目录
还在为每个控件手写事件处理代码而头疼吗?还在用textBox1.Text = user.Name这样的方式更新界面吗?如果你正从WinForm向WPF转型,那么数据绑定将是你遇到的第一个重大思维转变。
在WinForm中,我们习惯了命令式编程:告诉程序"怎么做";而在WPF中,数据绑定让我们转向声明式编程:告诉程序"做什么"。这不仅仅是语法的改变,更是开发思维的根本性转变。本文将带你从零开始理解WPF数据绑定的核心概念,让你的界面开发从此告别繁琐的手工代码。
💡 WinForm vs WPF:数据展示方式的根本差异
🔍 WinForm的痛点分析
在WinForm中,我们通常这样处理数据展示:
c#// WinForm中的传统做法
public partial class FrmUser : Form
{
private User currentUser;
public void DisplayUser(User user)
{
currentUser = user;
textBoxName.Text = user.Name;
textBoxEmail.Text = user.Email;
textBoxAge.Text = user.Age.ToString();
// 如果数据变化,需要手动更新,实际winform业务中我基本不这么做,费不了这事
user.PropertyChanged += (s, e) =>
{
switch(e.PropertyName)
{
case "Name":
textBoxName.Text = user.Name;
break;
case "Email":
textBoxEmail.Text = user.Email;
break;
// ... 更多重复代码
}
};
}
private void textBoxName_TextChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// 反向更新数据
currentUser.Name = textBoxName.Text;
}
}
问题显而易见:
- 大量重复的赋值代码
- 双向同步需要手写事件处理
- 界面逻辑与业务逻辑耦合严重
- 维护成本高,容易出错
Winform在属性绑定上是先天不足的。
✨ WPF数据绑定的优雅解决方案
让我们看看WPF是如何优雅地解决这个问题的:
xml<!-- WPF中的XAML -->
<Grid>
<StackPanel Margin="20">
<TextBox Text="{Binding Name, Mode=TwoWay}" />
<TextBox Text="{Binding Email, Mode=TwoWay}" />
<TextBox Text="{Binding Age, Mode=TwoWay}" />
</StackPanel>
</Grid>
c#using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Linq;
using System.Runtime.CompilerServices;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace AppDataBind
{
public class User : INotifyPropertyChanged
{
private string _name;
public string Name
{
get => _name;
set { _name = value; OnPropertyChanged(); }
}
private string _email;
public string Email
{
get => _email;
set { _email = value; OnPropertyChanged(); }
}
private int _age;
public int Age
{
get => _age;
set { _age = value; OnPropertyChanged(); }
}
public event PropertyChangedEventHandler PropertyChanged;
protected void OnPropertyChanged([CallerMemberName] string name = null)
{
PropertyChanged?.Invoke(this, new PropertyChangedEventArgs(name));
}
}
}
立即看到的好处:
- XAML中一行代码搞定双向绑定
- 数据变更自动同步到界面
- 界面变更自动同步到数据
- 代码简洁,逻辑清晰
🔥 数据绑定的核心概念深度解析
📊 1. 绑定表达式语法详解
xml<Window x:Class="AppDataBind.Window1"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:AppDataBind"
mc:Ignorable="d"
Title="音量控制面板" Height="600" Width="900"
Background="#F5F5F5"
WindowStartupLocation="CenterScreen">
<Window.Resources>
<Style x:Key="TitleTextStyle" TargetType="TextBlock">
<Setter Property="FontSize" Value="24"/>
<Setter Property="FontWeight" Value="Bold"/>
<Setter Property="Foreground" Value="#2C3E50"/>
<Setter Property="Margin" Value="0,0,0,20"/>
</Style>
<Style x:Key="LabelTextStyle" TargetType="TextBlock">
<Setter Property="FontSize" Value="14"/>
<Setter Property="Foreground" Value="#34495E"/>
