目录
在C#中,读写文本文件是一个常见的编程任务,无论是存储数据、记录日志还是配置设置。本文将详细介绍如何使用C#进行文件读写操作,并提供多个实用示例。
使用 System.IO 命名空间
在C#中,读写文件需要引入System.IO命名空间,它提供了一系列的类用于文件和流的操作。
写入文本文件
使用 StreamWriter
StreamWriter类用于向一个文本文件中写入字符。下面是一个使用StreamWriter写入文件的例子:
C#namespace AppIO
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string filePath = @".\a.txt";
// 使用using语句确保StreamWriter正确释放资源
using (StreamWriter writer = new StreamWriter(filePath))
{
writer.WriteLine("Hello, World!"); // 写入一行文本
writer.WriteLine("Welcome to C# file operations.");
}
Console.WriteLine("File written successfully.");
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
如果要追加文本到现有文件,可以使用StreamWriter的构造函数的重载版本:
C#namespace AppIO
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string filePath = @".\a.txt";
using (StreamWriter writer = new StreamWriter(filePath, true))
{
writer.WriteLine("This line is appended.");
}
Console.WriteLine("File written successfully.");
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
使用 File 类的静态方法
File类提供了一些静态方法,可以更简单地执行文件写入操作:
C#namespace AppIO
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string filePath = @".\a.txt";
string content = "This is a simple file content.";
File.WriteAllText(filePath, content); // 写入整个文件内容
string[] lines = { "First line", "Second line", "Third line" };
File.WriteAllLines(filePath, lines); // 写入一个字符串数组,每个元素为一行
File.AppendAllText(filePath, "This text is appended."); // 追加文本到文件末尾
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
读取文本文件
使用 StreamReader
StreamReader类用于从文本文件中读取字符。下面是一个使用StreamReader读取文件的例子:
C#namespace AppIO
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string filePath = @".\a.txt";
// 使用using语句确保StreamReader正确释放资源
using (StreamReader reader = new StreamReader(filePath))
{
string line;
while ((line = reader.ReadLine()) != null) // 逐行读取直到文件末尾
{
Console.WriteLine(line);
}
}
Console.WriteLine("File read successfully.");
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
使用 File 类的静态方法
与写入操作类似,File类也提供了一些静态方法来简化文件读取:
C#namespace AppIO
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string filePath = @".\a.txt";
string content = File.ReadAllText(filePath); // 读取整个文件内容
string[] lines = File.ReadAllLines(filePath); // 读取文件的所有行到一个字符串数组
foreach (var line in lines)
{
Console.WriteLine(line);
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
实用示例
读取配置文件
配置文件通常包含键值对,以下是如何读取简单配置文件的示例:
C#namespace AppIO
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string configFilePath = @".\config.txt";
var configDictionary = new Dictionary<string, string>();
foreach (var line in File.ReadAllLines(configFilePath))
