目录
在Windows平台的Python开发中,我们经常需要处理各种配置文件。无论是桌面应用、自动化脚本还是上位机程序,合理的配置管理都是项目成功的关键。今天就来深入探讨Python中最经典的配置文件格式——ini文件的读写操作。本文将从实际开发需求出发,通过丰富的代码示例,让你掌握ini文件操作的所有技巧,轻松应对各种配置管理场景。
🤔 为什么选择ini配置文件?
在众多配置文件格式中,ini文件有着独特的优势:
结构清晰:采用节(section)和键值对的层次结构,即使非技术人员也能轻松理解
兼容性强:Windows系统原生支持,许多传统软件都使用这种格式
可读性好:纯文本格式,支持注释,便于维护和调试
典型的ini文件结构如下:
Ini; 这是注释
[database]
host = localhost
port = 3306
username = admin
password = 123456
[logging]
level = INFO
file_path = ./logs/app.log
max_size = 10MB
🛠️ Python内置工具:configparser模块
Python标准库提供了configparser模块,这是处理ini文件的首选工具。让我们从基础用法开始:
📖 读取ini配置文件
Pythonimport configparser
def read_config():
# 创建ConfigParser对象
config = configparser.ConfigParser()
# 读取配置文件
config.read('config.ini', encoding='utf-8')
# 获取所有节名
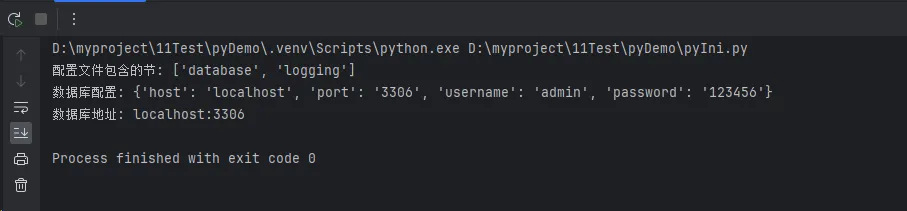
sections = config.sections()
print(f"配置文件包含的节: {sections}")
# 读取特定节的所有键值对
db_config = dict(config['database'])
print(f"数据库配置: {db_config}")
# 读取具体的配置项
host = config.get('database', 'host')
port = config.getint('database', 'port') # 自动转换为整数
print(f"数据库地址: {host}:{port}")
return config
# 使用示例
if __name__ == "__main__":
config = read_config()
✍️ 写入和修改配置
Pythonimport configparser
def create_config():
config = configparser.ConfigParser()
# 添加数据库配置节
config.add_section('database')
config.set('database', 'host', 'localhost')
config.set('database', 'port', '3306')
config.set('database', 'username', 'admin')
config.set('database', 'password', '123456')
# 添加日志配置节
config.add_section('logging')
config.set('logging', 'level', 'INFO')
config.set('logging', 'file_path', './logs/app.log')
config.set('logging', 'max_size', '10MB')
# 写入文件
with open('config.ini', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
config.write(f)
print("配置文件创建成功!")
def update_config():
config = configparser.ConfigParser()
config.read('config.ini', encoding='utf-8')
# 修改现有配置
config.set('database', 'password', 'new_password')
# 添加新的配置项
if not config.has_section('app'):
config.add_section('app')
config.set('app', 'version', '1.0.0')
config.set('app', 'debug', 'False')
# 保存修改
with open('config.ini', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
config.write(f)
print("配置更新完成!")