<Setter Property="Margin" Value="0,0,0,10"/>
</Style>
<Style x:Key="ValueTextStyle" TargetType="TextBlock">
<Setter Property="FontSize" Value="18"/>
<Setter Property="FontWeight" Value="Bold"/>
<Setter Property="Foreground" Value="#3498DB"/>
<Setter Property="Margin" Value="0,8,0,0"/>
</Style>
</Window.Resources>
<StackPanel Margin="40" VerticalAlignment="Top">
<TextBlock Text="🔊 音量控制面板" Style="{StaticResource TitleTextStyle}"/>
<Border Background="White" CornerRadius="10" Padding="30"
BorderBrush="#E0E0E0" BorderThickness="1" Margin="0,0,0,20">
<StackPanel>
<TextBlock Text="音量调节" Style="{StaticResource LabelTextStyle}"/>
<Border Background="#ECEFF1" CornerRadius="8" Padding="15" Margin="0,0,0,15">
<StackPanel>
<Slider x:Name="VolumeSlider"
Minimum="0"
Maximum="100"
Value="50"
TickFrequency="10"
IsSnapToTickEnabled="True"
Height="40"
Margin="0,0,0,10"
Foreground="#3498DB"/>
<StackPanel Orientation="Horizontal" HorizontalAlignment="Center">
<TextBlock Text="0" Width="40" TextAlignment="Left" FontSize="11" Foreground="#7F8C8D"/>
<TextBlock Text="25" Width="40" TextAlignment="Center" FontSize="11" Foreground="#7F8C8D"/>
<TextBlock Text="50" Width="40" TextAlignment="Center" FontSize="11" Foreground="#7F8C8D"/>
<TextBlock Text="75" Width="40" TextAlignment="Center" FontSize="11" Foreground="#7F8C8D"/>
<TextBlock Text="100" Width="40" TextAlignment="Right" FontSize="11" Foreground="#7F8C8D"/>
</StackPanel>
</StackPanel>
</Border>
<TextBlock Text="{Binding ElementName=VolumeSlider, Path=Value, StringFormat=当前音量:{0:F0}%}"
Style="{StaticResource ValueTextStyle}"/>
<StackPanel Orientation="Horizontal" Margin="0,15,0,0">
<TextBlock Text="音量等级:" Style="{StaticResource LabelTextStyle}" Margin="0,0,10,0"/>
<TextBlock x:Name="VolumeLevel" FontSize="14" FontWeight="Bold"
Foreground="#27AE60"/>
</StackPanel>
<Separator Margin="0,20,0,20" Background="#BDC3C7" Height="2"/>
<Grid>
<Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<ColumnDefinition Width="*"/>
<ColumnDefinition Width="*"/>
<ColumnDefinition Width="*"/>
</Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<StackPanel Grid.Column="0">
<TextBlock Text="最小值" Style="{StaticResource LabelTextStyle}"/>
<TextBlock Text="{Binding ElementName=VolumeSlider, Path=Minimum}"
FontSize="16" FontWeight="Bold" Foreground="#E74C3C"/>
</StackPanel>
<StackPanel Grid.Column="1" HorizontalAlignment="Center">
<TextBlock Text="当前值" Style="{StaticResource LabelTextStyle}" HorizontalAlignment="Center"/>
<TextBlock Text="{Binding ElementName=VolumeSlider, Path=Value, StringFormat={}{0:F0}}"
FontSize="16" FontWeight="Bold" Foreground="#3498DB" HorizontalAlignment="Center"/>
</StackPanel>
