目录
当学习 C# 编程语言时,了解变量声明和数据类型是非常重要的。本课程将详细介绍 C# 中的变量声明和常见数据类型,包括基本数据类型、引用类型、常量和变量的声明规则等内容。
1. 变量声明和命名规则
1.1 变量声明
在 C# 中,变量是用于存储数据的内存位置,可以通过变量名来引用这些数据。变量声明的一般形式如下:
C#<数据类型> <变量名>;
例如:
C#internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int age;
string name;
double salary;
}
}
1.2 命名规则
- 变量名可以包含字母、数字和下划线,但必须以字母或下划线开头。
- 变量名区分大小写。
- 变量名不能与关键字相同。
2. 基本数据类型
C# 提供了多种基本数据类型,用于存储不同类型的数据,包括整数、浮点数、字符、布尔值等。
2.1 整数类型
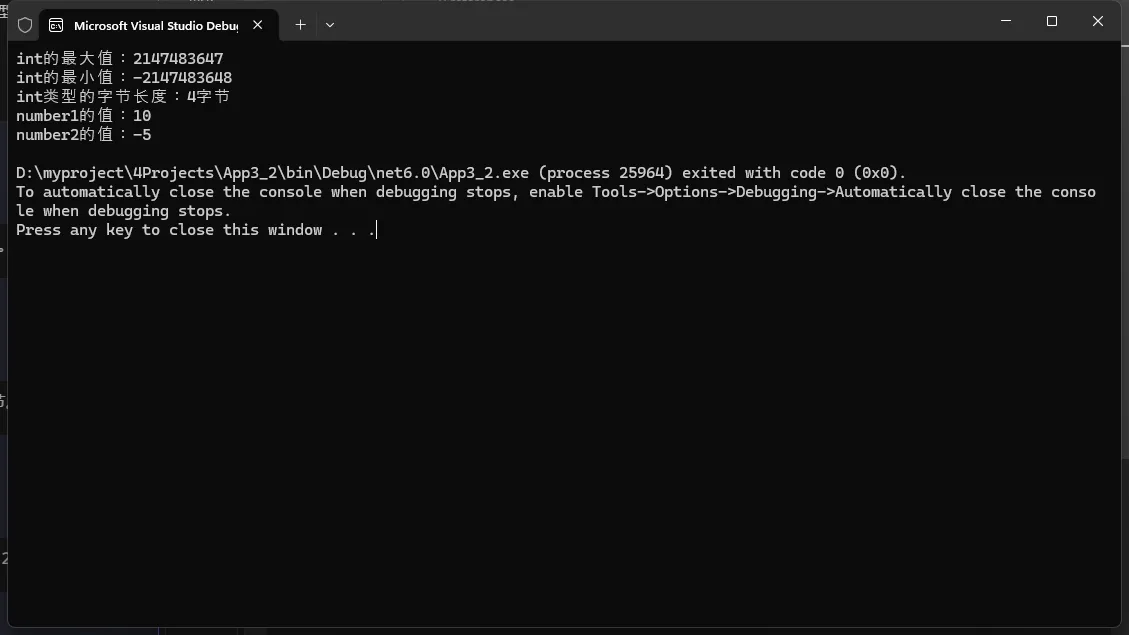
int:用于存储整数,通常占用 4 字节。
C#static void Main(string[] args)
{
int number1 = 10;
int number2 = -5;
// 输出int类型的最大值和最小值
Console.WriteLine($"int的最大值:{int.MaxValue}");
Console.WriteLine($"int的最小值:{int.MinValue}");
// 输出int类型的字节长度
Console.WriteLine($"int类型的字节长度:{sizeof(int)}字节");
// 输出变量值
Console.WriteLine($"number1的值:{number1}");
Console.WriteLine($"number2的值:{number2}");
}
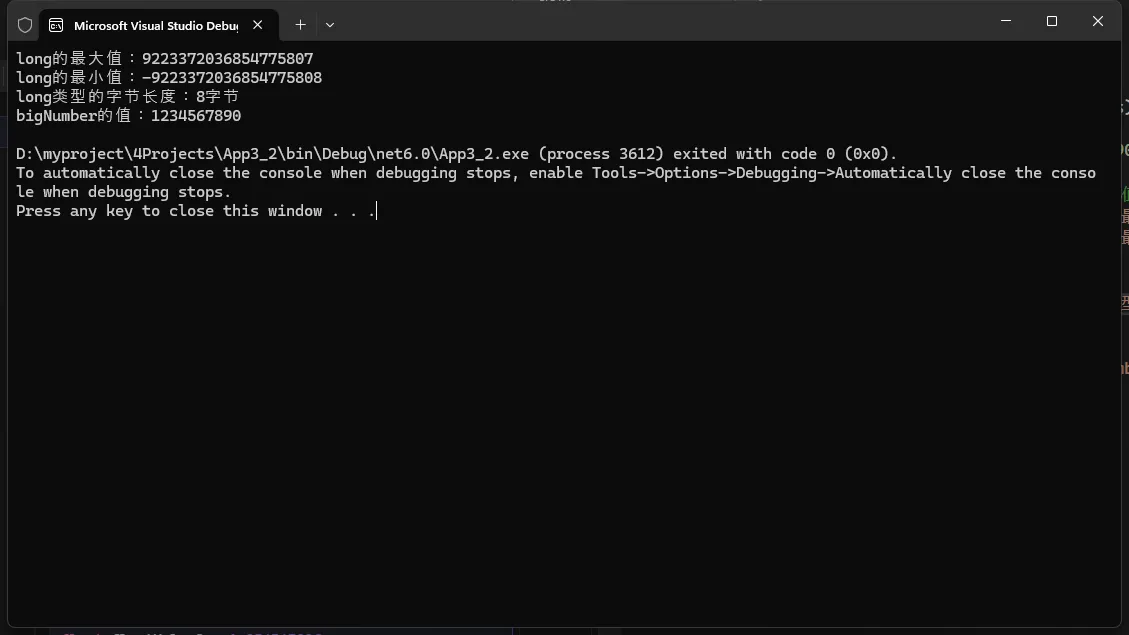
long:用于存储长整数,通常占用 8 字节。
C#static void Main(string[] args)
{
long bigNumber = 1234567890L;
// 输出long类型的最大值和最小值
Console.WriteLine($"long的最大值:{long.MaxValue}");
Console.WriteLine($"long的最小值:{long.MinValue}");
// 输出long类型的字节长度
Console.WriteLine($"long类型的字节长度:{sizeof(long)}字节");
// 输出变量值
Console.WriteLine($"bigNumber的值:{bigNumber}");
}
short:用于存储短整数,通常占用 2 字节。
C#short smallNumber = 100;
byte:用于存储无符号字节,范围为 0 到 255。
C#byte smallUnsignedNumber = 200;
2.2 浮点数类型
float:用于存储单精度浮点数,通常占用 4 字节。
C#float floatValue1 = 3.14f;
float floatValue2 = 1.23456789f;
double:用于存储双精度浮点数,通常占用 8 字节。
C#double doubleValue1 = 3.141592653589793;
double doubleValue2 = 1234.56789;
2.3 字符类型
char:用于存储单个字符,占用 2 字节。