create_config()
update_config()
💼 实战案例:Windows桌面应用配置管理
让我们通过一个完整的配置管理类来展示最佳实践:
Pythonimport configparser
import os
from pathlib import Path
class ConfigManager:
def __init__(self, config_file='app_config.ini'):
self.config_file = config_file
self.config = configparser.ConfigParser()
# 确保配置文件存在
if not os.path.exists(config_file):
self._create_default_config()
else:
self.load_config()
def _create_default_config(self):
"""创建默认配置文件"""
# 应用程序基本配置
self.config.add_section('app')
self.config.set('app', 'title', 'Python桌面应用')
self.config.set('app', 'version', '1.0.0')
self.config.set('app', 'window_width', '1024')
self.config.set('app', 'window_height', '768')
self.config.set('app', 'auto_save', 'True')
# 数据库配置
self.config.add_section('database')
self.config.set('database', 'driver', 'sqlite')
self.config.set('database', 'path', './data/app.db')
self.config.set('database', 'backup_interval', '24')
# 用户偏好设置
self.config.add_section('preferences')
self.config.set('preferences', 'theme', 'light')
self.config.set('preferences', 'language', 'zh-CN')
self.config.set('preferences', 'font_size', '12')
self.save_config()
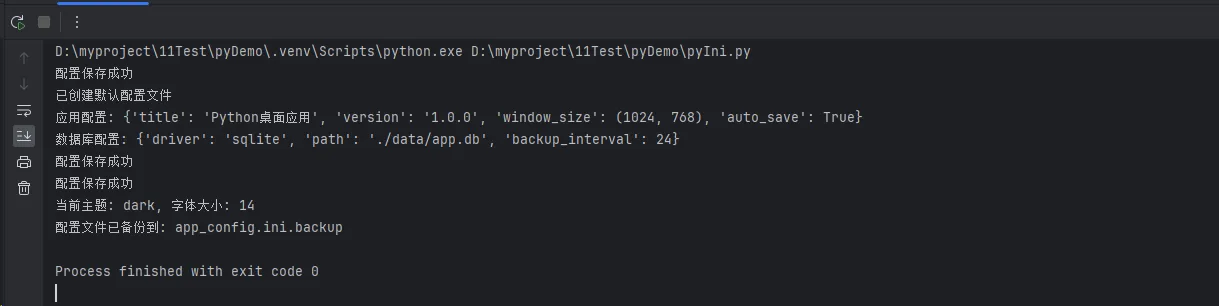
print("已创建默认配置文件")
def load_config(self):
"""加载配置文件"""
try:
self.config.read(self.config_file, encoding='utf-8')
print("配置文件加载成功")
except Exception as e:
print(f"配置文件加载失败: {e}")
self._create_default_config()
def save_config(self):
"""保存配置到文件"""
try:
with open(self.config_file, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
self.config.write(f)
print("配置保存成功")
except Exception as e:
print(f"配置保存失败: {e}")
def get_app_config(self):
"""获取应用程序配置"""
return {
'title': self.config.get('app', 'title'),
'version': self.config.get('app', 'version'),
'window_size': (
self.config.getint('app', 'window_width'),
self.config.getint('app', 'window_height')
),
'auto_save': self.config.getboolean('app', 'auto_save')
}
def get_database_config(self):
"""获取数据库配置"""
return {
'driver': self.config.get('database', 'driver'),
'path': self.config.get('database', 'path'),
'backup_interval': self.config.getint('database', 'backup_interval')
}
def update_preference(self, key, value):
"""更新用户偏好设置"""