<StackPanel Grid.Column="2" HorizontalAlignment="Right">
<TextBlock Text="最大值" Style="{StaticResource LabelTextStyle}" HorizontalAlignment="Right"/>
<TextBlock Text="{Binding ElementName=VolumeSlider, Path=Maximum}"
FontSize="16" FontWeight="Bold" Foreground="#27AE60" HorizontalAlignment="Right"/>
</StackPanel>
</Grid>
<StackPanel Orientation="Horizontal" Margin="0,20,0,0" Height="40">
<Button Content="静音" Width="100" Margin="0,0,10,0"
Click="MuteButton_Click" Background="#E74C3C" Foreground="White"
FontSize="12" FontWeight="Bold"/>
<Button Content="重置为50%" Width="120" Margin="0,0,10,0"
Click="ResetButton_Click" Background="#3498DB" Foreground="White"
FontSize="12" FontWeight="Bold"/>
<Button Content="最大音量" Width="100"
Click="MaxButton_Click" Background="#27AE60" Foreground="White"
FontSize="12" FontWeight="Bold"/>
</StackPanel>
<TextBlock Text="音量调节历史" Style="{StaticResource LabelTextStyle}" Margin="0,20,0,10"/>
<ListBox x:Name="VolumeHistory" Height="100" Background="#F8F9FA"
BorderBrush="#BDC3C7" BorderThickness="1" Padding="10"/>
</StackPanel>
</Border>
</StackPanel>
</Window>
c#using System;
using System.Windows;
using System.Windows.Controls;
namespace AppDataBind
{
public partial class Window1 : Window
{
private double _previousVolume = 50;
public Window1()
{
InitializeComponent();
VolumeSlider.ValueChanged += VolumeSlider_ValueChanged;
UpdateVolumeLevel();
VolumeHistory.Items.Add($"[{DateTime.Now:HH:mm:ss}] 初始音量:50%");
}
private void VolumeSlider_ValueChanged(object sender, RoutedPropertyChangedEventArgs<double> e)
{
UpdateVolumeLevel();
AddToHistory();
}
private void UpdateVolumeLevel()
{
double volume = VolumeSlider.Value;
string level;
if (volume == 0)
level = "🔇 已静音";
else if (volume < 30)
level = "🔈 低音量";
else if (volume < 70)
level = "🔉 中等音量";
else
level = "🔊 高音量";
VolumeLevel.Text = level;
}
private void AddToHistory()
{
string record = $"[{DateTime.Now:HH:mm:ss}] 音量:{VolumeSlider.Value:F0}%";
if (VolumeHistory.Items.Count > 10)
VolumeHistory.Items.RemoveAt(0);
VolumeHistory.Items.Add(record);
VolumeHistory.ScrollIntoView(VolumeHistory.Items[VolumeHistory.Items.Count - 1]);
}
private void MuteButton_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
if (VolumeSlider.Value > 0)
{
_previousVolume = VolumeSlider.Value;
VolumeSlider.Value = 0;
}
else
{
VolumeSlider.Value = _previousVolume;
}
}
private void ResetButton_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
VolumeSlider.Value = 50;
}
private void MaxButton_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
VolumeSlider.Value = 100;
}
}
}
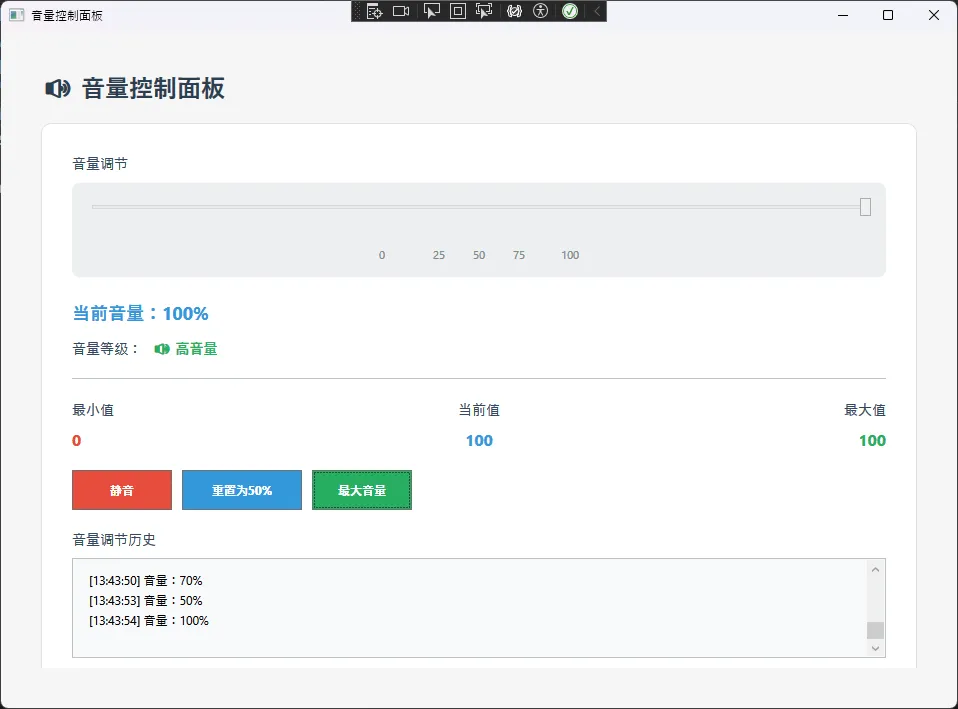
🎛️ 2. 绑定模式完全指南
c#public enum BindingMode
{
OneWay, // 单向:源→目标
TwoWay, // 双向:源↔目标
OneTime, // 一次性:源→目标(仅初始化时)
