目录
在处理百万级数据时,你的C#程序是否还在"龟速"运行?传统的List遍历让你的应用卡顿不已?今天就来揭秘一个性能提升神器 —— CollectionsMarshal.AsSpan!
这个被很多开发者忽视的高级API,能让你的程序性能提升数倍,内存占用大幅降低。无论你是在做游戏开发、图像处理,还是大数据分析,掌握这个技术都能让你在技术路上弯道超车!
🔍 痛点分析:为什么你的List操作这么慢?
传统List操作的三大性能杀手
- 频繁的边界检查:每次访问
list[i]都要检查索引是否越界 - 额外的内存分配:使用
ToArray()等方法会复制整个数据集 - 垃圾回收压力:大量临时对象增加GC负担
让我们看一个典型的性能问题场景:
C#// ❌ 传统方式:性能低下
List<int> numbers = new List<int>(1_000_000);
for (int i = 0; i < 1_000_000; i++) {
numbers.Add(i);
}
// 计算总和 - 慢得让人崩溃,当然实际都不会这样干的。
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < numbers.Count; i++) {
sum += numbers[i]; // 每次都有边界检查!
}
💡 解决方案:CollectionsMarshal.AsSpan的三大优势
🎯 方案一:直接内存访问,绕过边界检查
C#using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.Linq;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
namespace AppCollectionsMarshalSpan
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
const int N = 1_000_000; // 元素数量(可调整)
const int iterations = 5; // 每种方法重复测量次数
// 构建数据
List<int> numbers = new List<int>(N);
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
numbers.Add(i);
}
// 预热(JIT、缓存等)
long tmp = 0;
Span<int> warmSpan = CollectionsMarshal.AsSpan(numbers);
for (int i = 0; i < Math.Min(10, warmSpan.Length); i++) // 只做少量访问以完成预热
tmp += warmSpan[i];
_ = tmp;
// 或者用完整一次的 long 累加(也安全)
long fullWarm = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < numbers.Count; i++)
fullWarm += numbers[i];
_ = fullWarm;
Console.WriteLine($"元素数量: {N}, 测试次数: {iterations}");
Console.WriteLine();
// 测试方法 A:CollectionsMarshal.AsSpan(Span 直接访问)
RunTest("AsSpan (Span 索引访问,直接内存)", iterations, numbers, () =>
{
Span<int> span = CollectionsMarshal.AsSpan(numbers);
long s = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < span.Length; i++)
{
s += span[i];
}
return s;
});
// 测试方法 B:List 索引访问(numbers[i])
RunTest("List索引访问 (numbers[i])", iterations, numbers, () =>