self.config.set('preferences', key, str(value))
self.save_config()
def get_preference(self, key, default=None):
"""获取用户偏好设置"""
try:
return self.config.get('preferences', key)
except (configparser.NoSectionError, configparser.NoOptionError):
return default
def backup_config(self, backup_path=None):
"""备份配置文件"""
if backup_path is None:
backup_path = f"{self.config_file}.backup"
try:
import shutil
shutil.copy2(self.config_file, backup_path)
print(f"配置文件已备份到: {backup_path}")
return True
except Exception as e:
print(f"配置备份失败: {e}")
return False
# 使用示例
def demo_config_manager():
# 创建配置管理器实例
config_mgr = ConfigManager()
# 获取配置信息
app_config = config_mgr.get_app_config()
print(f"应用配置: {app_config}")
db_config = config_mgr.get_database_config()
print(f"数据库配置: {db_config}")
# 更新用户偏好
config_mgr.update_preference('theme', 'dark')
config_mgr.update_preference('font_size', '14')
# 获取偏好设置
theme = config_mgr.get_preference('theme')
font_size = config_mgr.get_preference('font_size')
print(f"当前主题: {theme}, 字体大小: {font_size}")
# 备份配置
config_mgr.backup_config()
if __name__ == "__main__":
demo_config_manager()
🔧 高级技巧与最佳实践
🛡️ 安全性考虑
对于敏感信息(如密码),不建议直接存储在ini文件中。可以结合简单的编码:
Pythonimport base64
import configparser
import os
class SecureConfigManager:
def __init__(self, config_file='secure_config.ini'):
self.config_file = config_file
self.config = configparser.ConfigParser()
self.load_config()
def encode_password(self, password):
"""简单的密码编码(仅用于演示,实际项目请使用更安全的方法)"""
return base64.b64encode(password.encode()).decode()
def decode_password(self, encoded_password):
"""解码密码"""
return base64.b64decode(encoded_password.encode()).decode()
def set_secure_value(self, section, key, value):
"""设置需要编码的值"""
if not self.config.has_section(section):
self.config.add_section(section)
encoded_value = self.encode_password(value)
self.config.set(section, key, encoded_value)
self.save_config()
def get_secure_value(self, section, key):
"""获取解码后的值"""
try:
encoded_value = self.config.get(section, key)
return self.decode_password(encoded_value)
except Exception as e:
print(f"获取安全值失败: {e}")
return None
def load_config(self):
if os.path.exists(self.config_file):
self.config.read(self.config_file, encoding='utf-8')
