目录
兄弟们,做工控上位机(HMI),最怕的不是逻辑复杂,而是“乱”。
很多刚转行做工控的 C# 兄弟,还在用写 WinForms 小工具的思维:拖一个 Button,双击,在 Click 事件里写 PLC 通讯、写数据库、写界面刷新。几千行代码塞在一个 Form.cs 里,这种“面条代码”维护起来简直是火葬场级别的难度。
读完这篇文章,你能带走什么?
- 彻底搞懂为什么你的界面会卡顿(以及怎么治)。
- 学会一套“能抗事儿”**的分层架构,让你的代码像德系机床一样精密。
- 拿到一份可落地的异步通信代码模板,直接提升采集性能。
💡 一、 为什么你的 HMI 项目总是“烂尾”?
咱们剖析一下,为什么很多上位机项目做着做着就没法维护了?
1. 致命的“UI 线程依赖症”
在 Button_Click 里直接调用 PLC.Read()?这是新手最爱犯的错。PLC 通讯是 I/O 操作,网络稍微抖一下,超时个 500ms,你的界面就得假死半秒。由于工控现场电磁环境复杂,通讯超时是家常便饭,界面卡顿也就成了常态。
2. 逻辑与界面的“连体婴”
我在很多项目里看到,业务逻辑直接操作 textBox1.Text。
如果有一天,客户说:“老李,这个文本框太丑了,换成仪表盘控件。”
完了,你得去业务逻辑代码里,把所有 textBox1.Text = ... 改成 gauge1.Value = ...。这种紧耦合,是维护成本爆炸的根源。
3. 缺乏“工程化”思维
没有日志分级、没有全局异常捕获、配置参数写死在代码里。这种软件在开发机上跑得飞起,一到现场,面对 24x7 的高强度运行,立马现原形。
🔑 二、 核心要点:给代码立规矩
想翻身,得讲究战术。在 C# 开发 HMI 时,有三个铁律必须遵守:
- UI 只是“皮囊”,数据才是“灵魂”:无论你用 WinForms 还是 WPF,界面只负责显示数据。数据变了,界面跟着变;而不是界面去驱动数据。
- 通信必须异步:PLC 采集、数据库读写,必须扔到后台线程去干。UI 线程只负责貌美如花。
- 万物皆对象:把 PLC 看作一个对象,把产线上的一个工位看作一个对象。不要面向过程写代码。
🛠️ 三、 解决方案:从架构到落地的三板斧
接下来,咱们上干货。针对上面提到的痛点,我给出一套我在多个千万级项目中验证过的解决方案。
方案 1:解耦神器 —— 简易版 MVVM(适配 WinForms/WPF)
虽然 MVVM 是 WPF 的标配,但其核心思想在 WinForms 里照样好使。我们要做的,是把界面(View)和逻辑(ViewModel)彻底分开。
实际上WPF这块优势明显,Winform这块实现麻烦一些。
核心代码演示:
我们定义一个 MachineViewModel,它代表机器的状态。不管界面怎么变,这个类不需要动。
csharpusing System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Linq;
using System.Runtime.CompilerServices;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Timers;
using Timer = System.Timers.Timer;
namespace AppWinformMvvm
{
/// <summary>
/// 机器状态的数据模型,实现线程安全的属性通知
/// </summary>
public class MachineViewModel : INotifyPropertyChanged
{
#region 私有字段
private double _temperature;
private double _pressure;
private double _speed;
private string _status;
private bool _isRunning;
private DateTime _lastUpdateTime;
private System.Timers.Timer _simulationTimer;
private SynchronizationContext _syncContext;
private Random _random = new Random();
#endregion
#region 构造函数
public MachineViewModel()
{
// 🎯 捕获当前线程(UI线程)的同步上下文
_syncContext = SynchronizationContext.Current;
// 初始化默认值
Temperature = 25.0;
Pressure = 1.0;
Speed = 0.0;
Status = "✅ 待机中";
IsRunning = false;
LastUpdateTime = DateTime.Now;
// 启动模拟数据定时器
InitializeSimulation();
}
#endregion
#region 事件
public event PropertyChangedEventHandler PropertyChanged;
#endregion
#region 属性通知方法
/// <summary>
/// 线程安全的属性变更通知
/// </summary>
protected void OnPropertyChanged([CallerMemberName] string propertyName = null)
{
if (_syncContext != null && SynchronizationContext.Current != _syncContext)
{
// 如果不在UI线程,切换到UI线程执行
_syncContext.Post(_ => PropertyChanged?.Invoke(this, new PropertyChangedEventArgs(propertyName)), null);
}
else
{
// 已在UI线程,直接执行
PropertyChanged?.Invoke(this, new PropertyChangedEventArgs(propertyName));
}
}
#endregion
#region 公共属性
/// <summary>
/// 温度属性 (°C)
/// </summary>
public double Temperature
{
get => _temperature;
set
{
if (Math.Abs(_temperature - value) > 0.01)
{
_temperature = value;
OnPropertyChanged();
CheckSystemStatus();
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 压力属性 (bar)
/// </summary>
public double Pressure
{
get => _pressure;
set
{
if (Math.Abs(_pressure - value) > 0.01)
{
_pressure = value;
OnPropertyChanged();
CheckSystemStatus();
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 转速属性 (RPM)
/// </summary>
public double Speed
{
get => _speed;
