目录
依赖注入(DI)是现代C#开发的核心部分,掌握三种生命周期模式对于构建高效、可维护的应用至关重要。本文通过详细的Console示例,帮助你彻底理解Scoped、Singleton和Transient的区别。
依赖注入生命周期简介
在C# .NET Core/.NET 5+应用程序中,依赖注入框架提供了三种主要的服务生命周期:
- Transient(瞬时): 每次请求时创建新实例
- Scoped(作用域): 在同一作用域内共享同一实例
- Singleton(单例): 整个应用程序共享同一实例
选择正确的生命周期对于应用程序性能和内存管理至关重要。接下来,我们将通过代码示例详细解析三者的区别。
项目环境准备
安装必要的NuGet包:
Bashdotnet add package Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection dotnet add package Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting
定义服务接口和实现
我们创建一个简单的服务接口和实现,用于演示不同生命周期:
C#using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using static AppDependencyInjection.Program;
namespace AppDependencyInjection
{
// 服务接口
public interface IExampleService
{
Guid Id { get; } // 用于识别服务实例
void DoSomething();
}
// 服务实现
public class ExampleService : IExampleService, IScopedService, ISingletonService
{
public Guid Id { get; }
public ExampleService()
{
// 在构造函数中生成唯一ID,用于标识实例
Id = Guid.NewGuid();
Console.WriteLine($"创建新的服务实例: {Id}");
}
public void DoSomething()
{
Console.WriteLine($"服务实例 {Id} 执行操作");
}
}
}
体验三种生命周期模式
下面是完整的控制台应用程序,演示了三种不同生命周期的行为:
C#using System;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting;
namespace DILifecycleDemo
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 创建Host生成器
var host = Host.CreateDefaultBuilder(args)
.ConfigureServices((context, services) =>
{
// 注册三种不同生命周期的服务
services.AddTransient<IExampleService, ExampleService>();
// 为了区分不同生命周期的服务,使用不同的接口
services.AddScoped<IScopedService, ExampleService>();
services.AddSingleton<ISingletonService, ExampleService>();
})
.Build();
Console.WriteLine("=== 依赖注入生命周期测试 ===");
// 测试Transient生命周期
TestTransientLifetime(host.Services);
// 测试Scoped生命周期
TestScopedLifetime(host.Services);
// 测试Singleton生命周期
TestSingletonLifetime(host.Services);
Console.WriteLine("\n按任意键退出...");
Console.ReadKey();
}
// 测试Transient生命周期的方法
static void TestTransientLifetime(IServiceProvider serviceProvider)
{
Console.WriteLine("\n=== Transient生命周期测试 ===");
Console.WriteLine("特点:每次请求都创建新实例");
// 第一次获取Transient服务
Console.WriteLine("\n第一次请求Transient服务:");
var transient1 = serviceProvider.GetService<IExampleService>();
transient1.DoSomething();
// 第二次获取Transient服务
Console.WriteLine("\n第二次请求Transient服务:");
var transient2 = serviceProvider.GetService<IExampleService>();
transient2.DoSomething();
// 比较实例ID以验证是否创建了不同的实例
Console.WriteLine($"\n两个实例是否相同: {transient1.Id == transient2.Id}");
