目录
在多线程和多进程编程中,同步是一个至关重要的概念。本文将详细探讨C#中的进程内同步和进程间同步,并提供丰富的示例来说明这两种同步机制的应用。
进程内同步
进程内同步是指在单个进程内部,多个线程之间协调对共享资源的访问。这种同步机制主要用于防止竞态条件,确保数据的一致性和完整性。
常用的进程内同步机制
C#提供了多种进程内同步机制,包括:
- lock关键字(Monitor类的语法糖)
- Mutex
- Semaphore和SemaphoreSlim
- ReaderWriterLockSlim
让我们通过一些例子来详细了解这些机制。
使用lock关键字
lock关键字是C#中最常用的同步机制之一,它实际上是Monitor类的语法糖。
C#using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace AppProcessSynchronization
{
public class BankAccount
{
private decimal balance;
private readonly object lockObject = new object(); // 使用 readonly 更安全
private string accountNumber;
public BankAccount(string accountNumber, decimal initialBalance = 0)
{
if (string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(accountNumber))
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(accountNumber));
if (initialBalance < 0)
throw new ArgumentException("Initial balance cannot be negative.", nameof(initialBalance));
this.accountNumber = accountNumber;
this.balance = initialBalance;
}
// 只读属性获取余额
public decimal Balance
{
get
{
lock (lockObject)
{
return balance;
}
}
}
public string AccountNumber => accountNumber;
public void Deposit(decimal amount)
{
if (amount <= 0)
throw new ArgumentException("Deposit amount must be positive.", nameof(amount));
lock (lockObject)
{
checked // 检查是否发生算术溢出
{
balance += amount;
}
}
}
public bool Withdraw(decimal amount)
{
if (amount <= 0)
throw new ArgumentException("Withdrawal amount must be positive.", nameof(amount));
lock (lockObject)
{
if (balance >= amount)
{
balance -= amount;
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
// 转账方法
public bool Transfer(BankAccount targetAccount, decimal amount)
{
if (targetAccount == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(targetAccount));
if (amount <= 0)
throw new ArgumentException("Transfer amount must be positive.", nameof(amount));
// 防止死锁:始终按照相同的顺序获取锁
BankAccount firstLock = this.accountNumber.CompareTo(targetAccount.accountNumber) < 0 ? this : targetAccount;
BankAccount secondLock = this.accountNumber.CompareTo(targetAccount.accountNumber) < 0 ? targetAccount : this;
lock (firstLock.lockObject)
{
lock (secondLock.lockObject)
{
if (balance >= amount)
{
balance -= amount;
targetAccount.balance += amount;
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
}
// 打印账户信息
public override string ToString()
{
return $"Account {accountNumber}: Balance = {Balance:C}";
}
}
}
C#namespace AppProcessSynchronization