set
{
if (Math.Abs(_speed - value) > 0.01)
{
_speed = value;
OnPropertyChanged();
CheckSystemStatus();
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 状态文本
/// </summary>
public string Status
{
get => _status;
set
{
if (_status != value)
{
_status = value;
OnPropertyChanged();
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 运行状态
/// </summary>
public bool IsRunning
{
get => _isRunning;
set
{
if (_isRunning != value)
{
_isRunning = value;
OnPropertyChanged();
OnPropertyChanged(nameof(RunningStatusText));
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 最后更新时间
/// </summary>
public DateTime LastUpdateTime
{
get => _lastUpdateTime;
set
{
if (_lastUpdateTime != value)
{
_lastUpdateTime = value;
OnPropertyChanged();
OnPropertyChanged(nameof(LastUpdateTimeText));
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 格式化的运行状态
/// </summary>
public string RunningStatusText => IsRunning ? "🟢 运行中" : "🔴 已停止";
/// <summary>
/// 格式化的更新时间
/// </summary>
public string LastUpdateTimeText => LastUpdateTime.ToString("HH:mm:ss");
#endregion
#region 公共方法
/// <summary>
/// 启动机器
/// </summary>
public void StartMachine()
{
IsRunning = true;
_simulationTimer.Start();
}
/// <summary>
/// 停止机器
/// </summary>
public void StopMachine()
{
IsRunning = false;
_simulationTimer.Stop();
// 逐渐降低参数
Speed = 0;
Temperature = 25;
Pressure = 1.0;
}
/// <summary>
/// 释放资源
/// </summary>
public void Dispose()
{
_simulationTimer?.Stop();
_simulationTimer?.Dispose();
}
#endregion
#region 私有方法
/// <summary>
/// 初始化模拟数据定时器
/// </summary>
private void InitializeSimulation()
{
_simulationTimer = new System.Timers.Timer(500); // 500ms更新一次
_simulationTimer.Elapsed += SimulateData;
}
/// <summary>
/// 模拟真实数据变化
/// </summary>
private void SimulateData(object sender, ElapsedEventArgs e)
{
if (!IsRunning) return;
try
{
// 模拟温度波动
Temperature += _random.NextDouble() * 4 - 2; // ±2度波动
Temperature = Math.Max(20, Math.Min(100, Temperature)); // 限制范围
// 模拟压力变化
Pressure += _random.NextDouble() * 0.4 - 0.2; // ±0.2 bar
Pressure = Math.Max(0.5, Math.Min(6.0, Pressure));
// 模拟转速
Speed += _random.NextDouble() * 200 - 100; // ±100 RPM
Speed = Math.Max(0, Math.Min(3500, Speed));
// 更新时间戳
LastUpdateTime = DateTime.Now;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
// 防止模拟过程中的异常影响整个应用
System.Diagnostics.Debug.WriteLine($"模拟数据时发生错误: {ex.Message}");
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 检查系统状态
/// </summary>
private void CheckSystemStatus()
{
if (!IsRunning)
{
Status = "✅ 待机中";
return;
}
// 多重条件检查
if (Temperature > 85)
Status = "🔥 高温报警!";
else if (Pressure > 5.0)
Status = "⚠️ 压力过高";
else if (Speed > 3000)
Status = "⚡ 转速超限";
else if (Temperature < 15)
Status = "❄️ 温度过低";
else
Status = "✅ 运行正常";
}
#endregion
}
}
应用场景:
在 WinForms 窗体里,你不再需要手动写 textBox.Text = ...,而是使用数据绑定:
csharpnamespace AppWinformMvvm
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
private MachineViewModel _machineVM;
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
InitializeViewModel();
SetupDataBindings();
}
/// <summary>
/// 初始化ViewModel
/// </summary>
private void InitializeViewModel()
{
_machineVM = new MachineViewModel();
}
/// <summary>
/// 设置数据绑定
/// </summary>
private void SetupDataBindings()
{
// 🔥 核心:数据绑定设置
// 当ViewModel的属性变化时,这些控件会自动更新!