C#char firstLetter = 'A';
char punctuation = '!';
在这些例子中,我们声明了两个字符类型的变量,并分别赋予了它们字符值。可以通过这些例子来了解字符类型变量只能存储单个字符,并且字符值需要用单引号括起来。他们也可以通过修改这些值来练习字符类型变量的赋值和修改操作。
2.4 布尔类型
-
bool:用于存储布尔值,只能是true或false。当学习 C# 中的布尔类型时,新手学员可以通过以下例子来了解布尔类型的用法:
C#bool isTrue = true;
bool isFalse = false;
在这些例子中,我们声明了两个布尔类型的变量,并分别赋予了它们布尔值。新手学员可以通过这些例子来了解布尔类型变量只能存储 `true` 或 `false` 两种值。他们也可以通过修改这些值来练习布尔类型变量的赋值和修改操作。
3. 引用类型
除了基本数据类型外,C# 还提供了引用类型,包括字符串、数组、类等。
3.1 字符串类型
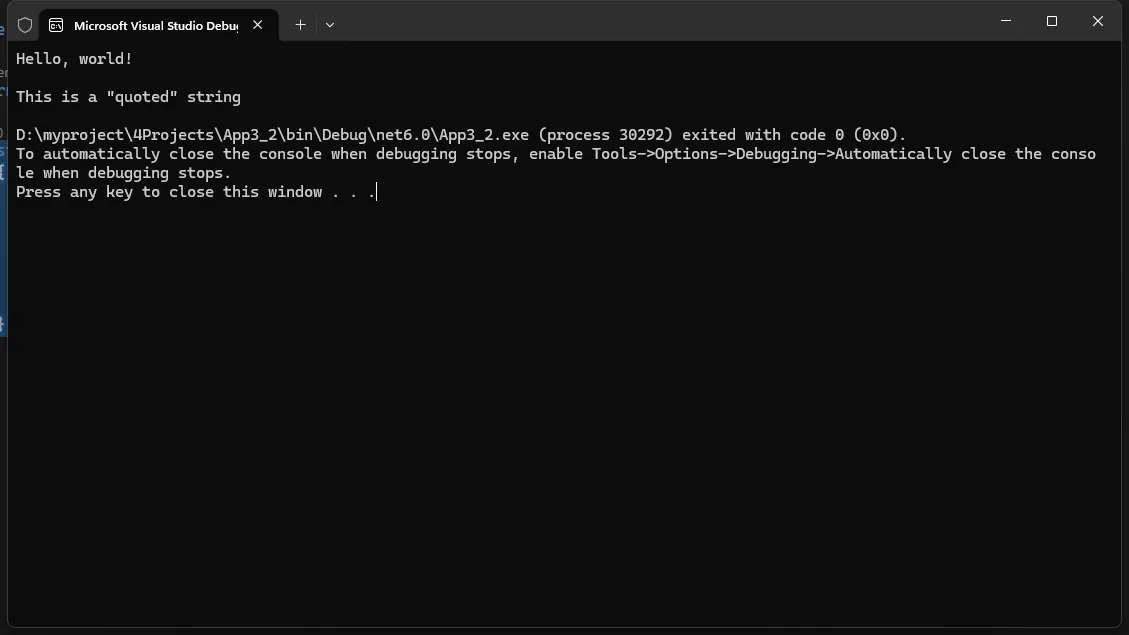
string:用于存储文本字符串。
C#static void Main(string[] args)
{
string greeting = "Hello, world!";
string emptyString = "";
string withEscape = "This is a \"quoted\" string";
Console.WriteLine(greeting);
Console.WriteLine(emptyString);
Console.WriteLine(withEscape);
}
在这些例子中,我们声明了三个字符串类型的变量,并分别赋予了它们不同的字符串值。新手学员可以通过这些例子来了解字符串类型变量可以存储文本数据,并且可以包含特殊字符和转义序列。他们也可以通过修改这些值来练习字符串类型变量的赋值和修改操作。
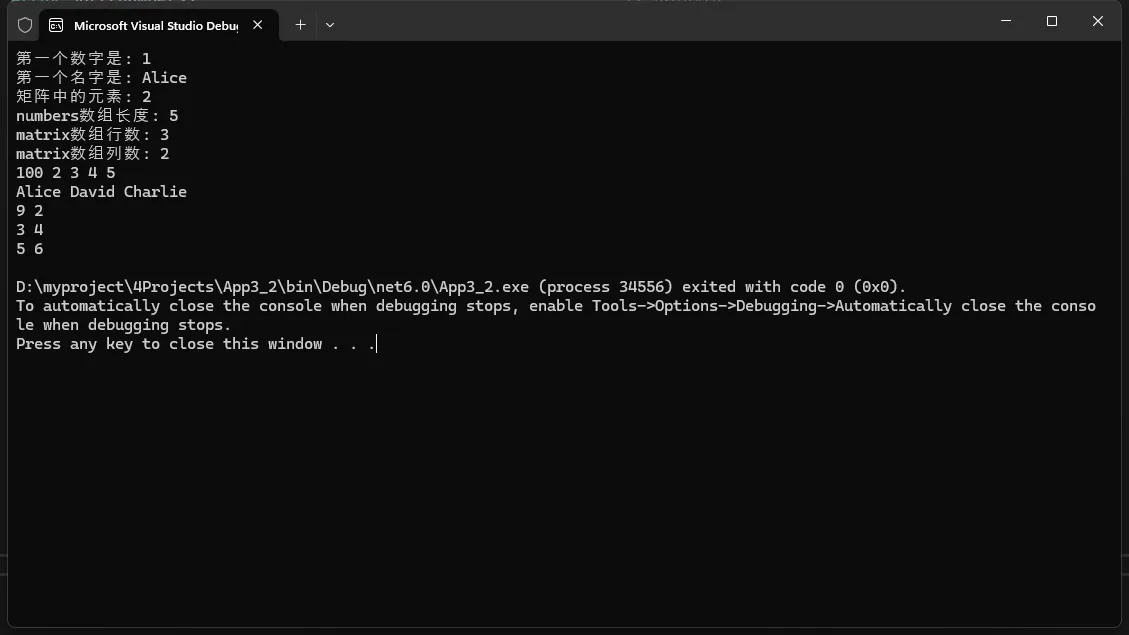
3.2 数组类型
- 用于存储同一类型的多个元素。
C#static void Main()
{
// 1. 数组的声明和初始化
int[] numbers = new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 }; // 一维数组初始化
string[] names = new string[] { "Alice", "Bob", "Charlie" }; // 字符串数组
int[,] matrix = new int[,] { { 1, 2 }, { 3, 4 }, { 5, 6 } }; // 二维数组
List<int> numberList = new List<int>() { 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 }; // 列表初始化
// 2. 访问数组元素
Console.WriteLine($"第一个数字是: {numbers[0]}"); // 访问一维数组元素
Console.WriteLine($"第一个名字是: {names[0]}"); // 访问字符串数组元素
Console.WriteLine($"矩阵中的元素: {matrix[0, 1]}"); // 访问二维数组元素
// 3. 修改数组元素
numbers[0] = 100; // 修改一维数组元素
names[1] = "David"; // 修改字符串数组元素