OneWayToSource, // 反向:目标→源
Default // 使用目标属性的默认模式
}
实战示例:
xml<Window x:Class="AppDataBind.Window2"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:AppDataBind"
mc:Ignorable="d"
Title="Window2" Height="450" Width="800">
<StackPanel Margin="10">
<TextBlock Text="WPF 数据绑定模式完整示例"
FontSize="20" FontWeight="Bold" Margin="0,0,0,20"/>
<!-- OneWay:只显示数据,用户不能编辑 -->
<Border BorderBrush="#CCCCCC" BorderThickness="1" Padding="15" Margin="0,0,0,15" Background="#F5F5F5">
<StackPanel>
<TextBlock Text="OneWay:只读模式" FontSize="14" FontWeight="Bold" Foreground="#0078D4"/>
<TextBlock Text="(数据从源到目标,单向流动)" FontSize="11" Foreground="#666"/>
<TextBlock Text="{Binding CreateTime, Mode=OneWay, StringFormat='创建时间: {0:yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss}'}"
FontSize="12" Margin="0,10,0,0" Foreground="#333"/>
</StackPanel>
</Border>
<!-- TwoWay:用户可以编辑,数据双向同步 -->
<Border BorderBrush="#CCCCCC" BorderThickness="1" Padding="15" Margin="0,0,0,15" Background="#F5F5F5">
<StackPanel>
<TextBlock Text="TwoWay:双向模式" FontSize="14" FontWeight="Bold" Foreground="#0078D4"/>
<TextBlock Text="(数据双向同步,用户编辑自动更新源)" FontSize="11" Foreground="#666"/>
<TextBlock Text="用户名:" Margin="0,10,0,5"/>
<TextBox Text="{Binding UserName, Mode=TwoWay, UpdateSourceTrigger=PropertyChanged}"
Padding="8" FontSize="12" Height="35"/>
<TextBlock Text="{Binding UserName, StringFormat='当前输入: {0}'}"
FontSize="11" Margin="0,5,0,0" Foreground="#666"/>
</StackPanel>
</Border>
<!-- OneTime:静态显示,性能最佳 -->
<Border BorderBrush="#CCCCCC" BorderThickness="1" Padding="15" Margin="0,0,0,15" Background="#F5F5F5">
<StackPanel>
<TextBlock Text="OneTime:一次性模式" FontSize="14" FontWeight="Bold" Foreground="#0078D4"/>
<TextBlock Text="(只在初始化时绑定一次,性能最佳)" FontSize="11" Foreground="#666"/>
<TextBlock Text="{Binding Version, Mode=OneTime, StringFormat='版本: {0}'}"
FontSize="12" Margin="0,10,0,0" Foreground="#333"/>
</StackPanel>
</Border>
<!-- OneWayToSource:用于输入控件更新源数据 -->
<Border BorderBrush="#CCCCCC" BorderThickness="1" Padding="15" Margin="0,0,0,15" Background="#F5F5F5">
<StackPanel>
<TextBlock Text="OneWayToSource:反向单向模式" FontSize="14" FontWeight="Bold" Foreground="#0078D4"/>
<TextBlock Text="(数据从目标到源,目标修改更新源)" FontSize="11" Foreground="#666"/>
<TextBlock Text="音量控制:" Margin="0,10,0,5"/>
<Slider Value="{Binding Volume, Mode=OneWayToSource, UpdateSourceTrigger=PropertyChanged}"
Minimum="0" Maximum="100" Height="30" Margin="0,5,0,5"/>
<TextBlock Text="{Binding Volume, StringFormat='当前音量: {0}%'}"
FontSize="11" Foreground="#666"/>
</StackPanel>
</Border>
</StackPanel>
</Window>
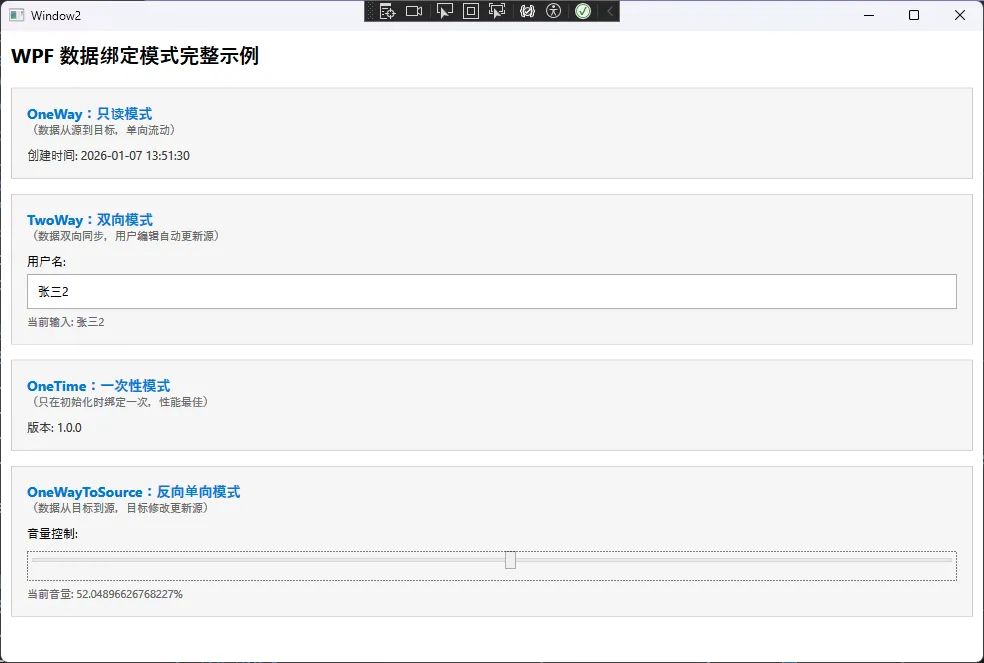
🔄 3. 值转换器:数据的"翻译官"
当数据类型与显示需求不匹配时,值转换器就派上用场了:
c#// 布尔值到可见性转换器
public class BoolToVisibilityConverter : IValueConverter
