文章中概述了 XAML 开发的六个关键主题,包括 XAML 文件的基本结构规范、资源的组织管理方式、命名空间的有效管理、样式与模板的管理策略、用户控件和自定义控件的开发指南,以及数据模板的最佳实践。这些主题涵盖了从基础架构到具体实现的各个方面,旨在帮助开发者构建结构清晰、易于维护的 WPF 应用程序,同时提供了提高开发效率和代码质量的实用指导。
XAML文件结构规范
基本结构示例
XML<Window x:Class="MyApp.MainWindow"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:MyApp"
Title="MainWindow" Height="450" Width="800">
<!-- 窗口资源字典 -->
<Window.Resources>
<!-- 这里放置窗口级别的资源 -->
</Window.Resources>
<!-- 根布局容器 -->
<Grid>
<!-- 内容布局 -->
</Grid>
</Window>
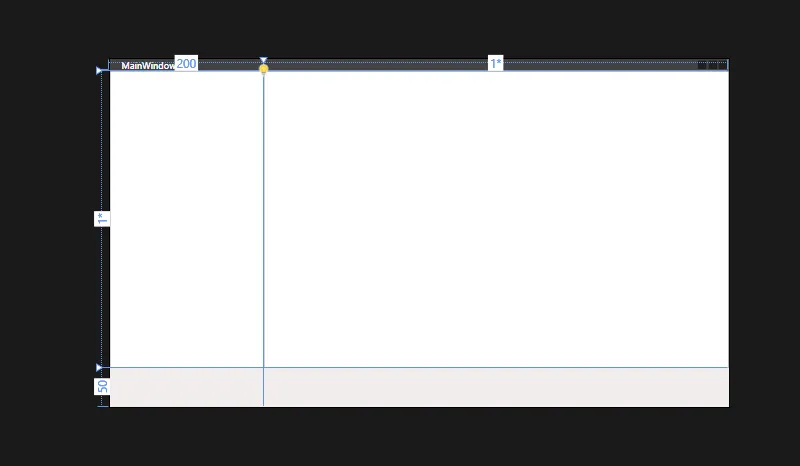
布局结构最佳实践
XML<Grid>
<!-- 1. 先定义行列 -->
<Grid.RowDefinitions>
<RowDefinition Height="Auto"/>
<RowDefinition Height="*"/>
<RowDefinition Height="50"/>
</Grid.RowDefinitions>
<Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<ColumnDefinition Width="200"/>
<ColumnDefinition Width="*"/>
</Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<!-- 2. 按照功能区域组织控件 -->
<!-- 顶部区域 -->
<StackPanel Grid.Row="0" Grid.ColumnSpan="2">
<!-- 顶部内容 -->
</StackPanel>
<!-- 左侧导航 -->
<ListBox Grid.Row="1" Grid.Column="0">
<!-- 导航项 -->
</ListBox>
<!-- 主要内容区 -->
<ContentControl Grid.Row="1" Grid.Column="1">
<!-- 主要内容 -->
</ContentControl>
<!-- 底部状态栏 -->
<StatusBar Grid.Row="2" Grid.ColumnSpan="2">
<!-- 状态信息 -->
</StatusBar>
</Grid>
概述
在WPF中,事件处理机制与传统的WinForms有很大的不同。WPF提供了更加灵活和强大的事件处理方式,包括XAML声明式事件绑定和代码后置事件处理两种主要方式。
WPF vs WinForms事件处理对比
主要区别
- 事件绑定方式
- WinForms:主要通过设计器自动生成代码或手动编写代码进行绑定
- WPF:可以在XAML中声明式绑定,也可以在代码后置中绑定
- 事件处理器位置
- WinForms:事件处理器代码通常集中在一个文件中
- WPF:支持分离式编程模型,可以更好地分离界面和逻辑
- 事件路由
- WinForms:简单的直接事件模型
- WPF:支持路由事件(Bubbling、Tunneling、Direct)
WPF事件处理示例
XAML声明式事件绑定
XML<Window x:Class="AppEvent.MainWindow"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:AppEvent"
mc:Ignorable="d"
Title="MainWindow" Height="450" Width="800">
<StackPanel>
<!-- 基本事件绑定 -->
