目录
在现代工业自动化中,数据监测与控制的复杂性与日俱增,如何高效、安全地记录操作日志成为了工程师们必须解决的关键问题。本文将介绍如何在利用面向切面编程(AOP)实现高效的日志记录,确保操作透明和可追溯,为安全监控提供保障。
🔍 问题分析
在开发中,各类设备(如传感器、控制器)以及不同的业务逻辑(如设备启动、停止等)需要频繁交互。每当调用这些操作时,都需要记录详细的日志以供后期审计和故障排查。然而,传统的日志记录方式往往需要在每个设备操作方法中手动添加日志代码,造成代码冗余,维护困难。
例如,以下操作需要记录状态变化和关键参数,但如果采用传统方法,代码将显得繁琐且难以维护。因此,采用一种通用且无侵入的方式实现日志记录就显得尤为重要。
💡 解决方案
以下是我们在工控领域中实现日志记录的可行方案:
- 通过自定义特性标记需要日志记录的方法,清晰表明哪些操作需要被记录。
- 动态代理模式:使用
Castle.DynamicProxy库为标记的方法生成代理,自动执行日志记录。 - 集中日志记录逻辑:通过拦截器,确保方法调用的日志记录在一处完成,避免代码重复。
下面我们将以具体代码示例逐步实现这一过程。
依赖
C#Castle.Core Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection
📜 代码实战
步骤1:定义自定义特性
首先,创建一个用于标记工控系统中需要日志记录的方法的自定义特性:
C#// 定义自定义特性
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Method)]
public class LoggingAttribute : Attribute
{
public string Description { get; }
public LoggingAttribute(string description = "")
{
Description = description;
}
}
这个特性允许为工控方法添加描述信息,这些信息将在日志记录时使用。
步骤2:创建拦截器
接下来,实现一个 IInterceptor 接口的拦截器,用于处理日志记录:
C#// 日志拦截器
public class LoggingInterceptor : IInterceptor
{
public void Intercept(IInvocation invocation)
{
var methodInfo = invocation.Method;
// 确保获取特性
var attribute = methodInfo.GetCustomAttribute<LoggingAttribute>();
Console.WriteLine($"Method: {methodInfo.Name}"); // 添加检查方法名称
var allAttributes = methodInfo.GetCustomAttributes();
foreach (var attr in allAttributes)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Attribute: {attr.GetType().Name}"); // 调试输出所有特性
}
if (attribute != null)
{
string description = !string.IsNullOrEmpty(attribute.Description) ? attribute.Description : "执行方法";
Console.WriteLine($"[开始] {description}: {methodInfo.Name}");
Console.WriteLine($"参数: {string.Join(", ", invocation.Arguments)}");
var startTime = DateTime.Now;
try
{
invocation.Proceed();
Console.WriteLine($"返回值: {invocation.ReturnValue}");
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"方法执行异常: {ex.Message}");
throw;
}
finally
{
var endTime = DateTime.Now;
var duration = (endTime - startTime).TotalMilliseconds;
Console.WriteLine($"[结束] {description}: {methodInfo.Name},耗时: {duration}ms");
}
}
else
{
// 如果没有特性,直接执行
invocation.Proceed();
}
}
}
步骤3:创建工控服务类
接着,创建一个包含工控设备操作逻辑的服务类:
注意其中方法一定要加上virtual
C#// 创建工控服务类
public class ControlService
{
[LoggingAttribute("启动设备")]
public virtual void StartDevice(string deviceName)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Starting device: {deviceName}");
}
[LoggingAttribute("停止设备")]
public virtual void StopDevice(string deviceName)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Stopping device: {deviceName}");
}
public virtual void NormalOperation()
{
Console.WriteLine("Device is operating normally.");
}
}
在这个服务类中,我们为 StartDevice 和 StopDevice 方法添加了日志特性,而 NormalOperation 方法没有被标记,故不会被拦截。
步骤4:创建代理工厂
为了简化代理对象的创建,编写代理工厂:
C#// 创建代理工厂
public static class ProxyFactory
{
public static T Create<T>() where T : class, new()
{
var generator = new ProxyGenerator();
var interceptor = new LoggingInterceptor();
return generator.CreateClassProxy<T>(interceptor);
}
}
步骤5:配置依赖注入
最后,创建扩展方法进行依赖注入配置:
C#// 进行依赖注入配置
public static class ServiceCollectionExtensions
{
public static IServiceCollection AddProxiedScoped<TService>(this IServiceCollection services)
where TService : class, new()
{
services.AddScoped(typeof(TService), serviceProvider => {
return ProxyFactory.Create<TService>();
});
return services;
}
}
使用示例
以下是如何使用上述组件的示例代码:
C#using System;
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