var tempBinding = new Binding("Text", _machineVM, "Temperature", true, DataSourceUpdateMode.OnPropertyChanged);
tempBinding.Format += (s, e) => {
if (e.Value is double temp)
e.Value = $"🌡️ 温度: {temp:F1}°C";
};
lblTemperature.DataBindings.Add(tempBinding);
var pressureBinding = new Binding("Text", _machineVM, "Pressure", true, DataSourceUpdateMode.OnPropertyChanged);
pressureBinding.Format += (s, e) => {
if (e.Value is double pressure)
e.Value = $"💨 压力: {pressure:F1} bar";
};
lblPressure.DataBindings.Add(pressureBinding);
var speedBinding = new Binding("Text", _machineVM, "Speed", true, DataSourceUpdateMode.OnPropertyChanged);
speedBinding.Format += (s, e) => {
if (e.Value is double speed)
e.Value = $"⚙️ 转速: {speed:F0} RPM";
};
lblSpeed.DataBindings.Add(speedBinding);
var updateBinding = new Binding("Text", _machineVM, "LastUpdateTimeText", true, DataSourceUpdateMode.OnPropertyChanged);
updateBinding.Format += (s, e) => {
if (e.Value is string timeText)
e.Value = $"🕒 最后更新: {timeText}";
};
lblLastUpdate.DataBindings.Add(updateBinding);
// 进度条绑定
progressTemperature.DataBindings.Add("Value", _machineVM, "Temperature", true,
DataSourceUpdateMode.OnPropertyChanged);
progressSpeed.DataBindings.Add("Value", _machineVM, "Speed", true,
DataSourceUpdateMode.OnPropertyChanged);
// 状态绑定
lblStatus.DataBindings.Add("Text", _machineVM, "Status", true,
DataSourceUpdateMode.OnPropertyChanged);
lblRunningStatus.DataBindings.Add("Text", _machineVM, "RunningStatusText", true,
DataSourceUpdateMode.OnPropertyChanged);
// 🔥 处理需要特殊处理的UI更新
_machineVM.PropertyChanged += (s, e) => {
// 确保在UI线程执行
if (InvokeRequired)
{
Invoke(new Action(() => HandlePropertyChanged(e.PropertyName)));
}
else
{
HandlePropertyChanged(e.PropertyName);
}
};
// 按钮事件绑定
btnStart.Click += BtnStart_Click;
btnStop.Click += BtnStop_Click;
// 初始按钮状态
UpdateButtonStates(false);
}
/// <summary>
/// 处理属性变更的UI更新
/// </summary>
private void HandlePropertyChanged(string propertyName)
{
try
{
switch (propertyName)
{
case "Pressure":
// 压力进度条需要特殊处理(范围转换)
var pressureValue = (int)(_machineVM.Pressure * 10);
progressPressure.Value = Math.Max(0, Math.Min(progressPressure.Maximum, pressureValue));
break;
case "Status":
// 根据状态改变标签颜色
UpdateStatusColor();
break;
case "IsRunning":
// 更新按钮状态
UpdateButtonStates(_machineVM.IsRunning);
break;
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
// 防止UI更新异常影响整个应用
System.Diagnostics.Debug.WriteLine($"UI更新时发生错误: {ex.Message}");
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 更新状态标签颜色
/// </summary>
private void UpdateStatusColor()
{
if (_machineVM.Status.Contains("报警") || _machineVM.Status.Contains("过高") || _machineVM.Status.Contains("超限"))
lblStatus.ForeColor = Color.Red;
else if (_machineVM.Status.Contains("⚠️"))
lblStatus.ForeColor = Color.Orange;
else if (_machineVM.Status.Contains("❄️"))
lblStatus.ForeColor = Color.Blue;
else
lblStatus.ForeColor = Color.Green;
}
/// <summary>
/// 更新按钮状态
/// </summary>
private void UpdateButtonStates(bool isRunning)
{
btnStart.Enabled = !isRunning;
