目录
在C#这样的静态类型语言中,鸭子类型(Duck Typing)通常不像在动态语言中那样自然。鸭子类型的核心思想是:"如果它走起来像鸭子,叫起来像鸭子,那么它就是鸭子"—— 即关注对象的行为而非其类型。本文将详细介绍如何在C#中通过缓存和表达式树技术实现高性能的鸭子类型模式,以及这种模式在实际项目中的应用。
鸭子类型与C#的挑战
在传统C#开发中,我们通常通过接口来定义行为规范。但这种方式要求所有类型显式实现接口,缺乏灵活性。使用反射可以解决这个问题,但会带来严重的性能损失。那么如何在保持鸭子类型灵活性的同时,又能获得接近原生代码的性能呢?
高性能鸭子类型的三大技术支柱
我们将使用三种关键技术来实现高性能的鸭子类型:
- 反射:用于首次发现和识别类型的能力
- 表达式树:用于构建和编译高性能委托
- 并发缓存:存储已处理类型的委托,避免重复的反射和编译开销
完整实现案例:智能日志系统
下面我们将构建一个智能日志系统,它可以记录任何拥有GetLogMessage()方法的对象,无需这些对象实现特定接口。
核心实现
C#using System;
using System.Collections.Concurrent;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Linq.Expressions;
using System.Reflection;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace AppDuck
{
public class CachedDuckTypingLogger
{
// 缓存委托:Type => Func<object, string>
private readonly ConcurrentDictionary<Type, Func<object, string>> _messageGetterCache =
new ConcurrentDictionary<Type, Func<object, string>>();
/// <summary>
/// 记录任何具有GetLogMessage方法的对象
/// </summary>
public void Log(object item)
{
try
{
// 获取日志消息获取器
var messageGetter = GetOrCreateMessageGetter(item.GetType());
if (messageGetter != null)
{
// 获取并记录消息
string message = messageGetter(item);
Console.WriteLine($"[{DateTime.Now:yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss}] {message}");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine($"[ERROR] 无法记录类型为 {item.GetType().Name} 的对象 - 未实现GetLogMessage方法");
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"[ERROR] 记录时发生异常: {ex.Message}");
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 从缓存获取或创建消息获取委托
/// </summary>
private Func<object, string> GetOrCreateMessageGetter(Type type)
{
return _messageGetterCache.GetOrAdd(type, t =>
{
// 查找GetLogMessage方法
MethodInfo method = t.GetMethod("GetLogMessage", Type.EmptyTypes);
if (method == null || method.ReturnType != typeof(string))
return null;
// 创建表达式树
ParameterExpression param = Expression.Parameter(typeof(object), "obj");
UnaryExpression convertedParam = Expression.Convert(param, t);
MethodCallExpression methodCall = Expression.Call(convertedParam, method);
// 编译表达式树为委托
return Expression.Lambda<Func<object, string>>(methodCall, param).Compile();
});
}
}
}
示例实体类
下面是一系列可用于测试的实体类:
C#using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace AppDuck
{
/// <summary>
/// 用户实体
/// </summary>
public class User
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public string Email { get; set; }
public string GetLogMessage()
{
return $"User: {Id} | {Name} | {Email}";
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 产品实体
/// </summary>
public class Product
{
public string Code { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public decimal Price { get; set; }
public string GetLogMessage()
{
return $"Product: {Code} | {Name} | ${Price}";
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 订单实体
/// </summary>
public class Order
{
public string OrderNumber { get; set; }
public decimal Total { get; set; }
public int Items { get; set; }
public string GetLogMessage()
{
return $"Order: {OrderNumber} | Total: ${Total} | Items: {Items}";
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 自定义可记录对象
/// </summary>
public class CustomLoggable
{
public string Message { get; set; }
public string GetLogMessage()
{
return $"Custom: {Message}";
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 不可记录的对象 - 没有GetLogMessage方法
/// </summary>
public class NonLoggable
{
public string Data { get; set; } = "无法记录的数据";