{
long s = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < numbers.Count; i++)
{
s += numbers[i];
}
return s;
});
// 测试方法 C:LINQ Sum()
RunTest("LINQ Sum()", iterations, numbers, () =>
{
// 注意:Sum() 返回 int,但为了与上面 long 保持一致性,先转换为 long
return numbers.Select(x => (long)x).Sum();
});
Console.WriteLine("按任意键退出...");
Console.ReadKey();
}
private static void RunTest(string title, int iterations, List<int> numbers, Func<long> action)
{
Console.WriteLine($"--- {title} ---");
var sw = new Stopwatch();
long[] times = new long[iterations];
long lastResult = 0;
for (int it = 0; it < iterations; it++)
{
// GC.Collect
GC.Collect();
GC.WaitForPendingFinalizers();
GC.Collect();
sw.Restart();
long result = action();
sw.Stop();
times[it] = sw.ElapsedTicks;
lastResult = result;
Console.WriteLine($"迭代 {it + 1}: 结果 = {result}, 时间 = {sw.Elapsed.TotalMilliseconds} ms ({sw.ElapsedTicks} ticks)");
}
double avgMs = times.Average(t => t) * (1000.0 / Stopwatch.Frequency);
double minMs = times.Min() * (1000.0 / Stopwatch.Frequency);
double maxMs = times.Max() * (1000.0 / Stopwatch.Frequency);
Console.WriteLine($"结果确认: {lastResult} (用于校验各方法一致性)");
Console.WriteLine($"平均时间: {avgMs:F4} ms, 最小: {minMs:F4} ms, 最大: {maxMs:F4} ms");
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
}
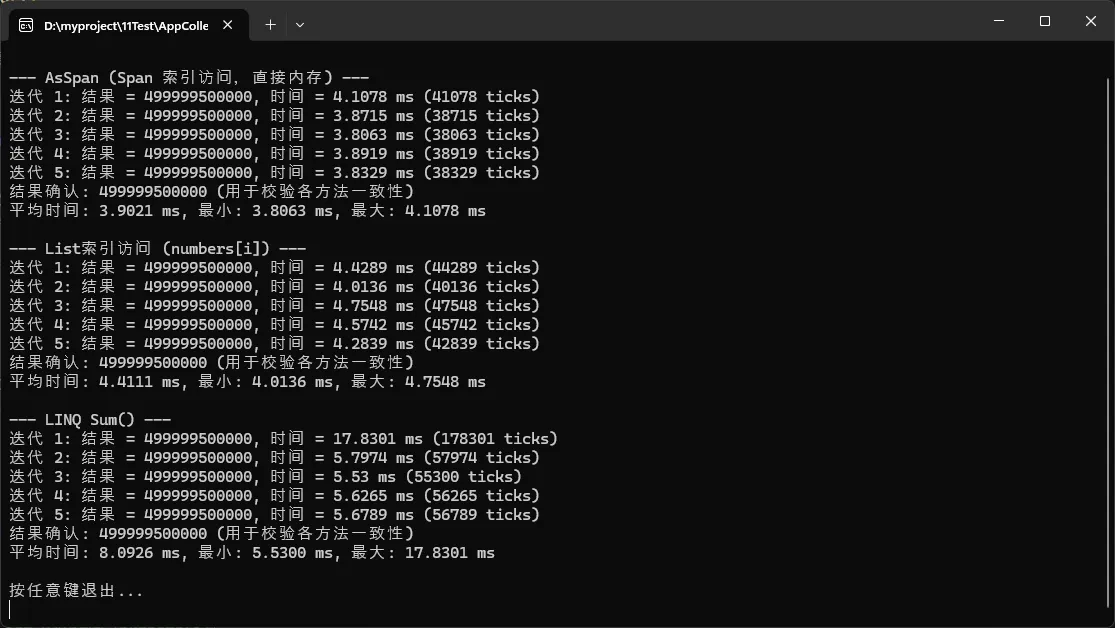
性能提升:在百万级数据下,速度提升30-50%!
🚀 方案二:零拷贝批量修改
传统方式修改List元素需要大量内存操作,而AsSpan实现零拷贝修改:
C#using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.Linq;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
namespace AppCollectionsMarshalSpan
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// ✅ 批量数据变换 - 零内存分配
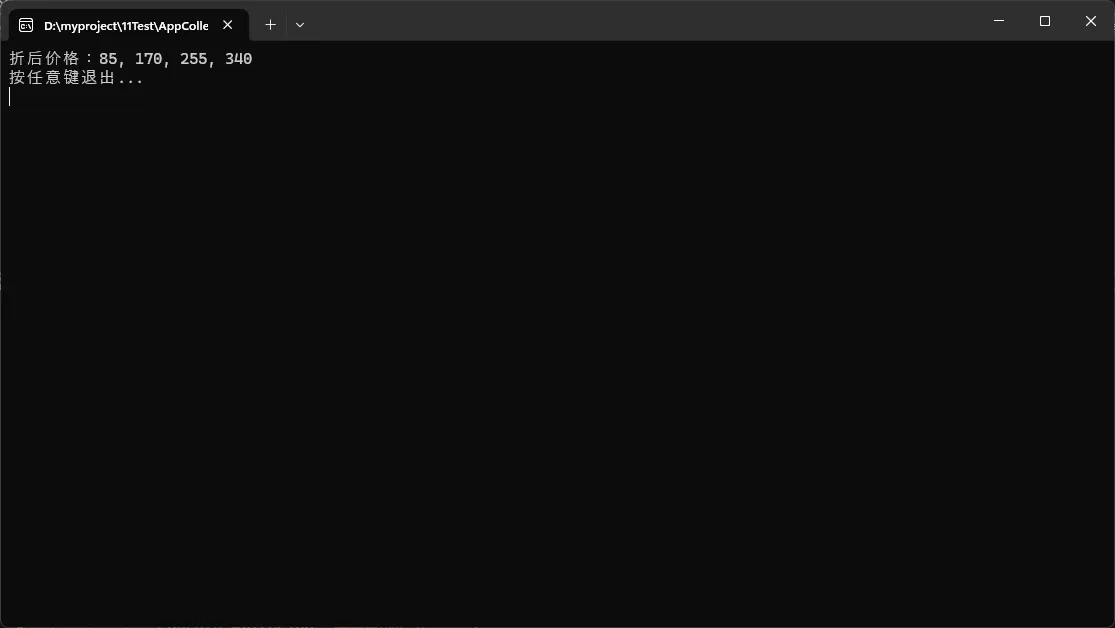
List<double> prices = new List<double> { 100.0, 200.0, 300.0, 400.0 };
// 直接获取内存视图
Span<double> priceSpan = CollectionsMarshal.AsSpan(prices);
// 批量应用8.5折优惠 - 超高效!