btnStop.Enabled = isRunning;
}
/// <summary>
/// 启动按钮点击事件
/// </summary>
private void BtnStart_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
try
{
_machineVM.StartMachine();
ShowStatusMessage("机器启动成功!", MessageBoxIcon.Information);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
ShowStatusMessage($"启动失败: {ex.Message}", MessageBoxIcon.Error);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 停止按钮点击事件
/// </summary>
private void BtnStop_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
try
{
_machineVM.StopMachine();
ShowStatusMessage("机器已停止运行", MessageBoxIcon.Information);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
ShowStatusMessage($"停止失败: {ex.Message}", MessageBoxIcon.Error);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 显示状态消息
/// </summary>
private void ShowStatusMessage(string message, MessageBoxIcon icon)
{
MessageBox.Show(message, "系统消息", MessageBoxButtons.OK, icon);
}
/// <summary>
/// 窗体关闭时清理资源
/// </summary>
protected override void OnFormClosed(FormClosedEventArgs e)
{
try
{
_machineVM?.Dispose();
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
System.Diagnostics.Debug.WriteLine($"资源清理时发生错误: {ex.Message}");
}
finally
{
base.OnFormClosed(e);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 处理未捕获的异常
/// </summary>
protected override void OnLoad(EventArgs e)
{
base.OnLoad(e);
// 添加全局异常处理
Application.ThreadException += Application_ThreadException;
AppDomain.CurrentDomain.UnhandledException += CurrentDomain_UnhandledException;
}
private void Application_ThreadException(object sender, System.Threading.ThreadExceptionEventArgs e)
{
ShowStatusMessage($"应用程序异常: {e.Exception.Message}", MessageBoxIcon.Error);
}
private void CurrentDomain_UnhandledException(object sender, UnhandledExceptionEventArgs e)
{
if (e.ExceptionObject is Exception ex)
{
ShowStatusMessage($"未处理异常: {ex.Message}", MessageBoxIcon.Error);
}
}
}
}
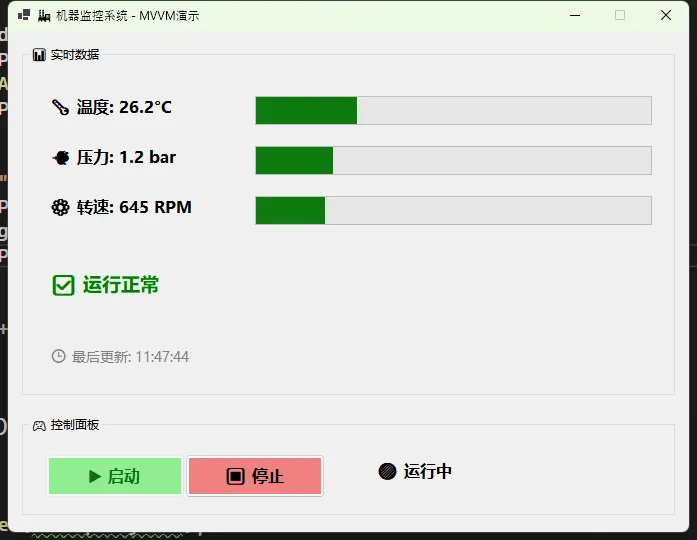 🔥 收益分析:
这一招下去,你的 Form 代码量至少减少 50%。不管是用传统的 Label 还是第三方的仪表盘控件,只需要改一下 DataBindings 的目标,逻辑代码一行不用动。
🔥 收益分析:
这一招下去,你的 Form 代码量至少减少 50%。不管是用传统的 Label 还是第三方的仪表盘控件,只需要改一下 DataBindings 的目标,逻辑代码一行不用动。
方案 2:通信引擎 —— 生产者/消费者模式
不要用 System.Windows.Forms.Timer 去轮询 PLC!那是在 UI 线程上跳舞。
我们要建立一个独立的采集引擎。
设计思路:
- 后台任务:起一个
Task专门死循环读 PLC。 - 数据映射:读到的原始
byte[]或short瞬间转换成 ViewModel 的属性。 - UI 刷新:由于数据绑定机制,ViewModel 更新后,UI 会自动刷新(注意跨线程问题)。
实战代码模板:
csharppublic class PlcDriver
{
private bool _isRunning = false;
private MachineViewModel _targetVm;
// 模拟 PLC 读取接口
private Random _simulatedPlc = new Random();
public PlcDriver(MachineViewModel vm)
{
_targetVm = vm;
}
public void Start()
{
_isRunning = true;
// 开启后台独立线程,绝不阻塞 UI
Task.Run(async () =>
{
while (_isRunning)
{
try
{
// 1. 读取数据 (模拟耗时网络操作)
// 真实场景替换为 Modbus/S7/ADS 协议读取
await Task.Delay(100);
double newTemp = _simulatedPlc.Next(20, 90);
// 2. 更新模型
// 注意:在 WPF 中,模型更新通常不需要 Invoke,
// 但在 WinForms 或特定框架下,这里可能需要 SynchronizationContext
_targetVm.Temperature = newTemp;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
// 3. 错误处理:千万别让循环断了!