matrix[0, 0] = 9; // 修改二维数组元素
// 4. 数组长度和维度
Console.WriteLine($"numbers数组长度: {numbers.Length}"); // 获取数组长度
Console.WriteLine($"matrix数组行数: {matrix.GetLength(0)}"); // 获取二维数组的行数
Console.WriteLine($"matrix数组列数: {matrix.GetLength(1)}"); // 获取二维数组的列数
// 5. 数组遍历
// 使用for循环遍历
for (int i = 0; i < numbers.Length; i++)
{
Console.Write($"{numbers[i]} ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
// 使用foreach循环遍历
foreach (string name in names)
{
Console.Write($"{name} ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
// 遍历二维数组
for (int i = 0; i < matrix.GetLength(0); i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < matrix.GetLength(1); j++)
{
Console.Write($"{matrix[i, j]} ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
// 6. 数组方法
Array.Sort(numbers); // 数组排序
Array.Reverse(numbers); // 数组反转
int index = Array.IndexOf(names, "Alice"); // 查找元素索引
// 7. List<T>的特殊操作
numberList.Add(60); // 添加元素
numberList.Remove(30); // 删除元素
numberList.Insert(0, 5); // 在指定位置插入元素
bool contains = numberList.Contains(40); // 检查元素是否存在
// 8. 数组拷贝
int[] numbersCopy = new int[numbers.Length];
Array.Copy(numbers, numbersCopy, numbers.Length); // 数组拷贝
// 9. 数组转换
// 将数组转换为List
List<int> numbersList = numbers.ToList();
// 将List转换为数组
int[] numbersArray = numberList.ToArray();
// 10. LINQ操作 (需要 using System.Linq)
var evenNumbers = numbers.Where(n => n % 2 == 0); // 筛选偶数
var sum = numbers.Sum(); // 求和
var average = numbers.Average(); // 求平均值
var max = numbers.Max(); // 最大值
var min = numbers.Min(); // 最小值
}