def save_config(self):
with open(self.config_file, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
self.config.write(f)
# 使用示例
secure_config = SecureConfigManager()
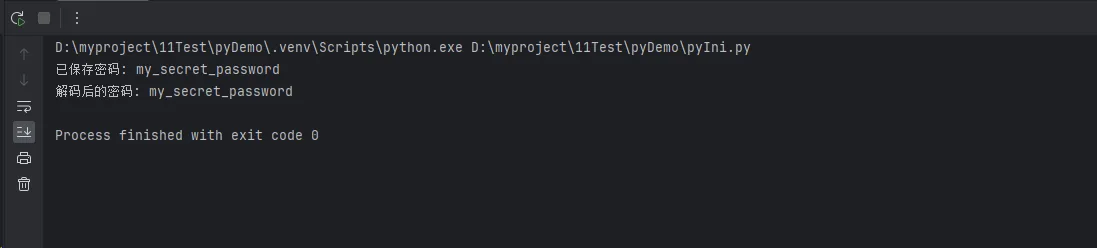
secure_config.set_secure_value('database', 'password', 'my_secret_password')
print(f"已保存密码: {secure_config.get_secure_value('database', 'password')}")
password = secure_config.get_secure_value('database', 'password')
print(f"解码后的密码: {password}")
🎨 配置文件模板功能
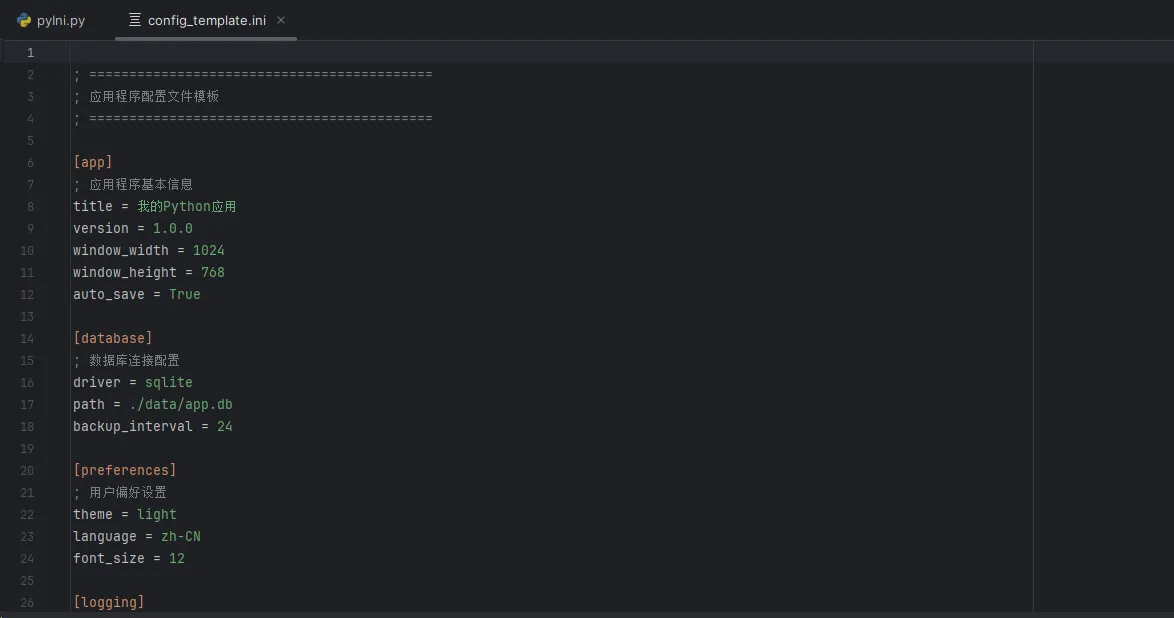
Pythondef create_config_template():
"""创建配置文件模板,方便用户自定义"""
template = """
; ===========================================
; 应用程序配置文件模板
; ===========================================
[app]
; 应用程序基本信息
title = 我的Python应用
version = 1.0.0
window_width = 1024
window_height = 768
auto_save = True
[database]
; 数据库连接配置
driver = sqlite
path = ./data/app.db
backup_interval = 24
[preferences]
; 用户偏好设置
theme = light
language = zh-CN
font_size = 12
[logging]
; 日志配置
level = INFO
file_path = ./logs/app.log
max_file_size = 10MB
backup_count = 5
"""
with open('config_template.ini', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write(template)
print("配置模板已创建,请根据需要修改后重命名为config.ini")

🔄 配置文件验证
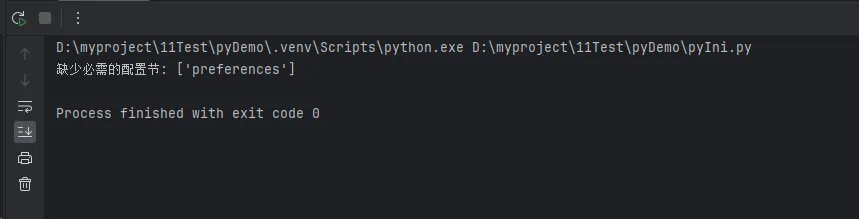
Pythondef validate_config(config_file='config.ini'):
"""验证配置文件的完整性"""
required_sections = ['app', 'database', 'preferences']
required_keys = {
'app': ['title', 'version', 'window_width', 'window_height'],
'database': ['driver', 'path'],
'preferences': ['theme', 'language']
}
config = configparser.ConfigParser()
try:
config.read(config_file, encoding='utf-8')
# 检查必需的节
missing_sections = []
for section in required_sections:
if not config.has_section(section):
missing_sections.append(section)
if missing_sections:
print(f"缺少必需的配置节: {missing_sections}")
return False
# 检查必需的键
missing_keys = {}
for section, keys in required_keys.items():
section_missing = []
for key in keys:
if not config.has_option(section, key):
section_missing.append(key)
if section_missing:
missing_keys[section] = section_missing
if missing_keys:
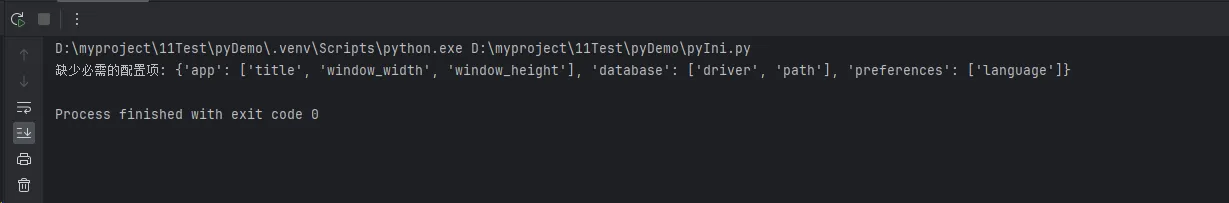
print(f"缺少必需的配置项: {missing_keys}")
return False
print("配置文件验证通过!")