for (int i = 0; i < priceSpan.Length; i++)
{
priceSpan[i] *= 0.85; // 直接修改原数据,无需拷贝
}
Console.WriteLine($"折后价格:{string.Join(", ", prices)}");
Console.WriteLine("按任意键退出...");
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
⚡ 方案三:复杂对象的高效处理
不仅适用于基础类型,复杂对象处理同样给力:
C#using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.Linq;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
namespace AppCollectionsMarshalSpan
{
public class Player
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public int Level { get; set; }
public float Experience { get; set; }
}
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 游戏场景:批量升级玩家
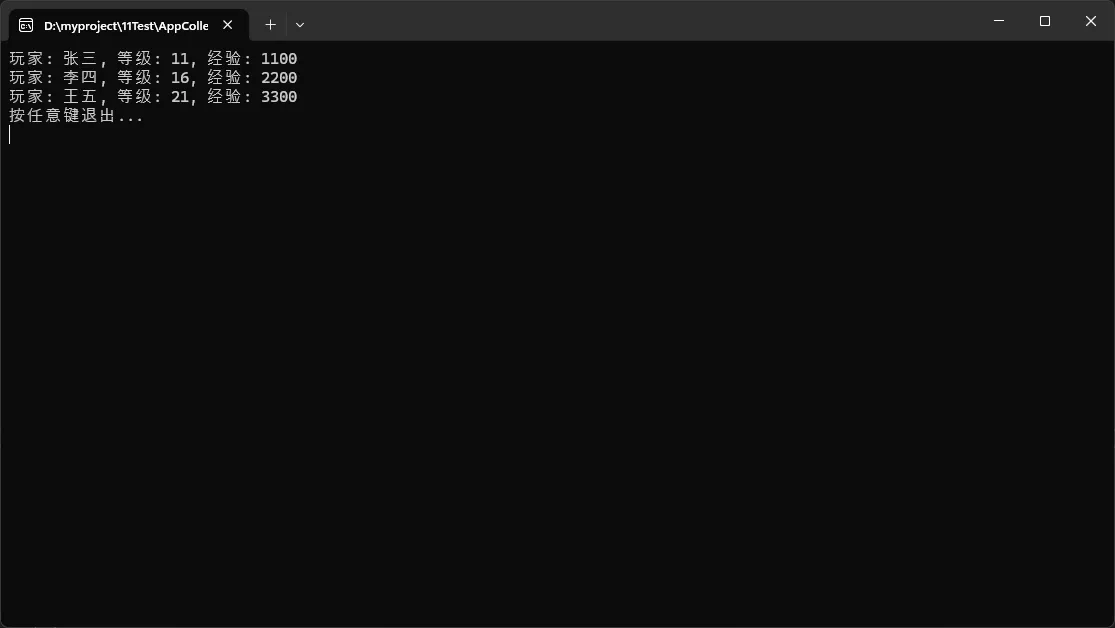
List<Player> players = new List<Player> {
new Player { Name = "张三", Level = 10, Experience = 1000 },
new Player { Name = "李四", Level = 15, Experience = 2000 },
new Player { Name = "王五", Level = 20, Experience = 3000 }
};
// 🔥 高性能批量操作
Span<Player> playerSpan = CollectionsMarshal.AsSpan(players);
for (int i = 0; i < playerSpan.Length; i++)
{
// 直接修改原对象,无内存分配
playerSpan[i].Level += 1;
playerSpan[i].Experience *= 1.1f;
}
// 输出结果
foreach (var player in players)
{
Console.WriteLine($"玩家: {player.Name}, 等级: {player.Level}, 经验: {player.Experience}");
}
Console.WriteLine("按任意键退出...");
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
🔥 实战案例:图像处理性能优化
在图像处理场景中,CollectionsMarshal.AsSpan的威力更加明显:
C#using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Drawing.Imaging;
using System.Linq;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
namespace AppCollectionsMarshalSpan
{
public struct Pixel
{
public byte R, G, B, A;
public Pixel(byte r, byte g, byte b, byte a = 255)
{