在这些例子中,我们展示了不同类型的数组的声明和初始化方式。可以通过这些例子来了解如何声明和初始化数组,并且可以通过修改数组元素的值来练习数组的基本操作,后面会有具体章节来写数组。
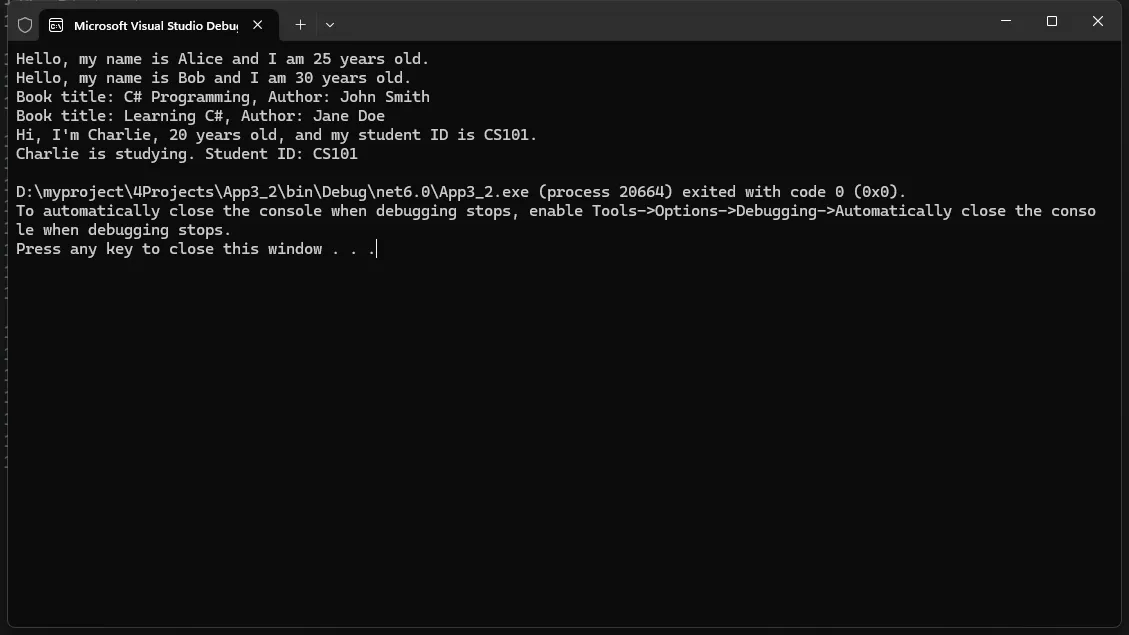
3.3 类类型(后面有专门文章来写)
- 通过类定义的自定义类型。
C#using System;
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 创建并使用Person类的实例
DemonstratePerson();
// 创建并使用Book类的实例
DemonstrateBook();
// 创建并使用Student类的实例
DemonstrateStudent();
}
static void DemonstratePerson()
{
// 创建Person类的实例并设置属性
Person person1 = new Person();
person1.Name = "Alice";
person1.Age = 25;
person1.Introduce();
// 创建另一个Person实例
Person person2 = new Person { Name = "Bob", Age = 30 }; // 使用对象初始化器
person2.Introduce();
}
static void DemonstrateBook()
{
// 使用构造函数创建Book实例
Book book1 = new Book("C# Programming", "John Smith");
Console.WriteLine($"Book title: {book1.Title}, Author: {book1.Author}");
// 创建另一个Book实例
Book book2 = new Book("Learning C#", "Jane Doe");
Console.WriteLine($"Book title: {book2.Title}, Author: {book2.Author}");
}
static void DemonstrateStudent()
{
// 创建并使用Student类的实例
Student student1 = new Student("Charlie", 20, "CS101");
student1.Introduce();
student1.Study();
}
}
// 定义Person类
public class Person
{
// 字段(Fields)
public string Name; // 公共字段,存储姓名
public int Age; // 公共字段,存储年龄
// 方法(Method)
public void Introduce()
{
Console.WriteLine($"Hello, my name is {Name} and I am {Age} years old.");
}
}
// 定义Book类
public class Book
{
// 字段
public string Title; // 书籍标题
public string Author; // 作者名称
// 构造函数(Constructor)
public Book(string title, string author)
{
Title = title; // 初始化标题
Author = author; // 初始化作者
}
// 方法
public void DisplayInfo()
{
Console.WriteLine($"Book: {Title} by {Author}");