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 创建两个账户
var account1 = new BankAccount("ACC001", 1000);
var account2 = new BankAccount("ACC002", 500);
// 启动多个线程进行操作
var tasks = new List<Task>();
// 存款操作
tasks.Add(Task.Run(() =>
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
account1.Deposit(100);
Thread.Sleep(100); // 模拟操作延迟
}
}));
// 取款操作
tasks.Add(Task.Run(() =>
{
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
account1.Withdraw(200);
Thread.Sleep(100);
}
}));
// 转账操作
tasks.Add(Task.Run(() =>
{
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++)
{
account1.Transfer(account2, 150);
Thread.Sleep(100);
}
}));
// 等待所有操作完成
Task.WaitAll(tasks.ToArray());
// 打印最终结果
Console.WriteLine(account1.ToString());
Console.WriteLine(account2.ToString());
}
}
}
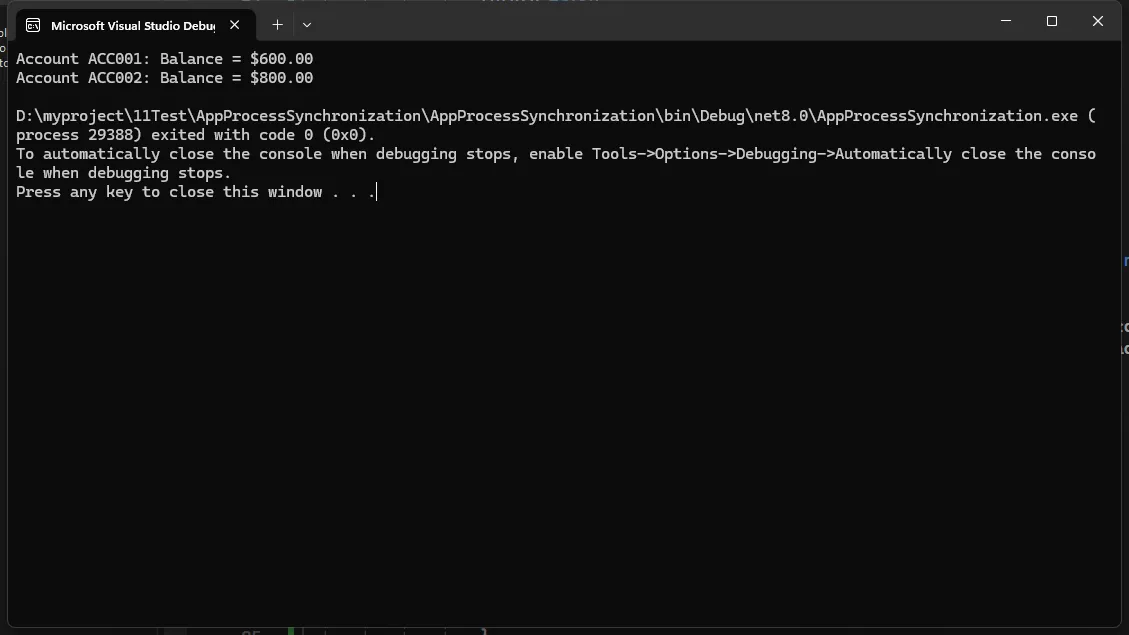
在这个例子中,lock关键字确保在同一时间只有一个线程可以访问账户余额,从而防止可能的竞态条件。
使用Semaphore控制并发访问
Semaphore和SemaphoreSlim用于限制同时访问某个资源的线程数量。
C#using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Data;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Microsoft.Data.SqlClient;
namespace AppProcessSynchronization
{
public class ConnectionPool : IDisposable
{
private readonly SemaphoreSlim semaphore;
private readonly List<SqlConnection> connections;
private readonly string connectionString;
private bool isDisposed;
public ConnectionPool(int maxConnections, string connectionString)
{
if (maxConnections <= 0)
throw new ArgumentException("最大连接数必须大于0", nameof(maxConnections));
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(connectionString))
throw new ArgumentException("连接字符串不能为空", nameof(connectionString));
this.connectionString = connectionString;
semaphore = new SemaphoreSlim(maxConnections, maxConnections);
connections = new List<SqlConnection>(maxConnections);
// 初始化连接池
for (int i = 0; i < maxConnections; i++)
{
connections.Add(new SqlConnection(connectionString));
}
}
public async Task<SqlConnection> GetConnectionAsync(CancellationToken cancellationToken = default)
{
if (isDisposed)
throw new ObjectDisposedException(nameof(ConnectionPool));
try
{
// 等待获取信号量
await semaphore.WaitAsync(cancellationToken);
// 获取一个可用的连接
SqlConnection connection;
lock (connections)
{
connection = connections.FirstOrDefault(c => c.State == ConnectionState.Closed);
// 如果没有可用连接,创建新的连接
if (connection == null)
{
connection = new SqlConnection(connectionString);
connections.Add(connection);
}
}
// 确保连接是打开的