// 故意没有实现GetLogMessage
}
}
性能测试实现
为了证明这种方法的性能优势,我们添加一个性能测试类:
C#using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace AppDuck
{
/// <summary>
/// 性能测试类
/// </summary>
public class PerformanceTest
{
public void RunTest(CachedDuckTypingLogger logger, object testObject)
{
const int iterations = 1000000;
Console.WriteLine($"执行 {iterations:N0} 次日志记录测试...");
// 禁用控制台输出以更准确地测量性能
var originalOut = Console.Out;
Console.SetOut(new System.IO.StringWriter());
// 预热
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++)
{
logger.Log(testObject);
}
// 计时测试
var stopwatch = System.Diagnostics.Stopwatch.StartNew();
for (int i = 0; i < iterations; i++)
{
logger.Log(testObject);
}
stopwatch.Stop();
// 恢复控制台输出
Console.SetOut(originalOut);
Console.WriteLine($"完成 {iterations:N0} 次迭代,耗时: {stopwatch.ElapsedMilliseconds} 毫秒");
Console.WriteLine($"平均每次调用: {(double)stopwatch.ElapsedMilliseconds / iterations * 1000:F3} 微秒");
// 与传统的反射方法比较
CompareWithReflection(testObject, iterations);
}
private void CompareWithReflection(object testObject, int iterations)
{
Console.WriteLine("\n与传统反射方法比较:");
var stopwatch = System.Diagnostics.Stopwatch.StartNew();
string result = null;
for (int i = 0; i < iterations; i++)
{
// 传统反射调用 - 每次都反射
var method = testObject.GetType().GetMethod("GetLogMessage", Type.EmptyTypes);
result = (string)method.Invoke(testObject, null);
}
stopwatch.Stop();
Console.WriteLine($"传统反射 - {iterations:N0} 次迭代,耗时: {stopwatch.ElapsedMilliseconds} 毫秒");
Console.WriteLine($"平均每次调用: {(double)stopwatch.ElapsedMilliseconds / iterations * 1000:F3} 微秒");
Console.WriteLine($"结果示例: {result}");
}
}
}
完整测试程序
下面是一个完整的程序,演示如何使用我们的鸭子类型实现:
C#namespace AppDuck
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 创建日志系统
var logger = new CachedDuckTypingLogger();
// 创建各种不同类型的对象
var user = new User { Id = 1, Name = "John Doe", Email = "john@example.com" };
var product = new Product { Code = "PRD-001", Name = "Laptop", Price = 999.99m };
var order = new Order { OrderNumber = "ORD-123", Total = 1299.50m, Items = 3 };
var customObject = new CustomLoggable { Message = "这是一个自定义消息" };
// 使用日志系统记录它们
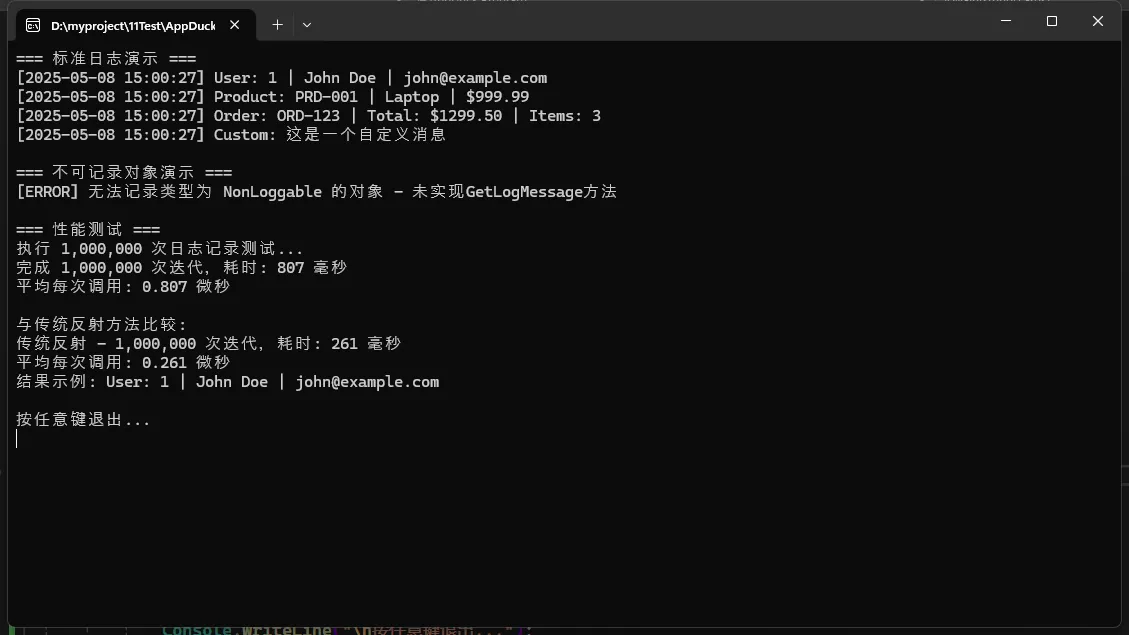
Console.WriteLine("=== 标准日志演示 ===");
logger.Log(user);
logger.Log(product);
logger.Log(order);
logger.Log(customObject);
// 无法记录的对象
var nonLoggable = new NonLoggable();
Console.WriteLine("\n=== 不可记录对象演示 ===");
logger.Log(nonLoggable); // 会显示错误信息
// 性能测试
Console.WriteLine("\n=== 性能测试 ===");
var perfTest = new PerformanceTest();
perfTest.RunTest(logger, user);
Console.WriteLine("\n按任意键退出...");
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
实现细节解析
缓存机制
ConcurrentDictionary<Type, Func<object, string>> 是我们实现的核心。它存储了每种类型的消息获取委托,确保我们只需对每种类型执行一次反射和表达式树编译。ConcurrentDictionary 是线程安全的,适用于多线程环境。
表达式树构建过程
表达式树构建是整个实现的关键部分:
- 创建一个参数表达式
param,类型为object - 将参数转换为目标类型
convertedParam - 创建方法调用表达式
methodCall - 编译表达式树为强类型委托
这一过程只在第一次遇到新类型时执行,后续调用将直接使用缓存的委托。
错误处理
我们的实现包括全面的错误处理:
- 检查目标方法是否存在
- 验证返回类型是否正确
- 捕获执行过程中的异常
这确保了系统的稳健性和可靠性。
使用注意事项
虽然这种实现非常强大,但在使用时需要注意以下几点:
- 内存占用:缓存委托会消耗内存,如果应用需要处理大量不同类型,应考虑内存占用。
- 首次调用开销:首次处理每种类型时有编译表达式树的开销,可能导致轻微延迟。
- 线程安全:示例中使用了
ConcurrentDictionary确保线程安全,但调用者需确保被调用对象自身的线程安全性。 - 错误处理:在生产环境中,应考虑更完善的错误日志和异常处理策略。
结论
通过结合反射、表达式树和缓存技术,我们实现了C#中高性能的鸭子类型模式。这种实现方式保持了鸭子类型的灵活性,同时提供了接近原生代码的执行性能。特别是在需要处理多种类型但每种类型会重复出现的场景下,这种模式可以显著提高应用性能。
这种技术可以应用于多种实际开发场景,为C#开发者提供了一种强大且灵活的编程工具,帮助我们构建更具适应性和可扩展性的应用程序。
本文作者:技术老小子
本文链接:
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!