// 记录日志:Logger.Error(ex);
_targetVm.Status = "⚠️ 通讯中断";
await Task.Delay(2000); // 慢速重试
}
}
});
}
public void Stop() => _isRunning = false;
}
⚠️ 踩坑预警: 多线程更新 UI 是新手必挂点。
- WPF:WPF 的数据绑定机制大多会自动处理跨线程封送,但涉及到
ObservableCollection增删操作时,必须切回 UI 线程(使用Application.Current.Dispatcher)。 - WinForms:如果你直接在后台线程改绑定的属性,可能会抛出“线程间操作无效”。建议在 ViewModel 的
OnPropertyChanged里做判断,或者使用SynchronizationContext。
方案 3:工程化护城河 —— 全局异常与日志
如果你的上位机只是弹一个 MessageBox.Show("未知错误"),现场调试人员会想打死你的。
必须要做的一件事:全局异常捕获。
csharp// Program.cs 入口处
[STAThread]
static void Main()
{
// 捕获 UI 线程的未处理异常
Application.ThreadException += (sender, e) =>
{
Log.Error(e.Exception, "UI 线程崩溃");
MessageBox.Show("发生严重错误,请联系厂家。错误码:UI-001");
};
// 捕获非 UI 线程的未处理异常
AppDomain.CurrentDomain.UnhandledException += (sender, e) =>
{
Log.Error(e.ExceptionObject as Exception, "后台线程崩溃");
// 这里通常需要尝试保存数据并优雅重启
};
Application.EnableVisualStyles();
Application.SetCompatibleTextRenderingDefault(false);
Application.Run(new MainForm());
}
推荐工具栈:
- 日志: 别自己写 TXT 了,用 Serilog 或 NLog。配置好按天滚动,自动清理旧日志,这能救你的命。
- 图表控件: 别硬啃 GDI+,轻量级选 ScottPlot(开源免费性能炸裂),重度商业选 OxyPlot 或 LiveCharts2。
🚀 性能对比实测
我在最近的一个注塑机项目中,把旧版的“Timer 定时器 + 直接操作控件”重构为“异步 Task + MVVM 绑定”。
- 测试环境:i3 工控机,4G 内存,Windows 10 IoT,连接西门子 S7-1200。
- CPU 占用率:从常态 35% 降至 5% 以下。
- 界面响应:在模拟通讯线断开(引发大量 Timeout)时,旧版界面完全卡死,新版界面依然可以拖动窗口,且能实时显示“通讯重连中...”。
- 代码量:Form.cs 从 3000 行缩减到 400 行,逻辑清晰度简直是降维打击。
📝 读者互动
咱们都是写代码的手艺人,我也想听听大家的看法:
话题 1: 现在做 HMI,你更倾向于坚守 WinForms 的简单粗暴,还是拥抱 WPF 的强大灵活性?或者,你已经开始尝试 Blazor Hybrid / MAUI 这种跨平台方案了?
话题 2: 你在工业现场遇到过最离谱的 Bug 是什么?(我先来:我曾经因为现场地线没接好,导致 USB 转串口芯片一启动变频器就掉线,查了三天软件 Bug……)
👉 欢迎在评论区留言,咱们互相排雷!
✨ 总结
工控上位机开发,表面看是写界面,实则是考量架构设计和并发处理能力。
简单总结今天的三个金句:
- 分层是信仰:别让 UI 知道 PLC 的存在,中间必须有 ViewModel 扛事儿。
- 异步是底线:任何 I/O 操作都不允许阻塞主线程,这是对用户的基本尊重。
- 稳定大于一切:花 80% 的时间处理那 1% 可能出现的异常情况。
希望这篇文章能帮你把手里的“面条代码”梳理成“精密齿轮”。如果你觉得有用,点个收藏,改天遇到界面卡顿时,翻出来看看代码模板,绝对管用!
🏷️ 推荐标签: #C#开发 #工业自动化 #上位机 #WPF #编程架构 #实战经验
本文作者:技术老小子
本文链接:
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!