<Button Content="点击我" Click="Button_Click" Margin="10"/>
<!-- 带参数的事件绑定 -->
<Button Content="带参数的按钮"
Click="Button_Click_WithParameter"
Tag="自定义参数"
Margin="10"/>
<!-- 多个事件的绑定 -->
<TextBox Text="输入些内容"
TextChanged="TextBox_TextChanged"
KeyDown="TextBox_KeyDown"
Margin="10"/>
</StackPanel>
</Window>
在WPF开发中,XAML的集合语法是一个非常重要的概念。它允许我们以声明式的方式定义和初始化各种集合类型的属性。本文将详细介绍XAML中的集合语法使用方法。
基本集合语法
XAML中的集合主要有两种表示方法:
- 标签语法(Property Element Syntax)
- 集合初始化语法(Collection Initialization Syntax)
标签语法示例
text<StackPanel> <!-- 使用标签语法添加子元素 --> <StackPanel.Children> <Button Content="按钮1"/> <Button Content="按钮2"/> <TextBlock Text="文本块"/> </StackPanel.Children> </StackPanel>
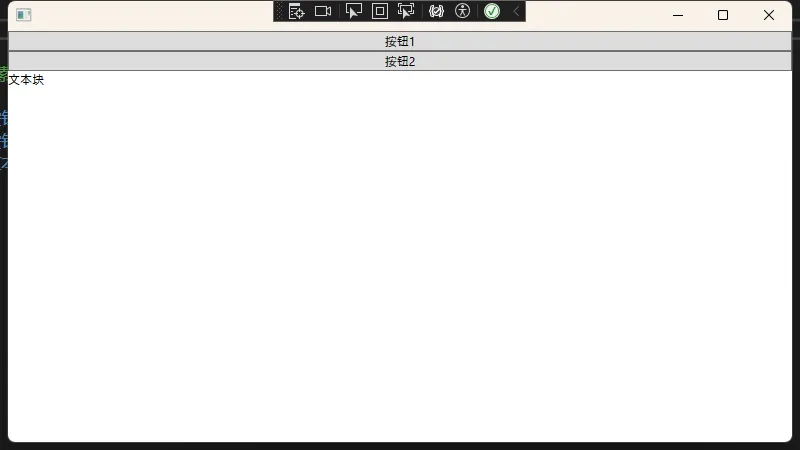
什么是属性元素语法
属性元素语法(Property Element Syntax)是XAML中一种特殊的语法形式,它允许我们以XML元素的形式来设置对象的属性,而不是使用传统的属性语法。这种语法特别适用于:
- 属性值比较复杂的情况
- 需要设置集合类型的属性
- 属性值本身就是一个对象的情况
基本语法格式
属性元素语法的基本格式为:
text<对象类型> <对象类型.属性名> 属性值 </对象类型.属性名> </对象类型>
个人觉得这一套逻辑其实比html 要好。
实际应用示例
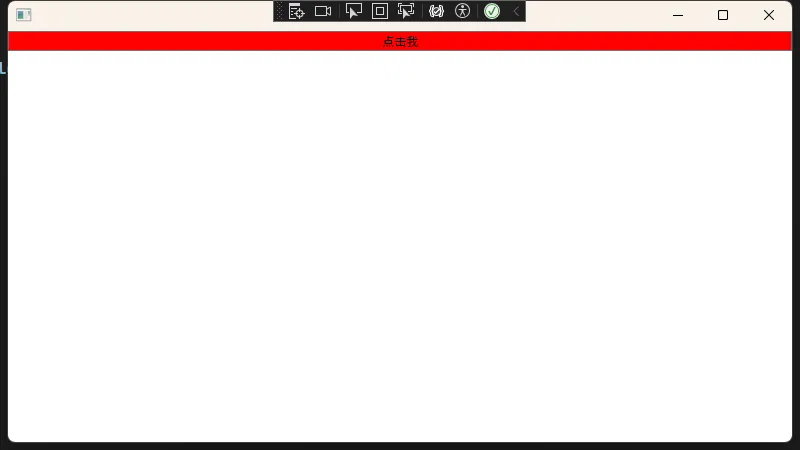
简单的背景色设置
以下两种写法是等价的:
text<!-- 传统属性语法 --> <Button Background="Red" Content="点击我"/> <!-- 属性元素语法 --> <Button Content="点击我"> <Button.Background> <SolidColorBrush Color="Red"/> </Button.Background> </Button>
什么是标记扩展?
标记扩展是XAML中一种特殊的语法机制,允许在属性赋值时动态计算或引用值,而不仅仅是使用简单的文本字符串。它们提供了一种在XAML中灵活处理值的方式,可以实现复杂的赋值逻辑。
常见的标记扩展
StaticResource 标记扩展
StaticResource用于引用已经定义的资源,通常在资源字典中。
text<Window.Resources> <SolidColorBrush x:Key="PrimaryBrush" Color="Blue"/> </Window.Resources> <Grid Background="{StaticResource PrimaryBrush}"> <!-- 使用静态资源 --> </Grid>
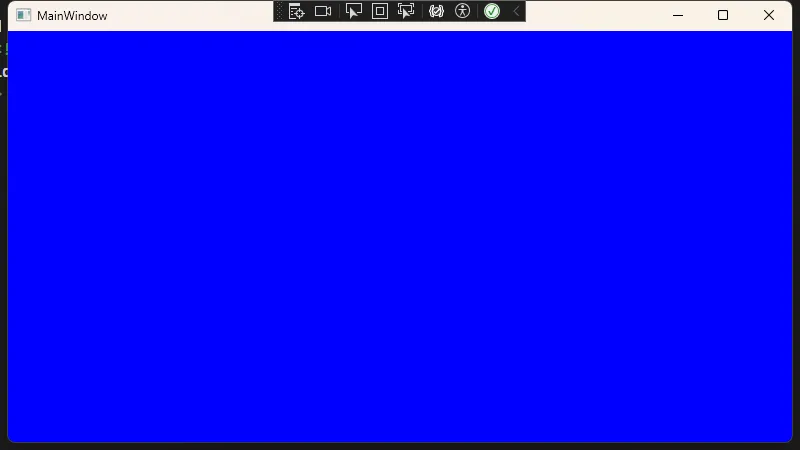
DynamicResource 标记扩展
与StaticResource类似,但会在运行时动态更新资源。
text<Window.Resources> <SolidColorBrush x:Key="ThemeBrush" Color="Green"/> </Window.Resources> <Button Background="{DynamicResource ThemeBrush}"> 动态资源按钮 </Button>