{
if (!string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(line) && !line.StartsWith("#")) // 忽略空行和注释
{
var keyValue = line.Split('=');
if (keyValue.Length == 2)
{
configDictionary[keyValue[0].Trim()] = keyValue[1].Trim();
}
}
}
foreach (var key in configDictionary.Keys)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{key}: {configDictionary[key]}");
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
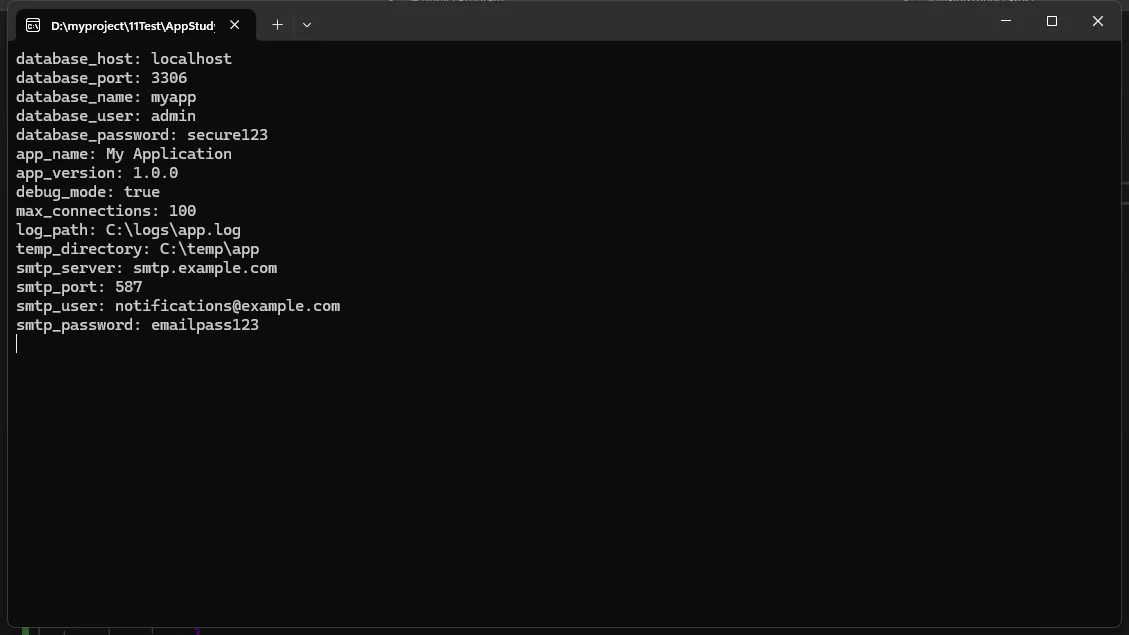
config.txt 配置文件
Markdown# 这是一个配置文件示例
# 以#开头的行会被视为注释
# 数据库设置
database_host=localhost
database_port=3306
database_name=myapp
database_user=admin
database_password=secure123
# 应用程序设置
app_name=My Application
app_version=1.0.0
debug_mode=true
max_connections=100
# 文件路径
log_path=C:\logs\app.log
temp_directory=C:\temp\app
# 邮件设置
smtp_server=smtp.example.com
smtp_port=587
smtp_user=notifications@example.com
smtp_password=emailpass123
写入日志文件
记录应用程序的操作到日志文件是一个常见的需求,以下是如何实现的示例:
C#namespace AppIO
{
internal class Program
{
// 日志记录方法
static void LogMessage(string message, string logFilePath)
{
try
{
// 确保日志文件的目录存在
string directoryPath = Path.GetDirectoryName(logFilePath);
if (!Directory.Exists(directoryPath))
{
Directory.CreateDirectory(directoryPath);
}
// 创建带时间戳的日志条目
string timestamp = DateTime.Now.ToString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
string logEntry = $"{timestamp}: {message}\n";
// 将日志条目追加到文件
File.AppendAllText(logFilePath, logEntry);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
// 如果写入日志失败,至少在控制台显示错误
Console.WriteLine($"无法写入日志: {ex.Message}");
}
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 设置日志文件路径
string logFilePath = @".\app.log";
try
{
// 记录应用程序启动
LogMessage("Application started", logFilePath);
// 模拟应用程序的主要功能
Console.WriteLine("应用程序正在运行...");
// 执行一些示例操作
PerformSampleOperations();
// 记录应用程序完成
LogMessage("Application finished successfully", logFilePath);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
// 记录任何未处理的异常
LogMessage($"Application terminated with error: {ex.Message}", logFilePath);
Console.WriteLine($"发生错误: {ex.Message}");
}
}
static void PerformSampleOperations()
{
// 这里可以是应用程序的实际功能
Console.WriteLine("执行操作1...");
// 模拟一些处理时间
System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(1000);
Console.WriteLine("执行操作2...");
// 模拟一些处理时间
System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(1000);
Console.WriteLine("所有操作完成");
}
}
}
通过上述示例,我们可以看到C#提供了多种方法来读写文本文件,从使用StreamWriter和StreamReader进行细粒度的文件操作,到使用File类的静态方法快速完成文件的读写任务。根据具体需求,开发者可以选择最适合的方法来实现文件读写操作。
本文作者:技术老小子
本文链接:
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!
目录