if (connection.State != ConnectionState.Open)
{
await connection.OpenAsync(cancellationToken);
}
return connection;
}
catch (Exception)
{
// 如果获取连接过程中出现错误,释放信号量
semaphore.Release();
throw;
}
}
public void ReleaseConnection(SqlConnection connection)
{
if (connection == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(connection));
if (isDisposed)
throw new ObjectDisposedException(nameof(ConnectionPool));
try
{
// 关闭连接
if (connection.State != ConnectionState.Closed)
{
connection.Close();
}
}
finally
{
// 确保信号量被释放
semaphore.Release();
}
}
public void Dispose()
{
Dispose(true);
GC.SuppressFinalize(this);
}
protected virtual void Dispose(bool disposing)
{
if (!isDisposed)
{
if (disposing)
{
// 关闭所有连接
foreach (var connection in connections)
{
connection.Dispose();
}
connections.Clear();
// 释放信号量
semaphore.Dispose();
}
isDisposed = true;
}
}
}
}
这个例子展示了如何使用SemaphoreSlim来实现一个简单的数据库连接池,限制同时打开的连接数量。
使用ReaderWriterLockSlim实现读写锁
ReaderWriterLockSlim允许多个线程同时读取资源,但写入时需要独占访问。
C#using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace AppProcessSynchronization
{
public class ThreadSafeCache<TKey, TValue> : IDisposable
{
private readonly Dictionary<TKey, TValue> cache = new Dictionary<TKey, TValue>();
private readonly ReaderWriterLockSlim cacheLock = new ReaderWriterLockSlim();
private bool disposed;
// 尝试获取值
public bool TryGetValue(TKey key, out TValue value)
{
cacheLock.EnterReadLock();
try
{
return cache.TryGetValue(key, out value);
}
finally
{
cacheLock.ExitReadLock();
}
}
// 获取值,如果不存在则添加
public TValue GetOrAdd(TKey key, Func<TKey, TValue> valueFactory)
{
if (valueFactory == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(valueFactory));
cacheLock.EnterUpgradeableReadLock();
try
{
if (cache.TryGetValue(key, out TValue value))
{
return value;
}
cacheLock.EnterWriteLock();
try
{
// 双重检查,确保其他线程没有添加过
if (!cache.TryGetValue(key, out value))
{
value = valueFactory(key);
cache[key] = value;
}
return value;
}
finally
{
cacheLock.ExitWriteLock();
}
}
finally
{
cacheLock.ExitUpgradeableReadLock();
}
}
// 添加或更新值
public void AddOrUpdate(TKey key, TValue value)
{
cacheLock.EnterWriteLock();
try
{
cache[key] = value;
}
finally
{
cacheLock.ExitWriteLock();
}
}
// 尝试删除值
public bool TryRemove(TKey key)
{
cacheLock.EnterWriteLock();
try
{
return cache.Remove(key);
}
finally
{
cacheLock.ExitWriteLock();
}
}
// 清空缓存
public void Clear()
{
cacheLock.EnterWriteLock();
try
{
cache.Clear();
}
finally
{
