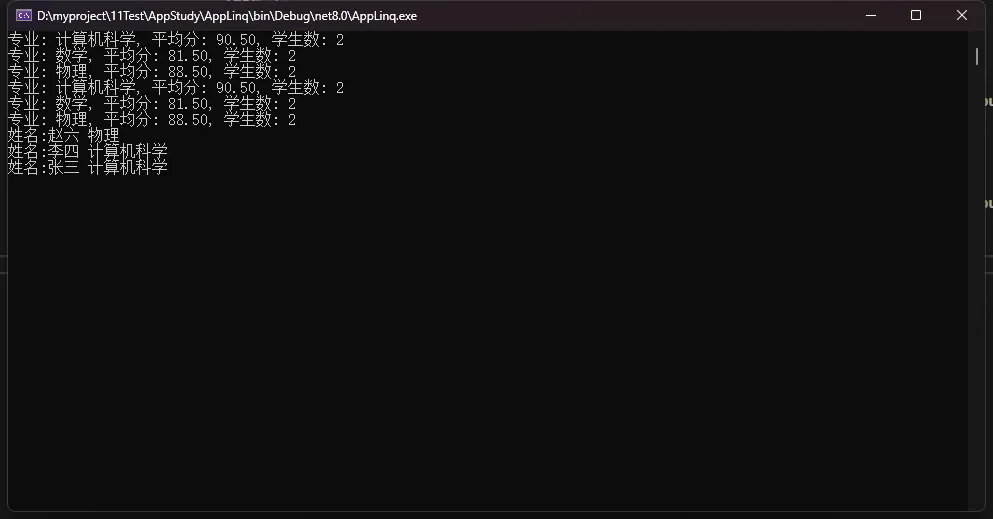
foreach (var result in queryExpression)
{
Console.WriteLine($"专业: {result.Major}, 平均分: {result.AverageScore:F2}, 学生数: {result.StudentCount}");
}
foreach (var result in methodSyntax)
{
Console.WriteLine($"专业: {result.Major}, 平均分: {result.AverageScore:F2}, 学生数: {result.StudentCount}");
}
foreach (var result in hybridQuery)
{
Console.WriteLine($"姓名:{result.Name} {result.Major}");
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
高级投影操作
LINQ的Select不仅可以简单地选择元素,还可以进行复杂的投影和转换。
C#namespace AppLinq
{
internal class Program
{
public class Department
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public List<Employee> Employees { get; set; }
}
public class Employee
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public int Salary { get; set; }
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 嵌套集合的处理
var departments = new List<Department>
{
new Department
{
Name = "研发部",
Employees = new List<Employee>
{
new Employee { Name = "张工", Salary = 12000 },
new Employee { Name = "李工", Salary = 15000 }
}
},
new Department
{
Name = "市场部",
Employees = new List<Employee>
{
new Employee { Name = "王经理", Salary = 18000 },
new Employee { Name = "赵助理", Salary = 8000 }
}
}
};
// 使用SelectMany扁平化处理嵌套集合,这个用法可以避免使用foreach遍历嵌套集合,我比较习惯
var allEmployees = departments.SelectMany(d => d.Employees,
(dept, emp) => new
{
Department = dept.Name,
EmployeeName = emp.Name,
emp.Salary
});
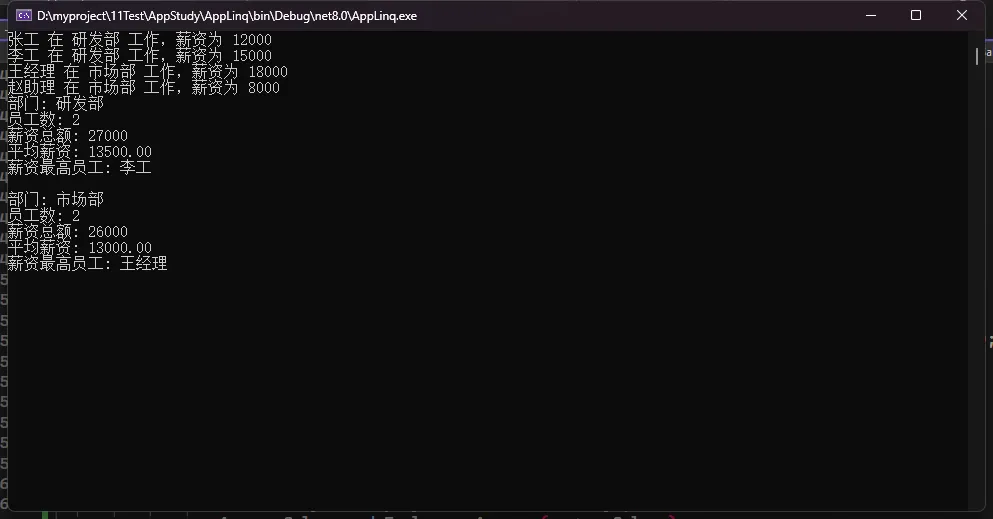
foreach (var emp in allEmployees)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{emp.EmployeeName} 在 {emp.Department} 工作,薪资为 {emp.Salary}");
}
// 使用复杂投影创建新对象
var employeeStats = departments.Select(d => new
{
DepartmentName = d.Name,
EmployeeCount = d.Employees.Count,
TotalSalary = d.Employees.Sum(e => e.Salary),
AverageSalary = d.Employees.Average(e => e.Salary),
HighestPaid = d.Employees.OrderByDescending(e => e.Salary).First().Name
});
foreach (var stat in employeeStats)
{
Console.WriteLine($"部门: {stat.DepartmentName}");
Console.WriteLine($"员工数: {stat.EmployeeCount}");
Console.WriteLine($"薪资总额: {stat.TotalSalary}");
Console.WriteLine($"平均薪资: {stat.AverageSalary:F2}");
Console.WriteLine($"薪资最高员工: {stat.HighestPaid}");
Console.WriteLine();
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
复杂聚合和自定义聚合操作