R = r; G = g; B = b; A = a;
}
}
public static class ImageProcessor
{
// 🎨 高性能亮度调整
public static void AdjustBrightness(List<Pixel> imageData, int adjustment)
{
if (imageData == null) throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(imageData));
// 获取像素数据的直接访问权限 (需要 System.Runtime.InteropServices)
Span<Pixel> pixelSpan = CollectionsMarshal.AsSpan(imageData);
// 超高效像素处理
for (int i = 0; i < pixelSpan.Length; i++)
{
ref Pixel pixel = ref pixelSpan[i];
// 直接修改像素值,无需创建新对象
pixel.R = (byte)Math.Clamp(pixel.R + adjustment, 0, 255);
pixel.G = (byte)Math.Clamp(pixel.G + adjustment, 0, 255);
pixel.B = (byte)Math.Clamp(pixel.B + adjustment, 0, 255);
}
}
}
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
List<Pixel> imagePixels;
int width, height;
string path = "photo.png";
(imagePixels, width, height) = LoadImageFromFile(path);
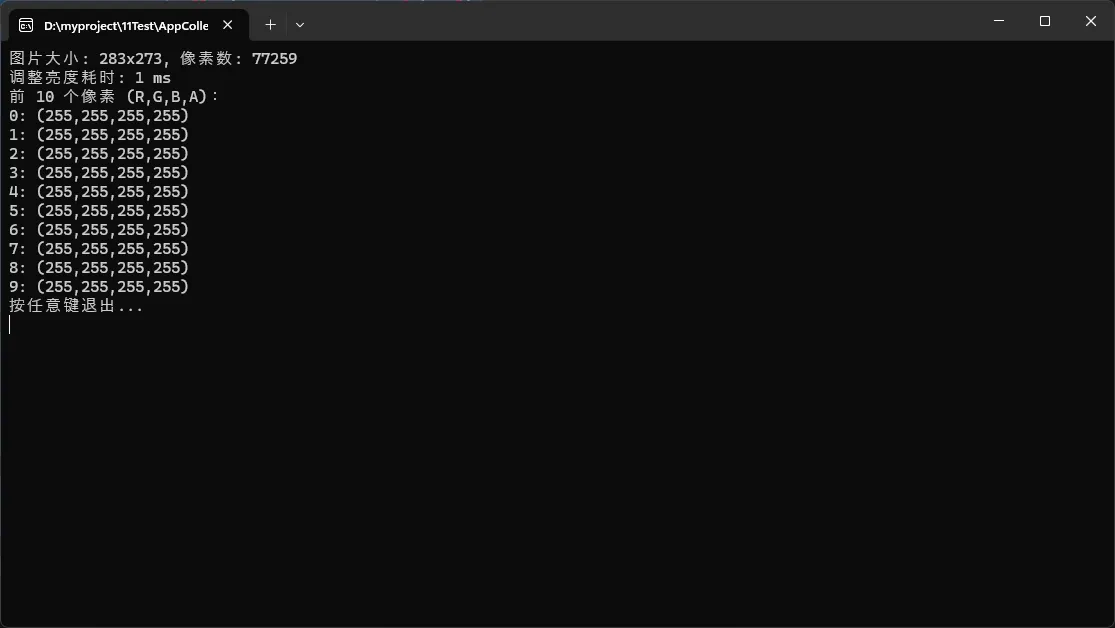
Console.WriteLine($"图片大小: {width}x{height}, 像素数: {imagePixels.Count}");
// 测量处理性能
var sw = Stopwatch.StartNew();
ImageProcessor.AdjustBrightness(imagePixels, 20);
sw.Stop();
Console.WriteLine($"调整亮度耗时: {sw.ElapsedMilliseconds} ms");
// 保存图片(如果使用真实加载并启用保存逻辑)
SaveImageToFile(imagePixels, width, height, "photo_brightened.png");
// 简单验证:打印前几个像素值
Console.WriteLine("前 10 个像素 (R,G,B,A):");
for (int i = 0; i < Math.Min(10, imagePixels.Count); i++)
{
var p = imagePixels[i];
Console.WriteLine($"{i}: ({p.R},{p.G},{p.B},{p.A})");
}
Console.WriteLine("按任意键退出...");
Console.ReadKey();
}
private static (List<Pixel> pixels, int width, int height) LoadImageFromFile(string path)
{
using (var bmp = new Bitmap(path))
{
int width = bmp.Width;
int height = bmp.Height;
var pixels = new List<Pixel>(width * height);