Console.WriteLine($"实例1 ID: {transient1.Id}");
Console.WriteLine($"实例2 ID: {transient2.Id}");
}
// 接口定义 - 为区分不同生命周期的服务
public interface IScopedService : IExampleService { }
public interface ISingletonService : IExampleService { }
// 测试Scoped生命周期的方法
static void TestScopedLifetime(IServiceProvider rootProvider)
{
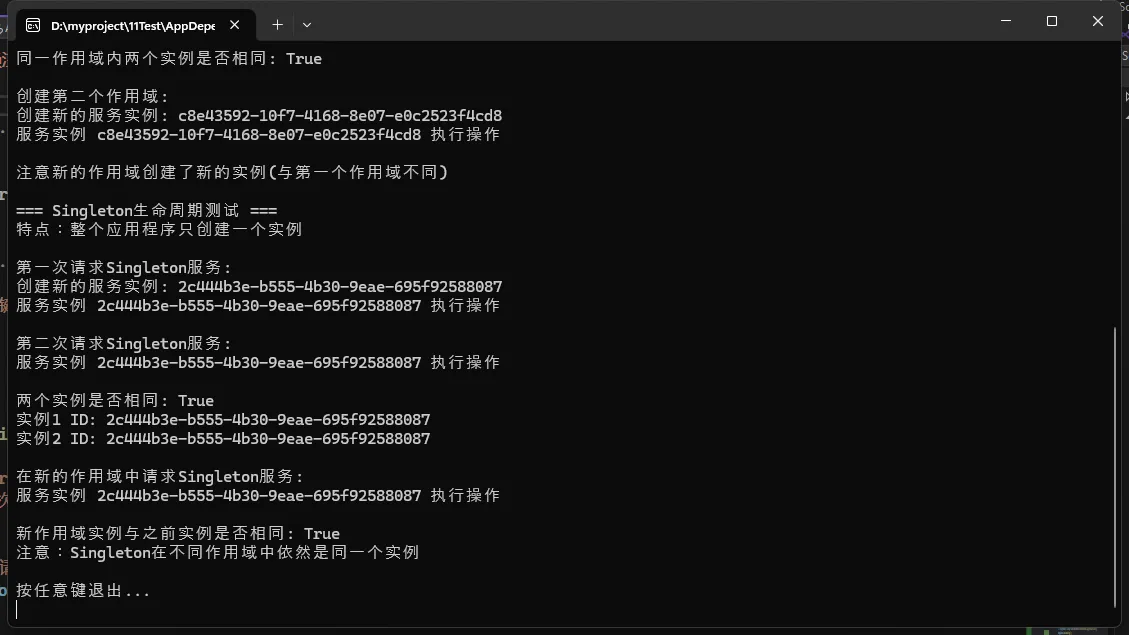
Console.WriteLine("\n=== Scoped生命周期测试 ===");
Console.WriteLine("特点:在同一作用域内共享实例,不同作用域使用不同实例");
// 创建第一个作用域
Console.WriteLine("\n创建第一个作用域:");
using (var scope1 = rootProvider.CreateScope())
{
// 在同一作用域内获取两次服务
Console.WriteLine("在第一个作用域内第一次请求:");
var scoped1 = scope1.ServiceProvider.GetService<IScopedService>();
scoped1.DoSomething();
Console.WriteLine("\n在第一个作用域内第二次请求:");
var scoped2 = scope1.ServiceProvider.GetService<IScopedService>();
scoped2.DoSomething();
// 比较同一作用域内的实例
Console.WriteLine($"\n同一作用域内两个实例是否相同: {scoped1.Id == scoped2.Id}");
}
// 创建第二个作用域
Console.WriteLine("\n创建第二个作用域:");
using (var scope2 = rootProvider.CreateScope())
{
var scoped3 = scope2.ServiceProvider.GetService<IScopedService>();
scoped3.DoSomething();
// 注意:第二个作用域会创建新的实例
Console.WriteLine("\n注意新的作用域创建了新的实例(与第一个作用域不同)");
}
}
// 测试Singleton生命周期的方法
static void TestSingletonLifetime(IServiceProvider serviceProvider)
{
Console.WriteLine("\n=== Singleton生命周期测试 ===");
Console.WriteLine("特点:整个应用程序只创建一个实例");
// 第一次获取Singleton服务
Console.WriteLine("\n第一次请求Singleton服务:");
var singleton1 = serviceProvider.GetService<ISingletonService>();
singleton1.DoSomething();
// 第二次获取Singleton服务
Console.WriteLine("\n第二次请求Singleton服务:");
var singleton2 = serviceProvider.GetService<ISingletonService>();
singleton2.DoSomething();
// 比较实例ID以验证是否使用了相同的实例
Console.WriteLine($"\n两个实例是否相同: {singleton1.Id == singleton2.Id}");
Console.WriteLine($"实例1 ID: {singleton1.Id}");
Console.WriteLine($"实例2 ID: {singleton2.Id}");
// 在不同作用域中获取Singleton服务
Console.WriteLine("\n在新的作用域中请求Singleton服务:");
using (var scope = serviceProvider.CreateScope())
{
var singleton3 = scope.ServiceProvider.GetService<ISingletonService>();
singleton3.DoSomething();
// 比较与之前实例
Console.WriteLine($"\n新作用域实例与之前实例是否相同: {singleton1.Id == singleton3.Id}");
Console.WriteLine("注意:Singleton在不同作用域中依然是同一个实例");
}
}
}
// ExampleService实现了所有接口
public class ExampleService : IExampleService, IScopedService, ISingletonService
{
public Guid Id { get; }
public ExampleService()
{
// 在构造函数中生成唯一ID,用于标识实例
Id = Guid.NewGuid();
Console.WriteLine($"创建新的服务实例: {Id}");
}