using System.Linq;
using System.Reflection;
using Castle.DynamicProxy;
// 定义自定义特性
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Method)]
public class LoggingAttribute : Attribute
{
public string Description { get; }
public LoggingAttribute(string description = "")
{
Description = description;
}
}
// 定义接口
public interface IService
{
void StartDevice(string deviceName);
void StopDevice(string deviceName);
void NormalOperation();
}
// 实现接口
public class ControlService
{
[LoggingAttribute("启动设备")]
public virtual void StartDevice(string deviceName)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Starting device: {deviceName}");
}
[LoggingAttribute("停止设备")]
public virtual void StopDevice(string deviceName)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Stopping device: {deviceName}");
}
public virtual void NormalOperation()
{
Console.WriteLine("Device is operating normally.");
}
}
// 日志拦截器
public class LoggingInterceptor : IInterceptor
{
public void Intercept(IInvocation invocation)
{
var methodInfo = invocation.Method;
// 确保获取特性
var attribute = methodInfo.GetCustomAttribute<LoggingAttribute>();
Console.WriteLine($"Method: {methodInfo.Name}"); // 添加检查方法名称
var allAttributes = methodInfo.GetCustomAttributes();
foreach (var attr in allAttributes)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Attribute: {attr.GetType().Name}"); // 调试输出所有特性
}
if (attribute != null)
{
string description = !string.IsNullOrEmpty(attribute.Description) ? attribute.Description : "执行方法";
Console.WriteLine($"[开始] {description}: {methodInfo.Name}");
Console.WriteLine($"参数: {string.Join(", ", invocation.Arguments)}");
var startTime = DateTime.Now;
try
{
invocation.Proceed();
Console.WriteLine($"返回值: {invocation.ReturnValue}");
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"方法执行异常: {ex.Message}");
throw;
}
finally
{
var endTime = DateTime.Now;
var duration = (endTime - startTime).TotalMilliseconds;
Console.WriteLine($"[结束] {description}: {methodInfo.Name},耗时: {duration}ms");
}
}
else
{
// 如果没有特性,直接执行
invocation.Proceed();
}
}
}
// 代理工厂
public static class ProxyFactory
{
public static T Create<T>() where T : class
{
var generator = new ProxyGenerator();
var interceptor = new LoggingInterceptor();
return generator.CreateClassProxy<T>(interceptor);
//return generator.CreateInterfaceProxyWithTarget<T>(obj, interceptor);
}
}
// 主程序入口
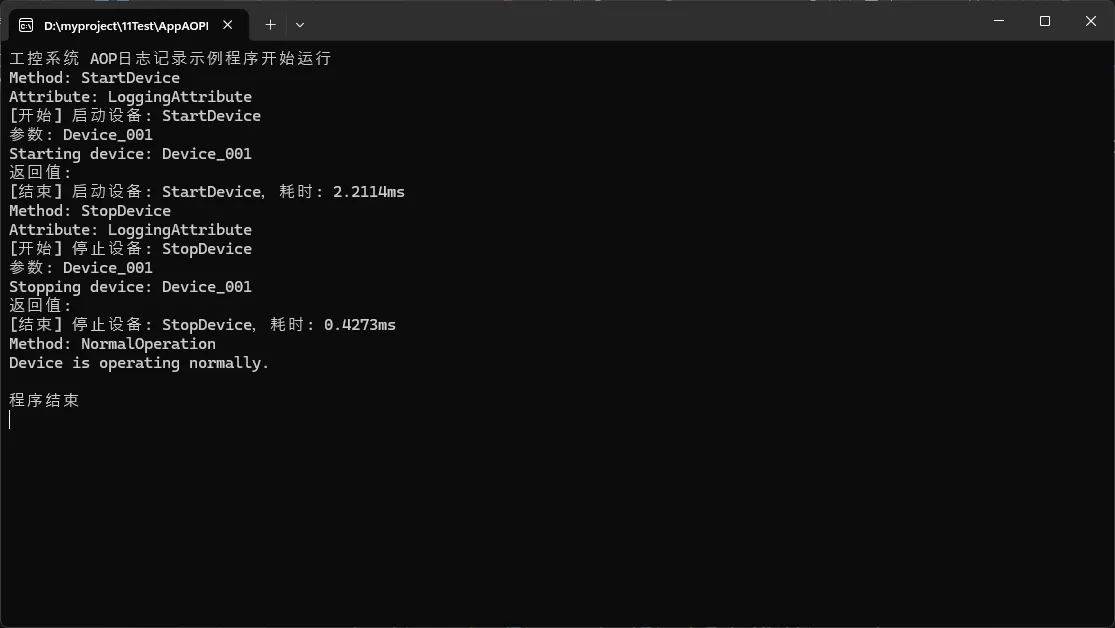
public class Program
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("工控系统 AOP日志记录示例程序开始运行");
ControlService controlServiceObj = new ControlService();
var controlService = ProxyFactory.Create<ControlService>();
controlService.StartDevice("Device_001");
controlService.StopDevice("Device_001");
controlService.NormalOperation();
Console.WriteLine("\n程序结束");
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
📋 常见坑点提醒
- 依赖注入配置:确保在依赖注入时为服务注册正确的生命周期,以确保代理正常工作。
- 性能监控:在高负载工控场景下,监控日志记录对系统性能的影响,适时优化。
- 日志数据处理:处理日志时应考虑安全性与隐私,不应记录敏感数据。
🎯 互动与传播
在探讨工控领域使用AOP进行日志记录的过程中,您是否在项目中应用过这种模式?是否遇到过其他日志记录的挑战?
- 金句总结:
- “清晰的操作日志是工控系统稳定运行的保障。”
- “精简的代码逻辑能大幅降低维护成本。”
- “通过AOP实现日志记录,可以提升系统的可追溯性。”
- 代码模板:
C#[Logging("操作说明")]
public 返回类型 操作名(参数类型 参数名)
{
// 操作逻辑
}
觉得有用请分享给更多同行,一起提升工控开发的技术能力!
✨ 结尾呼应
本文介绍了如何在工控领域通过面向切面编程(AOP)实现日志记录功能,涵盖了以下要点:
- 自定义特性的创建与应用,明确标记需要记录的操作。
- 动态代理的实现,自动处理日志记录,避免代码冗余。
- 依赖注入的合理配置,保障代码的高内聚和低耦合。
希望这篇文章能为您的工控系统开发提供实用和有效的帮助。
本文作者:技术老小子
本文链接:
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!