LINQ提供了多种聚合操作,还可以创建自定义聚合逻辑。
C#namespace AppLinq
{
internal class Program
{
public class Product
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public string Category { get; set; }
public double Price { get; set; }
public int Stock { get; set; }
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 复杂聚合示例
var products = new List<Product>
{
new Product { Name = "笔记本电脑", Category = "电子", Price = 5999, Stock = 10 },
new Product { Name = "手机", Category = "电子", Price = 2999, Stock = 25 },
new Product { Name = "耳机", Category = "配件", Price = 299, Stock = 50 },
new Product { Name = "充电器", Category = "配件", Price = 99, Stock = 100 },
new Product { Name = "书包", Category = "日用", Price = 199, Stock = 30 },
new Product { Name = "水杯", Category = "日用", Price = 59, Stock = 80 }
};
// 按类别计算库存价值
var inventoryValueByCategory = products
.GroupBy(p => p.Category)
.Select(g => new
{
Category = g.Key,
InventoryValue = g.Sum(p => p.Price * p.Stock),
ItemCount = g.Count(),
AveragePrice = g.Average(p => p.Price)
})
.OrderByDescending(g => g.InventoryValue);
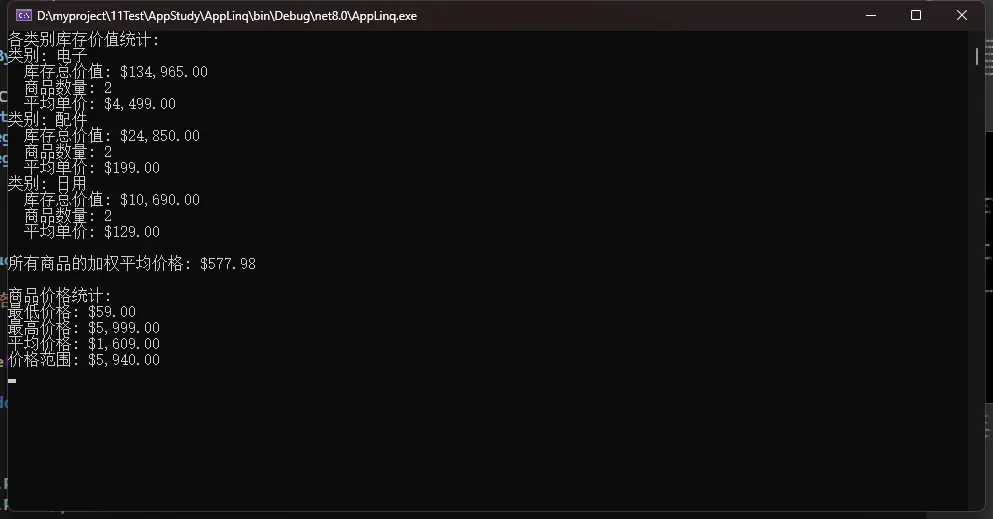
Console.WriteLine("各类别库存价值统计:");
foreach (var category in inventoryValueByCategory)
{
Console.WriteLine($"类别: {category.Category}");
Console.WriteLine($" 库存总价值: {category.InventoryValue:C}");
Console.WriteLine($" 商品数量: {category.ItemCount}");
Console.WriteLine($" 平均单价: {category.AveragePrice:C}");
}
// 自定义聚合 - 加权平均数
double weightedAverage = products
.Sum(p => p.Price * p.Stock) / products.Sum(p => p.Stock);
Console.WriteLine($"\n所有商品的加权平均价格: {weightedAverage:C}");
// 使用Aggregate实现自定义逻辑
var priceStatistics = products.Aggregate(
// 初始种子值 - 统计对象
new { Min = double.MaxValue, Max = double.MinValue, Sum = 0.0, Count = 0 },
// 累加函数
(acc, product) => new
{
Min = Math.Min(acc.Min, product.Price),
Max = Math.Max(acc.Max, product.Price),
Sum = acc.Sum + product.Price,
Count = acc.Count + 1
},
// 结果选择器
result => new
{
MinPrice = result.Min,
MaxPrice = result.Max,
AveragePrice = result.Sum / result.Count,
PriceRange = result.Max - result.Min
});
Console.WriteLine("\n商品价格统计:");
Console.WriteLine($"最低价格: {priceStatistics.MinPrice:C}");
Console.WriteLine($"最高价格: {priceStatistics.MaxPrice:C}");
Console.WriteLine($"平均价格: {priceStatistics.AveragePrice:C}");
Console.WriteLine($"价格范围: {priceStatistics.PriceRange:C}");
