目录
在Python开发过程中,尤其是数据分析和科学计算领域,我们经常需要处理大量的数组数据。想象一下,你花费了几个小时训练出的机器学习模型参数,或者经过复杂计算得到的分析结果,如果程序一关闭就全部丢失,那该有多心疼!
本文将深入解析NumPy数组的存储与加载技术,从基础的二进制存储到高级的压缩优化,帮你掌握数据持久化的核心技能。无论你是刚入门的Python开发者,还是需要处理大数据的工程师,这些实战技巧都将让你的开发效率翻倍提升。
🔍 问题分析:为什么需要数组持久化?
在实际的Python开发中,我们经常遇到以下场景:
📊 数据处理场景
- 科学计算:复杂的数值计算结果需要保存
- 机器学习:训练好的模型参数要持久化存储
- 数据分析:中间处理结果需要在不同程序间共享
- 上位机开发:传感器数据需要长期存储和分析
⚡ 性能考虑
相比于Python原生的pickle或JSON格式,NumPy提供的存储方案具有以下优势:
- 速度更快:二进制格式读写效率高
- 空间更省:专门针对数值数据优化
- 兼容性好:跨平台、跨版本兼容
💡 解决方案:NumPy存储方案全览
NumPy提供了多种数组存储方案,让我们逐一分析:
🎯 方案对比表
| 方法 | 适用场景 | 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|---|---|
save/load | 单个数组存储 | 简单快速 | 只能存储单个数组 |
savez/load | 多个数组存储 | 可存储多个数组 | 文件稍大 |
savez_compressed | 大数据存储 | 压缩比高 | 存取速度稍慢 |
savetxt/loadtxt | 文本格式需求 | 人类可读 | 精度损失,文件大 |
🛠️ 代码实战:从入门到精通
📁 基础存储:save() 和 load()
Pythonimport numpy as np
# 创建测试数据
data = np.random.rand(1000, 1000)
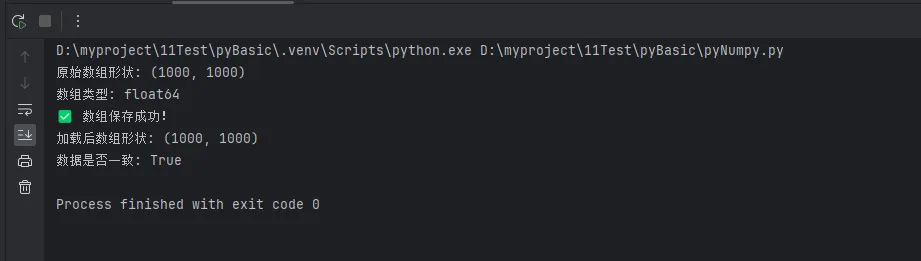
print(f"原始数组形状: {data.shape}")
print(f"数组类型: {data.dtype}")
# 保存数组到二进制文件
np.save('data.npy', data)
print("✅ 数组保存成功!")