cacheLock.ExitWriteLock();
}
}
// 获取缓存中的所有键
public ICollection<TKey> Keys
{
get
{
cacheLock.EnterReadLock();
try
{
return cache.Keys.ToList();
}
finally
{
cacheLock.ExitReadLock();
}
}
}
// 获取缓存数量
public int Count
{
get
{
cacheLock.EnterReadLock();
try
{
return cache.Count;
}
finally
{
cacheLock.ExitReadLock();
}
}
}
// 实现 IDisposable 接口
public void Dispose()
{
Dispose(true);
GC.SuppressFinalize(this);
}
protected virtual void Dispose(bool disposing)
{
if (!disposed)
{
if (disposing)
{
if (cacheLock != null)
{
cacheLock.Dispose();
}
}
disposed = true;
}
}
}
}
这个例子展示了如何使用ReaderWriterLockSlim来实现一个线程安全的缓存,允许多个线程同时读取缓存,但在写入时需要独占访问。
进程间同步
进程间同步用于协调多个独立进程之间对共享资源的访问。这种同步机制通常用于跨应用程序的场景。
常用的进程间同步机制
C#提供了几种进程间同步机制,包括:
- 命名Mutex
- 命名Semaphore
- 内存映射文件(MemoryMappedFile)
- 文件锁
让我们通过一些例子来详细了解这些机制。
使用命名Mutex
命名Mutex可以用于确保只有一个进程的实例在运行。
C#class Program
{
static Mutex mutex = new Mutex(true, "Global\\MyUniqueApplicationMutex");
static void Main(string[] args)
{
if (mutex.WaitOne(TimeSpan.Zero, true))
{
try
{
Console.WriteLine("Application is running. Press any key to exit.");
Console.ReadKey();
}
finally
{
mutex.ReleaseMutex();
}
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Another instance of the application is already running.");
}
}
}
这个例子展示了如何使用命名Mutex来确保应用程序只有一个实例在运行。
使用命名Semaphore控制跨进程资源访问
命名Semaphore可以用于限制跨多个进程的并发访问。
C#using System.Diagnostics;
using Microsoft.Data.SqlClient;
namespace AppProcessSynchronization
{
internal class Program
{
static Semaphore semaphore;
static string semaphoreName = "Global\\MySharedResourceSemaphore";
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 创建或打开一个命名信号量
// 参数含义:initialCount=2(初始可用数量), maximumCount=2(最大可用数量)
semaphore = new Semaphore(2, 2, semaphoreName);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
Task.Run(() => AccessSharedResource());
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
static async Task AccessSharedResource()
{
try
{
semaphore.WaitOne(); // 等待信号量
Console.WriteLine($"Process {Process.GetCurrentProcess().Id}, Thread {Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId} is accessing the resource.");
await Task.Delay(2000); // 模拟工作
}
finally
{
semaphore.Release(); // 释放信号量
}
}
}
}
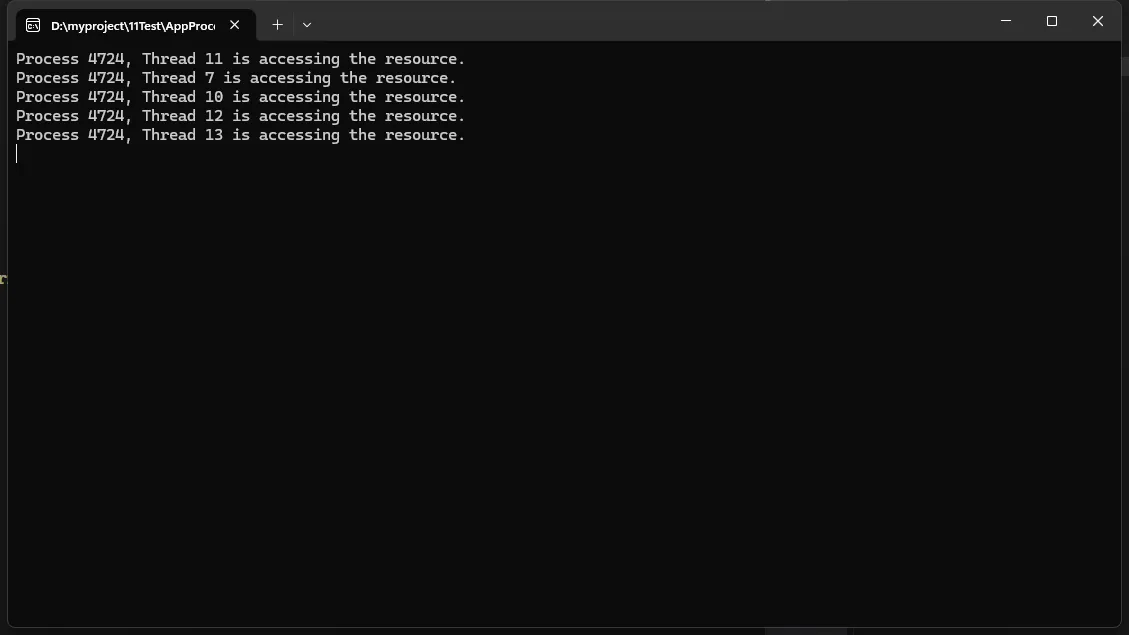
这个例子展示了如何使用命名Semaphore来限制跨多个进程对共享资源的并发访问。
使用MemoryMappedFile进行进程间通信
MemoryMappedFile可以用于在不同进程之间共享内存,实现高效的进程间通信。
C#static void ReadFromSharedMemory()
{
try
{
while (true)
{
try
{
// 尝试打开已存在的内存映射文件