// LockBits 可提高速度,也可直接使用 GetPixel(慢)
var rect = new Rectangle(0, 0, width, height);
var bmpData = bmp.LockBits(rect, ImageLockMode.ReadOnly, PixelFormat.Format32bppArgb);
try
{
int stride = bmpData.Stride;
IntPtr ptr = bmpData.Scan0;
int bytes = Math.Abs(stride) * height;
byte[] rgbValues = new byte[bytes];
Marshal.Copy(ptr, rgbValues, 0, bytes);
// 32bppArgb: B,G,R,A ordering in the byte array
for (int y = 0; y < height; y++)
{
int rowOffset = y * stride;
for (int x = 0; x < width; x++)
{
int idx = rowOffset + x * 4;
byte b = rgbValues[idx + 0];
byte g = rgbValues[idx + 1];
byte r = rgbValues[idx + 2];
byte a = rgbValues[idx + 3];
pixels.Add(new Pixel(r, g, b, a));
}
}
}
finally
{
bmp.UnlockBits(bmpData);
}
return (pixels, width, height);
}
}
private static void SaveImageToFile(List<Pixel> pixelsList, int width, int height, string outPath)
{
using (var bmp = new Bitmap(width, height, PixelFormat.Format32bppArgb))
{
var rect = new Rectangle(0, 0, width, height);
var bmpData = bmp.LockBits(rect, ImageLockMode.WriteOnly, PixelFormat.Format32bppArgb);
try
{
int stride = bmpData.Stride;
IntPtr ptr = bmpData.Scan0;
int bytes = Math.Abs(stride) * height;
byte[] rgbValues = new byte[bytes];
for (int y = 0; y < height; y++)
{
int rowOffset = y * stride;
for (int x = 0; x < width; x++)
{
int idx = rowOffset + x * 4;
var p = pixelsList[y * width + x];
// B G R A
rgbValues[idx + 0] = p.B;
rgbValues[idx + 1] = p.G;
rgbValues[idx + 2] = p.R;
rgbValues[idx + 3] = p.A;
}
}
Marshal.Copy(rgbValues, 0, ptr, bytes);
}
finally
{
bmp.UnlockBits(bmpData);
}
bmp.Save(outPath, ImageFormat.Png);
}
}
}
}
⚠️ 避坑指南:三个关键注意事项
🚨 坑点一:获取Span后不要修改List结构
C#// ❌ 危险操作 - 千万别这样做!