# 加载数组
loaded_data = np.load('data.npy')
print(f"加载后数组形状: {loaded_data.shape}")
# 验证数据完整性
print(f"数据是否一致: {np.array_equal(data, loaded_data)}")
💡 实战技巧:
.npy文件是NumPy专用的二进制格式- 自动保持原数组的dtype和shape
- 读写速度比文本格式快10-100倍
🗂️ 多数组存储:savez() 和 savez_compressed()
Pythonimport numpy as np
# 创建多个不同类型的数组
train_data = np.random.rand(800, 100).astype(np.float32)
test_data = np.random.rand(200, 100).astype(np.float32)
labels = np.random.randint(0, 10, size=800)
metadata = np.array(['model_v1.0', '2024-01-15'], dtype='U20')
print("🎯 多数组存储演示")
# 方法1:savez - 未压缩存储
np.savez('dataset.npz',
train=train_data,
test=test_data,
labels=labels,
meta=metadata)
# 方法2:savez_compressed - 压缩存储
np.savez_compressed('dataset_compressed.npz',
train=train_data,
test=test_data,
labels=labels,
meta=metadata)
# 加载多数组文件
with np.load('dataset.npz') as data:
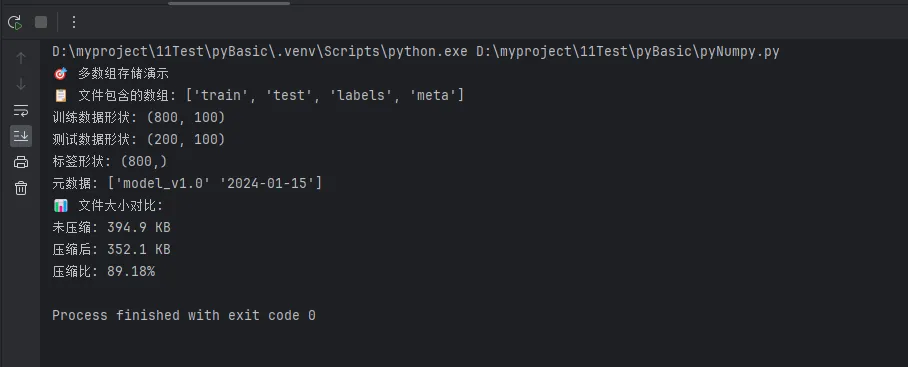
print(f"📋 文件包含的数组: {list(data.keys())}")
print(f"训练数据形状: {data['train'].shape}")
print(f"测试数据形状: {data['test'].shape}")
print(f"标签形状: {data['labels'].shape}")
print(f"元数据: {data['meta']}")
# 比较文件大小
import os
normal_size = os.path.getsize('dataset.npz')
compressed_size = os.path.getsize('dataset_compressed.npz')
print(f"📊 文件大小对比:")
print(f"未压缩: {normal_size/1024:.1f} KB")
print(f"压缩后: {compressed_size/1024:.1f} KB")
print(f"压缩比: {compressed_size/normal_size:.2%}")
📄 文本格式存储:适合数据交换
Python# 文本格式存储 - 适合小数组和数据交换
small_data = np.random.rand(10, 5)
# 保存为文本文件
np.savetxt('data.txt', small_data, fmt='%.4f', delimiter=',',
header='列1,列2,列3,列4,列5', comments='# ')
# 加载文本文件
loaded_text_data = np.loadtxt('data.txt', delimiter=',', skiprows=1)
print("📝 文本格式存储")
print("原始数据:")
print(small_data[:3])
print("加载后数据:")
print(loaded_text_data[:3])
🎯 高级应用:智能存储选择器
Pythondef smart_save(filename, *arrays, **named_arrays):
"""
智能选择最佳存储方案的函数
"""
import os
# 合并所有数组
all_arrays = list(arrays) + list(named_arrays.values())
total_size = sum(arr.nbytes for arr in all_arrays)
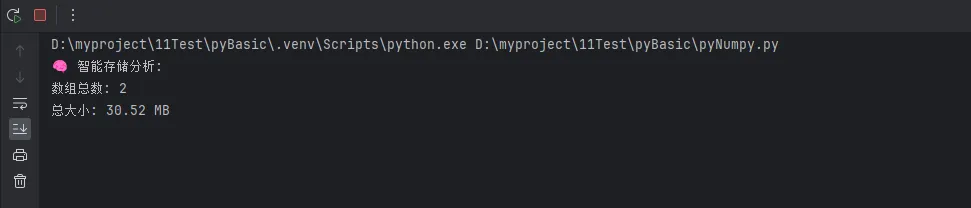
print(f"🧠 智能存储分析:")
print(f"数组总数: {len(all_arrays)}")
print(f"总大小: {total_size/1024/1024:.2f} MB")
