目录
在计算机科学中,双向链表是一种更为复杂的链表结构,与单链表相比,双向链表的节点不仅包含指向下一个节点的指针,还包含指向上一个节点的指针。这种双向链接使得双向链表可以从两个方向遍历。在本文中,我们将详细介绍如何在C#中实现双向链表,并提供多个示例。
双向链表节点的实现
首先,我们需要定义双向链表节点类DoublyLinkedListNode<T>:
C#public class DoublyLinkedListNode<T>
{
public T Value { get; set; }
public DoublyLinkedListNode<T> Next { get; set; }
public DoublyLinkedListNode<T> Previous { get; set; }
public DoublyLinkedListNode(T value)
{
Value = value;
Next = null;
Previous = null;
}
}
在上述代码中,DoublyLinkedListNode<T>类包含三个主要成员:Value用于存储节点数据,Next用于指向下一个节点,Previous用于指向前一个节点。
双向链表的实现
接下来,我们定义双向链表类DoublyLinkedList<T>,该类将使用DoublyLinkedListNode<T>节点:
C#// 定义一个泛型双向链表类
public class DoublyLinkedList<T>
{
// 链表的头节点
public DoublyLinkedListNode<T> Head { get; private set; }
// 链表的尾节点
public DoublyLinkedListNode<T> Tail { get; private set; }
// 构造函数,初始化时链表为空
public DoublyLinkedList()
{
Head = null;
Tail = null;
}
// 在链表的开始处添加一个新节点
public void AddFirst(T value)
{
// 创建一个新节点,其值为传入的value
DoublyLinkedListNode<T> newNode = new DoublyLinkedListNode<T>(value);
if (Head == null)
{
// 如果链表为空,则新节点同时成为头节点和尾节点
Head = Tail = newNode;
}
else
{
// 将新节点的下一个节点设置为当前的头节点
newNode.Next = Head;
// 将当前头节点的上一个节点设置为新节点
Head.Previous = newNode;
// 更新头节点为新节点
Head = newNode;
}
}
// 在链表的末尾添加一个新节点
public void AddLast(T value)
{
// 创建一个新节点,其值为传入的value
DoublyLinkedListNode<T> newNode = new DoublyLinkedListNode<T>(value);
if (Tail == null)
{
// 如果链表为空,则新节点同时成为头节点和尾节点
Head = Tail = newNode;
}
else
{
// 将新节点的上一个节点设置为当前的尾节点
newNode.Previous = Tail;
// 将当前尾节点的下一个节点设置为新节点
Tail.Next = newNode;
// 更新尾节点为新节点
Tail = newNode;
}
}
// 从链表中移除一个值为value的节点
public bool Remove(T value)
{
DoublyLinkedListNode<T> current = Head;
while (current != null)
{
if (current.Value.Equals(value))
{
// 如果不是头节点,则更新前一个节点的下一个节点
if (current.Previous != null)
{
current.Previous.Next = current.Next;
}
else
{
// 如果是头节点,则更新头节点为下一个节点
Head = current.Next;
}
// 如果不是尾节点,则更新下一个节点的前一个节点
if (current.Next != null)
{
current.Next.Previous = current.Previous;
}
else
{
// 如果是尾节点,则更新尾节点为前一个节点