return True
except Exception as e:
print(f"配置文件验证失败: {e}")
return False
📱 与GUI框架集成示例
在实际的Windows桌面应用开发中,配置管理通常与GUI框架紧密结合:
Pythonimport os
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import ttk, messagebox
import configparser
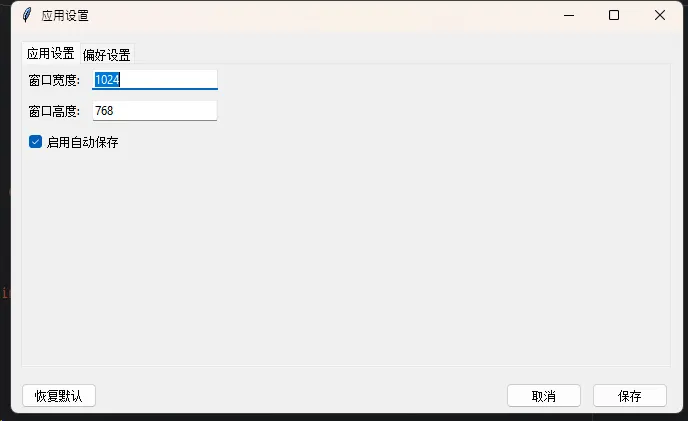
class SettingsWindow:
def __init__(self, parent, config_manager):
self.parent = parent
self.config_mgr = config_manager
self.window = tk.Toplevel(parent)
self.window.title("应用设置")
self.window.geometry("400x300")
self.create_widgets()
self.load_settings()
def create_widgets(self):
# 创建notebook用于分组设置
notebook = ttk.Notebook(self.window)
# 应用程序设置页面
app_frame = ttk.Frame(notebook)
notebook.add(app_frame, text="应用设置")
# 窗口大小设置
ttk.Label(app_frame, text="窗口宽度:").grid(row=0, column=0, sticky='w', padx=5, pady=5)
self.width_var = tk.StringVar()
ttk.Entry(app_frame, textvariable=self.width_var).grid(row=0, column=1, padx=5, pady=5)
ttk.Label(app_frame, text="窗口高度:").grid(row=1, column=0, sticky='w', padx=5, pady=5)
self.height_var = tk.StringVar()
ttk.Entry(app_frame, textvariable=self.height_var).grid(row=1, column=1, padx=5, pady=5)
# 自动保存设置
self.auto_save_var = tk.BooleanVar()
ttk.Checkbutton(app_frame, text="启用自动保存",
variable=self.auto_save_var).grid(row=2, column=0, columnspan=2, sticky='w', padx=5, pady=5)
# 偏好设置页面
pref_frame = ttk.Frame(notebook)
notebook.add(pref_frame, text="偏好设置")
# 主题设置
ttk.Label(pref_frame, text="主题:").grid(row=0, column=0, sticky='w', padx=5, pady=5)
self.theme_var = tk.StringVar()
theme_combo = ttk.Combobox(pref_frame, textvariable=self.theme_var,
values=['light', 'dark'], state='readonly')
theme_combo.grid(row=0, column=1, padx=5, pady=5)
# 字体大小设置
ttk.Label(pref_frame, text="字体大小:").grid(row=1, column=0, sticky='w', padx=5, pady=5)
self.font_size_var = tk.StringVar()
font_combo = ttk.Combobox(pref_frame, textvariable=self.font_size_var,
values=['10', '12', '14', '16', '18'], state='readonly')
font_combo.grid(row=1, column=1, padx=5, pady=5)
notebook.pack(fill='both', expand=True, padx=10, pady=10)
# 按钮框架
button_frame = ttk.Frame(self.window)
button_frame.pack(fill='x', padx=10, pady=5)
ttk.Button(button_frame, text="保存", command=self.save_settings).pack(side='right', padx=5)
ttk.Button(button_frame, text="取消", command=self.window.destroy).pack(side='right', padx=5)
ttk.Button(button_frame, text="恢复默认", command=self.reset_defaults).pack(side='left')
def load_settings(self):
"""从配置文件加载设置"""
app_config = self.config_mgr.get_app_config()
self.width_var.set(str(app_config['window_size'][0]))
self.height_var.set(str(app_config['window_size'][1]))