# 根据大小和数量选择存储方案
if len(all_arrays) == 1:
# 单个数组用save
np.save(filename + '.npy', all_arrays[0])
method = "save (单数组)"
elif total_size > 10 * 1024 * 1024: # 大于10MB用压缩
if named_arrays:
np.savez_compressed(filename + '_compressed.npz', **named_arrays)
else:
np.savez_compressed(filename + '_compressed.npz', *arrays)
method = "savez_compressed (大文件压缩)"
else:
# 普通多数组存储
if named_arrays:
np.savez(filename + '.npz', **named_arrays)
else:
np.savez(filename + '.npz', *arrays)
method = "savez (多数组)"
print(f"✅ 采用方案: {method}")
return method
# 使用智能存储器
large_data = np.random.rand(2000, 2000) # 大数组
small_data = np.random.rand(10, 10) # 小数组
# 大文件测试
smart_save('big_data', train=large_data, test=small_data)
# 小文件测试
smart_save('small_data', small=small_data)
🔧 实战优化技巧
Python# 技巧1:内存映射 - 处理超大数组
def create_memory_mapped_array(filename, shape, dtype=np.float32):
"""创建内存映射数组,适合超大数据"""
return np.memmap(filename, dtype=dtype, mode='w+', shape=shape)
# 创建1GB的大数组,但不占用内存
huge_array = create_memory_mapped_array('huge_data.dat', (10000, 10000), np.float32)
huge_array[0, 0] = 42 # 只有访问时才分配内存
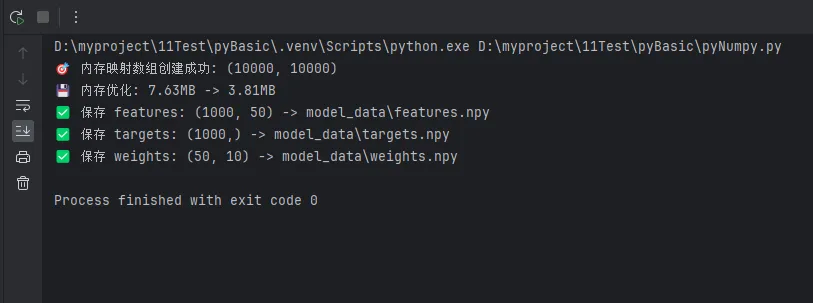
print(f"🎯 内存映射数组创建成功: {huge_array.shape}")
# 技巧2:数据类型优化
def optimize_dtype(arr):
"""自动优化数据类型以节省空间"""
if arr.dtype == np.float64:
# 检查是否可以降精度
if np.allclose(arr, arr.astype(np.float32)):
return arr.astype(np.float32)
elif arr.dtype == np.int64:
# 检查整数范围
if arr.min() >= -2**31 and arr.max() < 2**31:
return arr.astype(np.int32)
return arr
# 应用优化
original = np.random.rand(1000, 1000).astype(np.float64)
optimized = optimize_dtype(original)
print(f"💾 内存优化: {original.nbytes/1024/1024:.2f}MB -> {optimized.nbytes/1024/1024:.2f}MB")
# 技巧3:批量文件处理
def batch_save_arrays(arrays_dict, base_path):
"""批量保存多个数组文件"""
import os
os.makedirs(base_path, exist_ok=True)
for name, array in arrays_dict.items():
filepath = os.path.join(base_path, f"{name}.npy")
np.save(filepath, array)
print(f"✅ 保存 {name}: {array.shape} -> {filepath}")
# 批量保存示例
arrays_to_save = {
'features': np.random.rand(1000, 50),
'targets': np.random.randint(0, 2, 1000),
'weights': np.random.rand(50, 10)
}