Tail = current.Previous;
}
return true; // 成功移除节点
}
current = current.Next;
}
return false; // 未找到值为value的节点
}
// 打印链表中的所有节点
public void PrintList()
{
DoublyLinkedListNode<T> current = Head;
// 遍历链表
while (current != null)
{
// 打印当前节点的值和一个双向箭头
Console.Write(current.Value + " <-> ");
current = current.Next;
}
// 链表结束打印null
Console.WriteLine("null");
}
}
在上述DoublyLinkedList<T>类中,我们定义了几个关键方法:
AddFirst(T value): 在链表的开始处添加一个新节点。AddLast(T value): 在链表的末尾添加一个新节点。Remove(T value): 从链表中删除具有特定值的节点。PrintList(): 打印链表中的所有节点。
示例:使用双向链表
现在我们已经定义了双向链表的基本结构和操作,让我们来看几个使用这个数据结构的例子。
添加节点
C#DoublyLinkedList<int> list = new DoublyLinkedList<int>();
list.AddFirst(3);
list.AddFirst(2);
list.AddFirst(1);
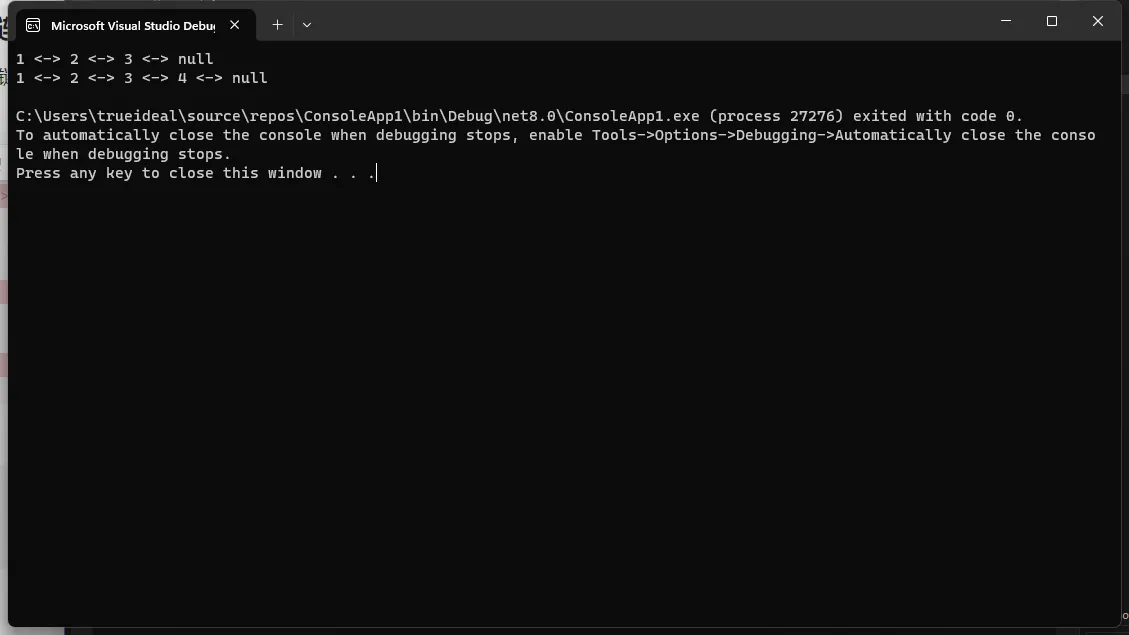
list.PrintList(); // 输出:1 <-> 2 <-> 3 <-> null
list.AddLast(4);
list.PrintList(); // 输出:1 <-> 2 <-> 3 <-> 4 <-> null
删除节点
C#list.Remove(3);
list.PrintList(); // 输出:1 <-> 2 <-> 4 <-> null
遍历链表
我们可以从头到尾或从尾到头遍历链表:
C#// 从头到尾遍历
DoublyLinkedListNode<int> current = list.Head;
while (current != null)
{
Console.Write(current.Value + " <-> ");
current = current.Next;
}
Console.WriteLine("null");
// 从尾到头遍历
current = list.Tail;
while (current != null)
{
Console.Write(current.Value + " <-> ");
current = current.Previous;
}
Console.WriteLine("null");
查找节点
我们可以添加一个方法来查找链表中的节点:
C#public DoublyLinkedListNode<T> Find(T value)
{
DoublyLinkedListNode<T> current = Head;
while (current != null)
{
if (current.Value.Equals(value))
{
return current;
}
current = current.Next;
}
return null;
}
然后使用这个方法:
C#DoublyLinkedListNode<int> node = list.Find(2);
if (node != null)
{
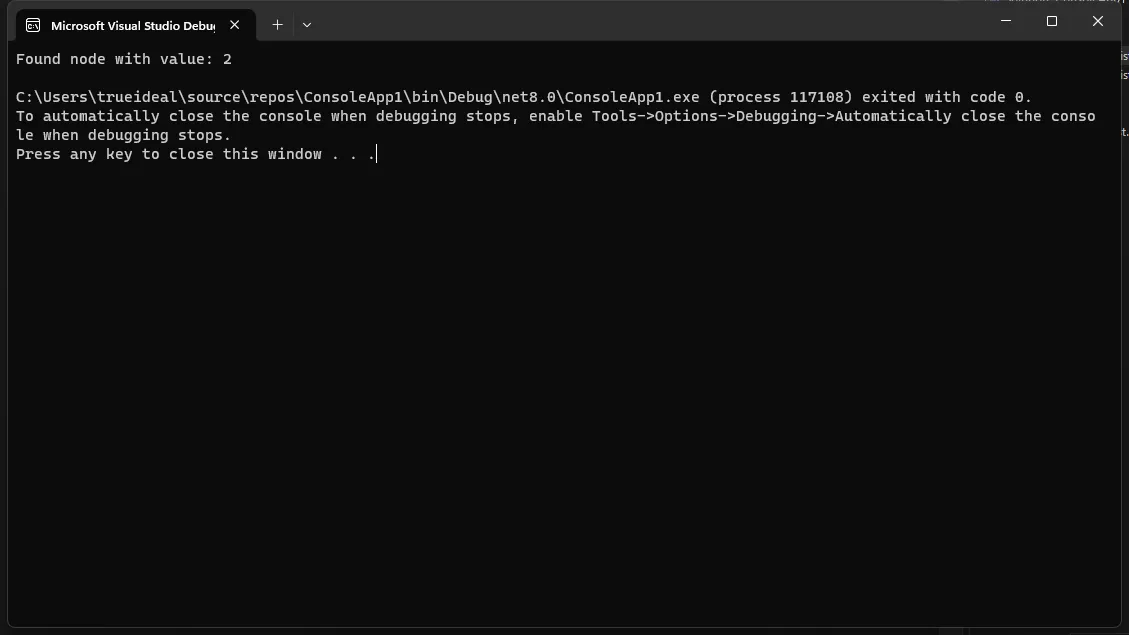
Console.WriteLine("Found node with value: " + node.Value);
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Node not found.");
}
// 输出:Found node with value: 2
总结
本文详细介绍了如何在C#中实现双向链表,包括定义链表节点、实现链表操作以及提供添加、删除和查找节点的示例。双向链表是一种灵活的数据结构,它允许我们从两个方向遍历节点,并且在节点的添加和删除操作上提供了更好的性能。掌握双向链表的实现和操作是深入理解数据结构的关键。
本文作者:技术老小子
本文链接:
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!
目录