{
public object Convert(object value, Type targetType, object parameter, CultureInfo culture)
{
if (value is bool boolValue)
return boolValue ? Visibility.Visible : Visibility.Collapsed;
return Visibility.Collapsed;
}
public object ConvertBack(object value, Type targetType, object parameter, CultureInfo culture)
{
return value is Visibility visibility && visibility == Visibility.Visible;
}
}
// 年龄到描述转换器
public class AgeToDescriptionConverter : IValueConverter
{
public object Convert(object value, Type targetType, object parameter, CultureInfo culture)
{
if (value is int age)
{
return age switch
{
< 18 => "未成年",
< 60 => "成年人",
_ => "老年人"
};
}
return "未知";
}
public object ConvertBack(object value, Type targetType, object parameter, CultureInfo culture)
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
}
在XAML中使用:
xml<Window x:Class="AppDataBind.Window3"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:AppDataBind"
mc:Ignorable="d"
Title="Window3" Height="450" Width="800">
<Window.Resources>
<local:BoolToVisibilityConverter x:Key="BoolToVisConverter" />
<local:AgeToDescriptionConverter x:Key="AgeToDescConverter" />
</Window.Resources>
<StackPanel Margin="20" VerticalAlignment="Top">
<TextBlock Text="WPF 转换器完整示例" FontSize="20" FontWeight="Bold" Margin="0,0,0,20"/>
<GroupBox Header="1. 布尔值控制可见性" Padding="10" Margin="0,0,0,20">
<StackPanel>
<CheckBox Content="启用编辑" IsChecked="{Binding IsEditable}" Margin="0,0,0,10"/>
<Button Content="编辑"
Background="#4CAF50"
Foreground="White"
Padding="10,8"
Visibility="{Binding IsEditable, Converter={StaticResource BoolToVisConverter}}"
Click="EditButton_Click"
Margin="0,0,0,5"/>
</StackPanel>
</GroupBox>
<GroupBox Header="2. 年龄到描述转换" Padding="10" Margin="0,0,0,20">
<StackPanel>
<StackPanel Orientation="Horizontal" Margin="0,0,0,10">
<TextBlock Text="年龄: " Width="60"/>
<TextBox Text="{Binding Age, UpdateSourceTrigger=PropertyChanged}"
Width="100" Padding="5"/>
</StackPanel>
<StackPanel Orientation="Horizontal">
<TextBlock Text="分类: " Width="60"/>
<TextBlock Text="{Binding Age, Converter={StaticResource AgeToDescConverter}}"
FontWeight="Bold"
Foreground="#2196F3"
Width="100"/>
</StackPanel>
<TextBlock Margin="0,10,0,0" TextWrapping="Wrap" FontSize="12" Foreground="#666">
<Run Text="年龄分类规则: "/>
<LineBreak/>
<Run Text="• 0-17: 未成年" Foreground="#FF9800"/>
<LineBreak/>
<Run Text="• 18-59: 成年人" Foreground="#4CAF50"/>
<LineBreak/>
<Run Text="• 60+: 老年人" Foreground="#F44336"/>
</TextBlock>
</StackPanel>
</GroupBox>
<GroupBox Header="3. 综合示例" Padding="10">
<Grid>
<Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<ColumnDefinition Width="Auto"/>
<ColumnDefinition Width="*"/>
</Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<Grid.RowDefinitions>
<RowDefinition Height="Auto"/>
<RowDefinition Height="Auto"/>
</Grid.RowDefinitions>
<TextBlock Text="姓名: " Grid.Row="0" Grid.Column="0" VerticalAlignment="Center"/>
<TextBlock Text="{Binding Name}" Grid.Row="0" Grid.Column="1"
Margin="10,0" VerticalAlignment="Center"/>
<TextBlock Text="状态: " Grid.Row="1" Grid.Column="0" VerticalAlignment="Center" Margin="0,10,0,0"/>
<TextBlock Text="{Binding Age, Converter={StaticResource AgeToDescConverter}}"
Grid.Row="1" Grid.Column="1"
Margin="10,10,0,0"
Foreground="#2196F3"
FontWeight="Bold"/>
</Grid>
</GroupBox>
</StackPanel>
</Window>
📈 高级数据绑定实战场景
🗂️ 1. 集合绑定:列表数据的完美展示
c#using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Collections.ObjectModel;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Linq;
using System.Runtime.CompilerServices;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows;
using System.Windows.Input;
namespace AppDataBind
{
public class UserListViewModel : INotifyPropertyChanged
{
private ObservableCollection<User> _users;
public ObservableCollection<User> Users
{
get => _users;
set { _users = value; OnPropertyChanged(); }
}
private User _selectedUser;
public User SelectedUser
{
get => _selectedUser;
set { _selectedUser = value; OnPropertyChanged(); }
}
public ICommand AddUserCommand { get; }
public ICommand DeleteUserCommand { get; }
public ICommand SaveUserCommand { get; }
public UserListViewModel()
{
Users = new ObservableCollection<User>
{
new User { Name = "张三", Age = 25, Email = "zhangsan@example.com" },
new User { Name = "李四", Age = 30, Email = "lisi@example.com" },
new User { Name = "王五", Age = 28, Email = "wangwu@example.com" }
};
// 初始化命令
AddUserCommand = new RelayCommand(_ => AddUser());
DeleteUserCommand = new RelayCommand(_ => DeleteUser(), _ => SelectedUser != null);
SaveUserCommand = new RelayCommand(_ => SaveUser());
}
private void AddUser()
{
var newUser = new User { Name = "新用户", Age = 0, Email = "" };
Users.Add(newUser);
SelectedUser = newUser;
}
private void DeleteUser()
{
if (SelectedUser != null)
{
Users.Remove(SelectedUser);
SelectedUser = null;
}
}
private void SaveUser()
{
// 这里可以添加保存逻辑,例如数据库操作
MessageBox.Show("用户信息已保存!");
}
public event PropertyChangedEventHandler PropertyChanged;
protected void OnPropertyChanged([CallerMemberName] string name = null)
{
PropertyChanged?.Invoke(this, new PropertyChangedEventArgs(name));
}
}
}
xml<Window x:Class="AppDataBind.Window4"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:AppDataBind"
mc:Ignorable="d"
Title="Window4" Height="450" Width="800">
<Window.Resources>
<Style TargetType="TextBox">
<Setter Property="Margin" Value="0,5"/>