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
LINQ性能优化技巧
使用LINQ时,了解性能优化技巧可以显著提升应用程序性能,如果你熟悉SQL脚本,其实也就明白先后的重要性了。
C#using System.Diagnostics;
namespace AppLinq
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
LinqPerformanceOptimization();
Console.ReadKey();
}
// 性能优化示例
static void LinqPerformanceOptimization()
{
var largeCollection = Enumerable.Range(1, 1000000).ToList();
Console.WriteLine("LINQ性能优化示例:");
// 示例1: Where之前进行排序
// 不好的做法 - 在筛选前进行排序
Stopwatch sw1 = Stopwatch.StartNew();
var result1 = largeCollection
.OrderBy(x => x)
.Where(x => x % 10 == 0)
.Take(100)
.ToList();
sw1.Stop();
// 好的做法 - 先筛选再排序
Stopwatch sw2 = Stopwatch.StartNew();
var result2 = largeCollection
.Where(x => x % 10 == 0)
.OrderBy(x => x)
.Take(100)
.ToList();
sw2.Stop();
Console.WriteLine($"排序后筛选: {sw1.ElapsedMilliseconds}ms");
Console.WriteLine($"筛选后排序: {sw2.ElapsedMilliseconds}ms");
// 示例2: 使用Any代替Count > 0
// 不好的做法
Stopwatch sw3 = Stopwatch.StartNew();
bool hasMatch1 = largeCollection.Count(x => x > 900000) > 0;
sw3.Stop();
// 好的做法
Stopwatch sw4 = Stopwatch.StartNew();
bool hasMatch2 = largeCollection.Any(x => x > 900000);
sw4.Stop();
Console.WriteLine($"使用Count>0: {sw3.ElapsedMilliseconds}ms");
Console.WriteLine($"使用Any: {sw4.ElapsedMilliseconds}ms");
// 示例3: 避免多次枚举
// 不好的做法 - 多次枚举
var query = largeCollection.Where(x => x % 100 == 0);
Stopwatch sw5 = Stopwatch.StartNew();
Console.WriteLine($"匹配元素数量: {query.Count()}");
Console.WriteLine($"最大值: {query.Max()}");
Console.WriteLine($"最小值: {query.Min()}");
sw5.Stop();
// 好的做法 - 转换为列表后再操作
Stopwatch sw6 = Stopwatch.StartNew();
var queryList = largeCollection.Where(x => x % 100 == 0).ToList();
Console.WriteLine($"匹配元素数量: {queryList.Count}");
Console.WriteLine($"最大值: {queryList.Max()}");
Console.WriteLine($"最小值: {queryList.Min()}");
sw6.Stop();
Console.WriteLine($"多次枚举: {sw5.ElapsedMilliseconds}ms");
Console.WriteLine($"单次枚举后保存: {sw6.ElapsedMilliseconds}ms");
}
}
}

总结
LINQ是C#中一个强大且灵活的特性,熟练掌握它可以大大提高编程效率和代码质量。本文通过多个详细的例子展示了LINQ的进阶应用技巧,包括查询表达式与方法语法的灵活切换、延迟执行与即时执行的理解、高级投影操作、自定义扩展方法、异步编程结合、复杂聚合和自定义聚合、XML和JSON处理以及性能优化技巧。
这些技巧不仅可以帮助您编写更简洁、更易于维护的代码,还能提高应用程序的性能。希望您通过这些例子能够更深入地理解和应用LINQ,充分发挥C#语言的强大功能。
记住,熟能生巧,多加练习是掌握LINQ进阶技巧的关键。在实际项目中尝试应用这些技巧,您会发现LINQ能够让您的代码更加优雅和高效。
本文作者:技术老小子
本文链接:
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!
目录