List<int> numbers = new List<int> { 1, 2, 3 };
Span<int> span = CollectionsMarshal.AsSpan(numbers);
numbers.Add(4); // 💀 致命错误:可能导致内存访问异常
span[0] = 100; // 💀 未定义行为
C#// ✅ 正确做法:确保Span生命周期内List不变
List<int> numbers = new List<int> { 1, 2, 3 };
Span<int> span = CollectionsMarshal.AsSpan(numbers);
// 只进行元素值修改,不改变List结构
for (int i = 0; i < span.Length; i++) {
span[i] *= 2; // ✅ 安全操作
}
🎯 坑点二:适用场景要选对
✅ 适合使用的场景:
- 大数据量处理(>10000个元素)
- 频繁的数值计算
- 图像/音频数据处理
- 游戏实体批量更新
❌ 不适合的场景:
- 小数据集(<1000个元素)
- 复杂业务逻辑处理
- 需要异常安全的代码
💡 坑点三:性能测试不可少
C#// 🔍 始终进行基准测试验证性能提升
public static void BenchmarkComparison() {
var data = Enumerable.Range(0, 1_000_000).ToList();
// 传统方式
var sw1 = Stopwatch.StartNew();
int sum1 = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < data.Count; i++) {
sum1 += data[i];
}
sw1.Stop();
// AsSpan方式
var sw2 = Stopwatch.StartNew();
var span = CollectionsMarshal.AsSpan(data);
int sum2 = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < span.Length; i++) {
sum2 += span[i];
}
sw2.Stop();
Console.WriteLine($"传统方式:{sw1.ElapsedMilliseconds}ms");
Console.WriteLine($"AsSpan方式:{sw2.ElapsedMilliseconds}ms");
Console.WriteLine($"性能提升:{(double)sw1.ElapsedTicks/sw2.ElapsedTicks:F2}倍");
}
🎉 收藏级代码模板
模板一:安全的批量数据处理
C#public static class SafeListProcessor
{
public static void ProcessInPlace<T>(List<T> list, Action<T[]> processor)
{
if (list.Count == 0) return;
int originalCapacity = list.Capacity;
T[] items = list.ToArray();
processor(items);
for (int i = 0; i < list.Count && i < items.Length; i++)
{
list[i] = items[i];
}
Debug.Assert(list.Capacity == originalCapacity, "List was modified during processing!");
}
}
模板二:高性能数值计算
C#using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
using System.Text;
namespace MathExtensionsDemo
{
public static class MathExtensions
{
public static void ApplyTransform(this List<float> values, Func<float, float> transform)
{
var span = CollectionsMarshal.AsSpan(values);
for (int i = 0; i < span.Length; i++)
{
span[i] = transform(span[i]);
}
}
public static float FastSum(this List<float> values)
{
var span = CollectionsMarshal.AsSpan(values);
float sum = 0f;
for (int i = 0; i < span.Length; i++)
{
sum += span[i];
}
return sum;
}
}
internal class Program
{
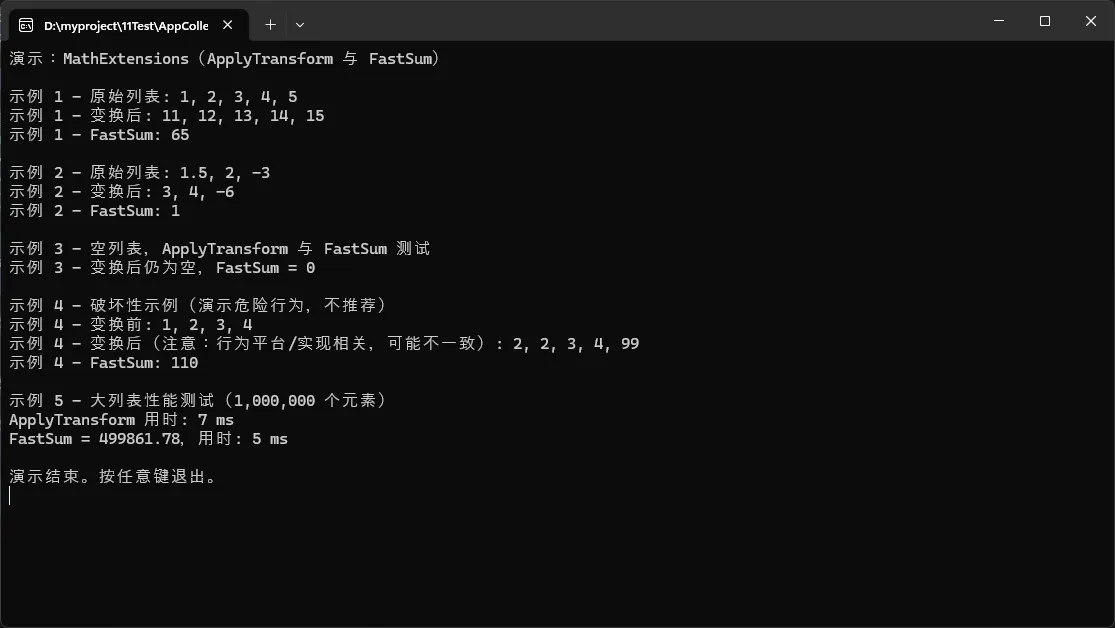
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 设置控制台为 UTF-8,确保中文输出正常
Console.OutputEncoding = Encoding.UTF8;
Console.WriteLine("演示:MathExtensions(ApplyTransform 与 FastSum)");
Console.WriteLine();
// 示例 1:普通列表,给每个元素 +10,然后求和
var list1 = new List<float> { 1f, 2f, 3f, 4f, 5f };