public void DoSomething()
{
Console.WriteLine($"服务实例 {Id} 执行操作");
}
}
}
三种生命周期详细对比
| 特性 | Transient | Scoped | Singleton |
|---|---|---|---|
| 创建时机 | 每次请求服务时 | 每个作用域第一次请求时 | 首次请求或应用启动时 |
| 实例数量 | 每次请求都创建新实例 | 每个作用域一个实例 | 整个应用程序只有一个实例 |
| 实例共享 | 不共享 | 同一作用域内共享 | 全局共享 |
| 内存占用 | 较高 | 中等 | 最低 |
| 适用场景 | 轻量级、无状态服务 | Web请求、数据库上下文 | 全局配置、缓存服务 |
| 线程安全 | 天然线程安全 | 需考虑作用域内的并发 | 必须实现线程安全 |
选择正确生命周期的最佳实践
何时使用Transient(瞬时服务)
- ✅ 轻量级、无状态的服务
- ✅ 不共享状态的服务
- ✅ 每次使用需要全新状态的服务
- ❌ 避免用于开销大的服务(如数据库连接)
C#// 注册Transient服务示例
services.AddTransient<IEmailFormatter, EmailFormatter>();
何时使用Scoped(作用域服务)
- ✅ Web应用中的请求级服务
- ✅ Entity Framework DbContext
- ✅ 需要在请求或操作期间保持状态的服务
- ❌ 避免在单例服务中注入作用域服务
C#// 注册Scoped服务示例
services.AddScoped<IUserRepository, UserRepository>();
services.AddScoped<DbContext, ApplicationDbContext>();
何时使用Singleton(单例服务)
- ✅ 全局配置服务
- ✅ 缓存服务
- ✅ 日志服务
- ✅ 重量级、创建成本高的服务
- ❌ 避免用于包含用户特定数据的服务
- ❌ 必须确保线程安全
C#// 注册Singleton服务示例
services.AddSingleton<IConfiguration, AppConfiguration>();
services.AddSingleton<ICacheService, RedisCacheService>();
常见陷阱和解决方案
作用域服务被单例服务依赖
问题: 当单例服务依赖于作用域服务时会导致问题,因为单例服务只创建一次,而它依赖的作用域服务会被锁定在创建单例时的那个作用域。
解决方案: 使用IServiceProvider和工厂模式:
C#public class SingletonService
{
private readonly IServiceProvider _serviceProvider;
public SingletonService(IServiceProvider serviceProvider)
{
_serviceProvider = serviceProvider;
}
public void DoWork()
{
// 在需要时获取作用域服务
using (var scope = _serviceProvider.CreateScope())
{
var scopedService = scope.ServiceProvider.GetService<IScopedService>();
scopedService.DoSomething();
}
}
}
内存泄漏风险
问题: 单例服务如果持有对临时对象的引用可能导致内存泄漏。
解决方案: 使用弱引用或事件处理模式:
C#public class CacheService
{
private readonly ConditionalWeakTable<object, object> _cache = new();
public void Add(object key, object value)
{
_cache.Add(key, value);
}
}
线程安全问题
问题: 单例服务被多线程访问导致竞态条件。
解决方案: 使用线程安全的数据结构和同步机制:
C#public class ThreadSafeSingleton
{
private readonly ConcurrentDictionary<string, object> _concurrentCache = new();
public void AddToCache(string key, object value)
{
_concurrentCache.AddOrUpdate(key, value, (k, v) => value);
}
}
总结
选择合适的依赖注入生命周期对于构建高效、可维护的C#应用至关重要:
- Transient: 每次请求创建新实例,适用于轻量级、无状态服务
- Scoped: 在作用域内共享实例,适用于请求级服务如DbContext
- Singleton: 应用程序全局共享一个实例,适用于配置、缓存等全局服务
通过本文的详细示例,您应该能够清晰地理解这三种生命周期的区别,并在实际项目中做出正确的选择。实际应用中,通常会混合使用这三种生命周期以获得最佳性能和资源利用率。
如果您有任何关于C#依赖注入生命周期的问题,欢迎在评论区留言讨论!
#C#开发 #依赖注入 #DotNet #ASPNETCore #编程技巧 #后端开发
本文作者:技术老小子
本文链接:
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!
目录