<Setter Property="Padding" Value="8"/>
<Setter Property="Height" Value="35"/>
<Setter Property="VerticalAlignment" Value="Top"/>
</Style>
<Style TargetType="Label">
<Setter Property="FontSize" Value="14"/>
<Setter Property="Margin" Value="0,10,0,0"/>
</Style>
</Window.Resources>
<Grid>
<Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<ColumnDefinition Width="300"/>
<ColumnDefinition Width="*"/>
</Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<StackPanel Grid.Column="0" Background="White">
<Label Content="用户列表" FontSize="16" FontWeight="Bold" Margin="10"/>
<ListBox Grid.Column="0"
ItemsSource="{Binding Users}"
SelectedItem="{Binding SelectedUser}"
DisplayMemberPath="Name"
Margin="10,0,10,10"
Height="300"
BorderThickness="1"
BorderBrush="#E0E0E0"/>
<StackPanel Orientation="Horizontal" Margin="10" HorizontalAlignment="Center">
<Button Content="添加"
Command="{Binding AddUserCommand}"
Width="80" Height="35" Margin="5"/>
<Button Content="删除"
Command="{Binding DeleteUserCommand}"
Width="80" Height="35" Margin="5"/>
</StackPanel>
</StackPanel>
<StackPanel Grid.Column="1" Margin="20" DataContext="{Binding SelectedUser}">
<Label Content="用户详细信息" FontSize="16" FontWeight="Bold"/>
<Label Content="姓名"/>
<TextBox Text="{Binding Name, Mode=TwoWay, UpdateSourceTrigger=PropertyChanged}"
Foreground="Black"/>
<Label Content="年龄"/>
<TextBox Text="{Binding Age, Mode=TwoWay, UpdateSourceTrigger=PropertyChanged}"
Foreground="Black"/>
<Label Content="邮箱"/>
<TextBox Text="{Binding Email, Mode=TwoWay, UpdateSourceTrigger=PropertyChanged}"
Foreground="Black"/>
<StackPanel Orientation="Horizontal" Margin="0,20,0,0">
<Button Content="保存"
Command="{Binding DataContext.SaveUserCommand, RelativeSource={RelativeSource AncestorType=Window}}"
Width="100" Height="40"/>
</StackPanel>
</StackPanel>
</Grid>
</Window>
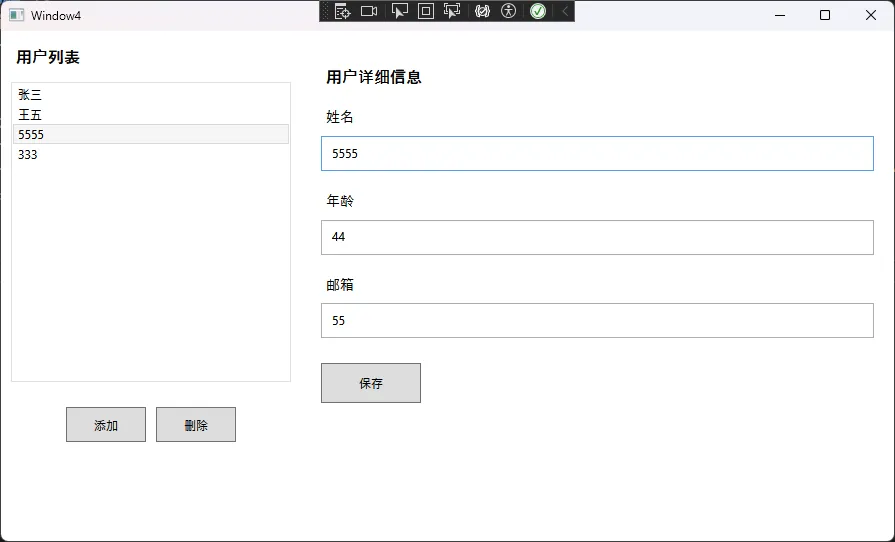
⚠️ 常见坑点:
- 使用
ObservableCollection而不是List,否则界面不会自动更新 - 绑定集合项的属性时,确保项目类实现了
INotifyPropertyChanged
🎨 2. 数据模板:自定义数据展示
xml<Window x:Class="AppDataBind.Window5"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:AppDataBind"
mc:Ignorable="d"
Title="Window5" Height="450" Width="800">
<Window.Resources>
<local:AgeToDescConverter x:Key="AgeToDescConverter"/>
<DataTemplate x:Key="UserTemplate">
<Border Background="#F0F0F0" CornerRadius="5" Padding="10" Margin="5">
<StackPanel>
<TextBlock Text="{Binding Name}"
FontWeight="Bold"
FontSize="16"
Margin="0,0,0,5"/>
<TextBlock Text="{Binding Email}"
Foreground="Gray"
Margin="0,0,0,5"/>
<StackPanel Orientation="Horizontal">
<TextBlock Text="年龄:" FontSize="14"/>
<TextBlock Text="{Binding Age}" FontSize="14"/>
<TextBlock Text="{Binding Age, Converter={StaticResource AgeToDescConverter}}"
Foreground="Blue"