batch_save_arrays(arrays_to_save, 'model_data')
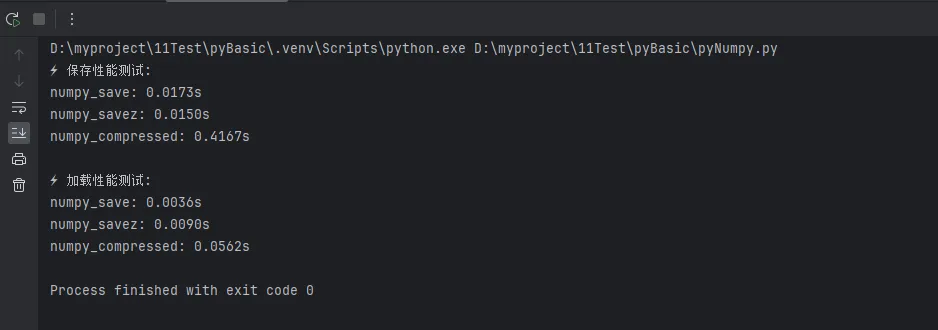
🚀 性能对比测试
Pythonimport time
def performance_test():
"""性能测试对比"""
test_data = np.random.rand(1000, 1000)
# 测试保存性能
methods = {
'numpy_save': lambda: np.save('test_save.npy', test_data),
'numpy_savez': lambda: np.savez('test_savez.npz', data=test_data),
'numpy_compressed': lambda: np.savez_compressed('test_comp.npz', data=test_data)
}
print("⚡ 保存性能测试:")
save_times = {}
for name, method in methods.items():
start_time = time.time()
method()
end_time = time.time()
save_times[name] = end_time - start_time
print(f"{name}: {save_times[name]:.4f}s")
# 测试加载性能
load_methods = {
'numpy_save': lambda: np.load('test_save.npy'),
'numpy_savez': lambda: np.load('test_savez.npz')['data'],
'numpy_compressed': lambda: np.load('test_comp.npz')['data']
}
print("\n⚡ 加载性能测试:")
for name, method in load_methods.items():
start_time = time.time()
loaded = method()
end_time = time.time()
print(f"{name}: {end_time - start_time:.4f}s")
# 运行性能测试
performance_test()
📚 最佳实践指南
✅ 推荐做法
- 选择合适的存储格式
Python# 单个数组 -> .npy
# 多个数组 -> .npz
# 大文件 -> .npz压缩
# 需要人工查看 -> .txt
- 数据完整性验证
Python# 保存后立即验证
original_data = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
np.save('verify_test.npy', original_data)
loaded_data = np.load('verify_test.npy')
assert np.array_equal(original_data, loaded_data), "数据不一致!"
- 异常处理
Pythondef safe_load(filepath):
"""安全加载数组文件"""
try:
return np.load(filepath)
except FileNotFoundError:
print(f"❌ 文件不存在: {filepath}")
return None
except Exception as e:
print(f"❌ 加载失败: {e}")
return None
❌ 常见陷阱
- 不要用文本格式存储大数组
- 不要忘记指定数据类型
- 不要在循环中频繁读写文件
- 注意跨平台的路径分隔符问题
🎯 总结:掌握数据持久化的三个关键点
通过本文的深入学习,相信你已经掌握了NumPy数组存储与加载的核心技术。让我们回顾一下三个关键要点:
- 🎯 选择合适的存储方案:根据数据规模和使用场景,灵活选择
.npy、.npz或压缩格式,让存储效率最大化。 - ⚡ 优化性能表现:通过数据类型优化、内存映射和智能压缩等技巧,显著提升读写速度和节省存储空间。
- 🛡️ 确保数据安全:建立完善的验证和异常处理机制,确保数据在存储和传输过程中的完整性。
这些Python开发和编程技巧不仅适用于数据科学项目,在上位机开发、工业自动化等领域同样大有用武之地。掌握了这些核心技能,你就能够自信地处理各种规模的数据持久化需求,让你的Python项目更加稳定可靠!
现在就开始实践这些技术吧,让数据存储不再成为你开发路上的绊脚石!
本文作者:技术老小子
本文链接:
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!
目录