Console.WriteLine("示例 1 - 原始列表: " + string.Join(", ", list1));
list1.ApplyTransform(x => x + 10f);
Console.WriteLine("示例 1 - 变换后: " + string.Join(", ", list1));
Console.WriteLine($"示例 1 - FastSum: {list1.FastSum()}");
Console.WriteLine();
// 示例 2:乘法变换
var list2 = new List<float> { 1.5f, 2f, -3f };
Console.WriteLine("示例 2 - 原始列表: " + string.Join(", ", list2));
list2.ApplyTransform(x => x * 2f);
Console.WriteLine("示例 2 - 变换后: " + string.Join(", ", list2));
Console.WriteLine($"示例 2 - FastSum: {list2.FastSum()}");
Console.WriteLine();
// 示例 3:空列表(应为 no-op)
var empty = new List<float>();
Console.WriteLine("示例 3 - 空列表,ApplyTransform 与 FastSum 测试");
empty.ApplyTransform(x => x + 1f); // 不会抛异常
Console.WriteLine("示例 3 - 变换后仍为空,FastSum = " + empty.FastSum());
Console.WriteLine();
// 示例 4:破坏性示例(演示风险 —— 不推荐在生产中这样做)
// 注意:在 transform 中修改原 list 的结构(Add/Remove)可能导致未定义行为或异常。
var list3 = new List<float>(capacity: 4) { 1f, 2f, 3f, 4f };
Console.WriteLine("示例 4 - 破坏性示例(演示危险行为,不推荐)");
Console.WriteLine("示例 4 - 变换前: " + string.Join(", ", list3));
try
{
list3.ApplyTransform(x =>
{
// 在处理器里修改原 list(会改变底层数组),这是危险操作
if (x == 2f)
{
list3.Add(99f);
}
return x + 1f;
});
Console.WriteLine("示例 4 - 变换后(注意:行为平台/实现相关,可能不一致): " + string.Join(", ", list3));
Console.WriteLine($"示例 4 - FastSum: {list3.FastSum()}");
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine("示例 4 - 处理期间抛出异常(这是预期风险的一部分):");
Console.WriteLine(ex);
}
Console.WriteLine();
// 示例 5:大列表性能测试(简单计时)
var rand = new Random(0);
var big = new List<float>(capacity: 1_000_000);
for (int i = 0; i < 1_000_000; i++)
big.Add((float)rand.NextDouble());
Console.WriteLine("示例 5 - 大列表性能测试(1,000,000 个元素)");
var sw = System.Diagnostics.Stopwatch.StartNew();
big.ApplyTransform(x => x * 1.000001f); // 轻微变化
sw.Stop();
Console.WriteLine($"ApplyTransform 用时: {sw.ElapsedMilliseconds} ms");
sw.Restart();
var sum = big.FastSum();
sw.Stop();
Console.WriteLine($"FastSum = {sum},用时: {sw.ElapsedMilliseconds} ms");
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine("演示结束。按任意键退出。");
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
🎯 核心要点总结
- 性能提升显著:
CollectionsMarshal.AsSpan通过直接内存访问,可将List操作性能提升30-50%,特别适合大数据处理场景。 - 零内存分配:避免了
ToArray()等方法的数据拷贝,大幅减少GC压力,让程序运行更流畅。 - 使用需谨慎:获取Span后避免修改List结构,选择合适的应用场景,并进行充分的性能测试验证。
掌握CollectionsMarshal.AsSpan这个高级技巧,你就掌握了C#高性能编程的一把利剑!在处理大数据、图像处理、游戏开发等场景中,这个技术能让你的代码性能脱颖而出。
💬 互动时间:
- 你在项目中遇到过哪些List性能瓶颈?
- 除了文中提到的场景,你还想到了哪些
AsSpan的应用场景?
如果这篇文章对你有帮助,别忘了转发给更多的C#同行!让更多开发者一起掌握这个性能优化神器!🚀
#C#开发 #性能优化 #编程技巧 #NET开发 #高性能编程
本文作者:技术老小子
本文链接:
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!
目录