self.auto_save_var.set(app_config['auto_save'])
self.theme_var.set(self.config_mgr.get_preference('theme', 'light'))
self.font_size_var.set(self.config_mgr.get_preference('font_size', '12'))
def save_settings(self):
"""保存设置到配置文件"""
try:
# 保存应用设置
self.config_mgr.config.set('app', 'window_width', self.width_var.get())
self.config_mgr.config.set('app', 'window_height', self.height_var.get())
self.config_mgr.config.set('app', 'auto_save', str(self.auto_save_var.get()))
# 保存偏好设置
self.config_mgr.update_preference('theme', self.theme_var.get())
self.config_mgr.update_preference('font_size', self.font_size_var.get())
self.config_mgr.save_config()
messagebox.showinfo("成功", "设置已保存!")
self.window.destroy()
except Exception as e:
messagebox.showerror("错误", f"保存设置失败: {e}")
def reset_defaults(self):
"""恢复默认设置"""
self.width_var.set('1024')
self.height_var.set('768')
self.auto_save_var.set(True)
self.theme_var.set('light')
self.font_size_var.set('12')
class ConfigManager:
def __init__(self, config_path='app_settings.ini'):
self.config_path = config_path
self.config = configparser.ConfigParser()
self.load_config()
def load_config(self):
if not os.path.exists(self.config_path):
# 初始化默认配置
self.config['app'] = {
'window_width': '1024',
'window_height': '768',
'auto_save': 'True'
}
self.config['preference'] = {
'theme': 'light',
'font_size': '12'
}
self.save_config()
else:
self.config.read(self.config_path, encoding='utf-8')
def save_config(self):
with open(self.config_path, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as configfile:
self.config.write(configfile)
def get_app_config(self):
app_cfg = self.config['app']
width = int(app_cfg.get('window_width', '1024'))
height = int(app_cfg.get('window_height', '768'))
auto_save = app_cfg.get('auto_save', 'True') == 'True'
return {'window_size': (width, height), 'auto_save': auto_save}
def get_preference(self, key, default=None):
return self.config['preference'].get(key, default)
def update_preference(self, key, value):
self.config['preference'][key] = value
if __name__ == '__main__':
root = tk.Tk()
root.withdraw()
config_mgr = ConfigManager() # 实例化配置管理器
s = SettingsWindow(root, config_mgr)
s.window.mainloop()
🎯 总结要点
通过本文的深入讲解,我们掌握了Python操作ini配置文件的核心技能:
🔑 核心技能掌握:从configparser模块的基础用法到高级特性,包括读取、写入、修改配置文件的各种方法,让你能够应对不同复杂度的配置管理需求。
💼 实战经验积累:通过完整的ConfigManager类和GUI集成示例,展示了真实项目中的最佳实践,包括安全性考虑、配置验证、模板创建等高级功能。
🚀 开发效率提升:掌握这些技巧后,你的Python应用将拥有更专业的配置管理能力,用户体验和代码维护性都会显著提升。
ini配置文件虽然看似简单,但在Windows平台的Python开发中却是不可或缺的技能。无论是桌面应用、自动化工具还是上位机程序,良好的配置管理都能让你的项目更加专业和易用。希望本文的内容能够帮助你在Python开发的道路上更进一步!
本文作者:技术老小子
本文链接:
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!