using (var mmf = MemoryMappedFile.OpenExisting("SharedMemory"))
{
Console.WriteLine("Connected to shared memory. Reading data...");
// 创建一个视图访问器来读取数据
using (var accessor = mmf.CreateViewAccessor())
{
// 读取之前写入的数据
int intValue = accessor.ReadInt32(0);
double doubleValue = accessor.ReadDouble(4);
// 读取字符串 (需要先读取字节然后转换)
byte[] stringBytes = new byte[20]; // 假设字符串不会超过20字节
accessor.ReadArray(12, stringBytes, 0, stringBytes.Length);
string stringValue = Encoding.ASCII.GetString(stringBytes).TrimEnd('\0');
Console.WriteLine("\nRead values from shared memory:");
Console.WriteLine($"Integer: {intValue}");
Console.WriteLine($"Double: {doubleValue}");
Console.WriteLine($"String: {stringValue}");
}
break; // 成功读取后退出循环
}
}
catch (FileNotFoundException)
{
Console.WriteLine("Waiting for shared memory to be created...");
Thread.Sleep(1000); // 等待1秒后重试
}
}
Console.WriteLine("\nPress any key to exit.");
Console.ReadKey();
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"An error occurred: {ex.Message}");
}
}
static void WriteToSharedMemory()
{
try
{
// 创建一个新的内存映射文件,大小为 1024 字节
using (var mmf = MemoryMappedFile.CreateNew("SharedMemory", 1024))
{
Console.WriteLine("Memory mapped file created. Starting to write data...");
// 创建一个视图访问器来访问共享内存
using (var accessor = mmf.CreateViewAccessor())
{
// 写入一个整数
accessor.Write(0, 42);
// 写入一个 double
accessor.Write(4, 3.14159);
// 写入字符串
string message = "Hello World!";
byte[] messageBytes = Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes(message);
// 首先写入字符串的长度
accessor.Write(12, messageBytes.Length);
// 然后写入字符串内容
accessor.WriteArray(16, messageBytes, 0, messageBytes.Length);
Console.WriteLine("Data written to shared memory:");
Console.WriteLine("Integer: 42");
Console.WriteLine("Double: 3.14159");
Console.WriteLine($"String: {message}");
}
Console.WriteLine("\nKeeping the program alive. Press any key to exit.");
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"An error occurred: {ex.Message}");
}
}
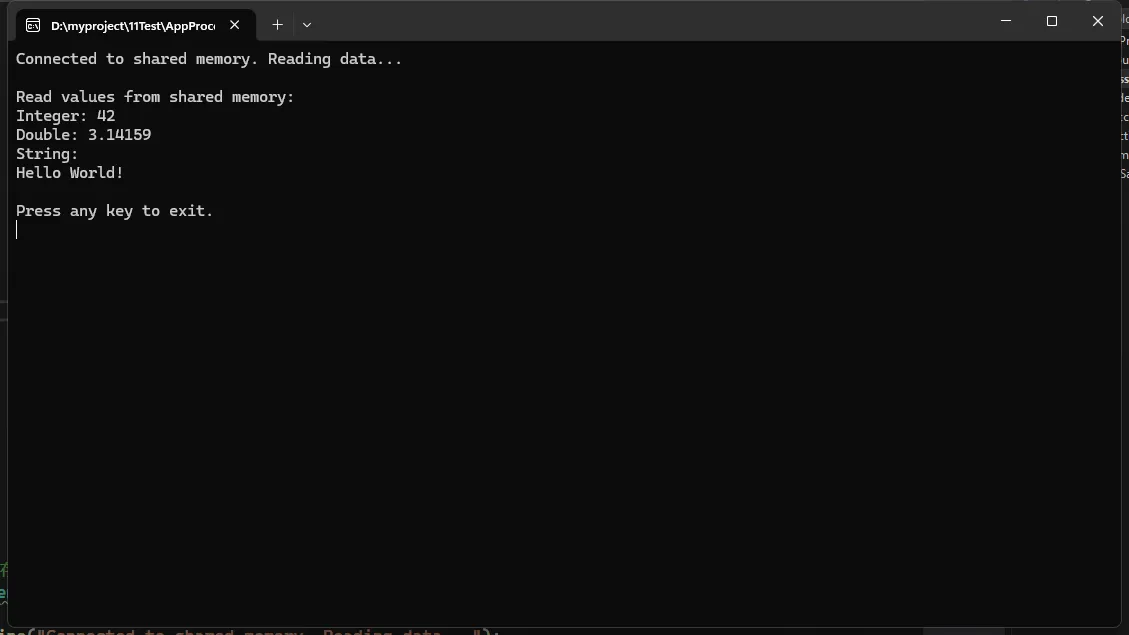
这个例子展示了如何使用MemoryMappedFile在两个不同的进程之间共享数据。
总结
进程内同步和进程间同步是C#多线程和多进程编程中的重要概念。进程内同步主要用于协调单个进程内多个线程之间的资源访问,而进程间同步则用于协调多个独立进程之间的资源访问。
选择合适的同步机制取决于具体的应用场景:
- 对于进程内的线程安全,可以使用
lock、Mutex、Semaphore或ReaderWriterLockSlim等机制。 - 对于进程间的同步,可以使用命名Mutex、命名Semaphore或MemoryMappedFile等机制。
无论选择哪种同步机制,都需要谨慎使用,以避免死锁和性能问题。在实际应用中,应该根据具体需求和性能要求来选择最合适的同步策略。
本文作者:技术老小子
本文链接:
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!