Margin="10,0,0,0"
FontSize="14"/>
</StackPanel>
</StackPanel>
</Border>
</DataTemplate>
</Window.Resources>
<Grid>
<StackPanel Orientation="Vertical" Margin="20">
<TextBlock Text="用户列表"
FontSize="24"
FontWeight="Bold"
Margin="0,0,0,20"/>
<ListBox ItemsSource="{Binding Users}"
ItemTemplate="{StaticResource UserTemplate}"
BorderBrush="#CCCCCC"
BorderThickness="1"
/>
</StackPanel>
</Grid>
</Window>
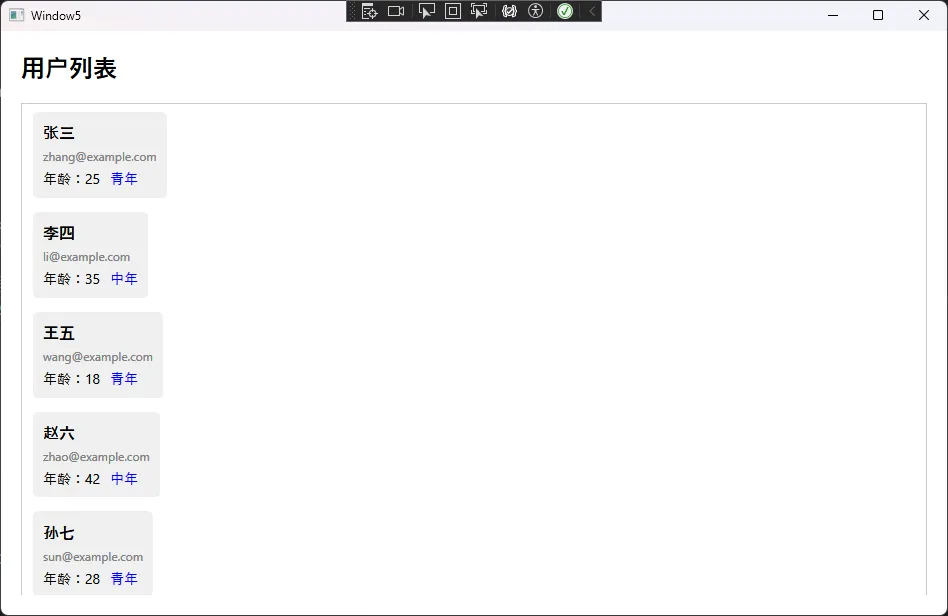
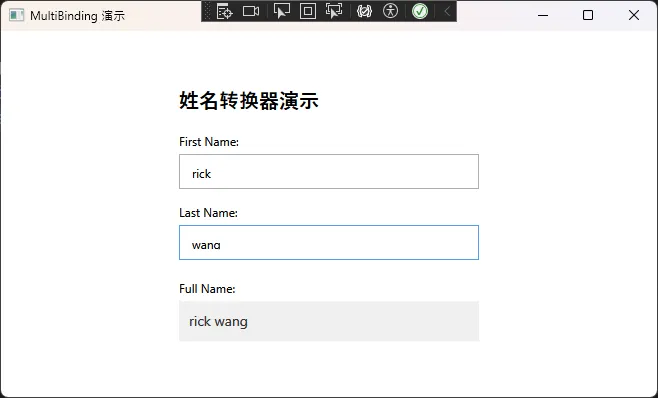
🔍 3. 多重绑定:组合多个数据源
c#public class FullNameConverter : IMultiValueConverter
{
public object Convert(object[] values, Type targetType, object parameter, CultureInfo culture)
{
if (values.Length >= 2 && values[0] is string firstName && values[1] is string lastName)
{
return $"{firstName} {lastName}";
}
return string.Empty;
}
public object[] ConvertBack(object value, Type[] targetTypes, object parameter, CultureInfo culture)
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
}
xml<Window x:Class="AppDataBind.Window6"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:AppDataBind"
mc:Ignorable="d"
Title="MultiBinding 演示"
Height="300"
Width="600"
WindowStartupLocation="CenterScreen">
<Window.Resources>
<local:FullNameConverter x:Key="FullNameConverter"/>
</Window.Resources>
<StackPanel VerticalAlignment="Center" HorizontalAlignment="Center" Width="300">
<TextBlock Text="姓名转换器演示" FontSize="20" FontWeight="Bold" Margin="0,0,0,20"/>
<TextBlock Text="First Name:" Margin="0,0,0,5"/>
<TextBox x:Name="FirstNameTextBox" Height="35" Padding="10" Margin="0,0,0,15"/>
<TextBlock Text="Last Name:" Margin="0,0,0,5"/>
<TextBox x:Name="LastNameTextBox" Height="35" Padding="10" Margin="0,0,0,20"/>
<TextBlock Text="Full Name:" Margin="0,0,0,5"/>
<TextBlock Height="40"
Background="#F0F0F0"
Padding="10"
VerticalAlignment="Center"
FontSize="14"
Foreground="#333">
<TextBlock.Text>
<MultiBinding Converter="{StaticResource FullNameConverter}">
<Binding ElementName="FirstNameTextBox" Path="Text"/>
<Binding ElementName="LastNameTextBox" Path="Text"/>
</MultiBinding>
</TextBlock.Text>
</TextBlock>
</StackPanel>
</Window>
🎉 总结:拥抱数据绑定的新世界
通过本文的深入讲解,相信你已经对WPF数据绑定有了全面的认识。让我们回顾三个核心要点:
🔑 核心要点1:思维转换
从WinForm的命令式编程转向WPF的声明式编程,让数据自动驱动界面更新,告别手工同步代码。
🔑 核心要点2:技术掌握
熟练掌握绑定语法、绑定模式、值转换器等核心技术,能够应对90%的实际开发场景。
🔑 核心要点3:最佳实践
遵循MVVM模式,注重性能优化和内存管理,编写可维护的高质量代码。
数据绑定不仅仅是WPF的一个功能特性,更是一种全新的开发范式。掌握了它,你的WPF开发效率将得到质的飞跃。从今天开始,让数据绑定成为你WPF开发的得力助手吧!
💬 互动时刻
- 你在从WinForm转WPF的过程中,遇到了哪些数据绑定的难点?
- 在实际项目中,你是如何平衡绑定的便利性和性能要求的?
💡 金句总结
- "数据绑定让界面开发从体力活变成了脑力活"
- "好的绑定设计让代码自解释,坏的绑定设计让人看不懂"
- "MVVM不是银弹,但数据绑定确实是WPF的灵魂"
觉得这篇文章对你有帮助?请转发给更多正在学习WPF的同行,让更多开发者受益!关注我们,获取更多C#开发实战技巧。
本文作者:技术老小子
本文链接:
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!