}
}
// 定义Student类(继承自Person)
public class Student : Person
{
// 额外的字段
public string StudentId; // 学生ID
// 构造函数
public Student(string name, int age, string studentId)
{
Name = name; // 设置从Person类继承的属性
Age = age; // 设置从Person类继承的属性
StudentId = studentId;
}
// 新增方法
public void Study()
{
Console.WriteLine($"{Name} is studying. Student ID: {StudentId}");
}
// 方法重写(扩展父类的方法)
public new void Introduce()
{
Console.WriteLine($"Hi, I'm {Name}, {Age} years old, and my student ID is {StudentId}.");
}
}
// 示例:使用属性(Properties)的类
public class Employee
{
private string name; // 私有字段
private int salary; // 私有字段
// 属性
public string Name
{
get { return name; }
set { name = value; }
}
public int Salary
{
get { return salary; }
set
{
if (value >= 0) // 添加验证
salary = value;
}
}
// 自动实现的属性
public string Department { get; set; }
// 构造函数
public Employee(string name, int salary, string department)
{
Name = name;
Salary = salary;
Department = department;
}
// 方法
public void DisplayInfo()
{
Console.WriteLine($"Employee: {Name}, Department: {Department}, Salary: {Salary}");
}
}
在这些例子中,我们展示了如何定义类、创建类的实例以及访问类的成员。可以通过这些例子来了解类的基本概念,以及如何使用类来组织和操作数据。他们也可以尝试修改类的成员和方法来练习类的使用。
3.4 Record类型(后面有专门文章来写)
在 C# 9 中,引入了一种新的数据类型叫做 Record。Record 是一种不可变的引用类型,它可以用来表示不可变的数据。使用 Record 类型可以简化数据对象的定义和操作。
以下是一个简单的 Record 类型的例子:
C#class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 演示Record的基本使用
DemonstrateBasicRecord();
// 演示Record的相等性比较
DemonstrateRecordEquality();
// 演示Record的不可变性和with表达式
DemonstrateImmutabilityAndWith();
// 演示带构造函数的Record
DemonstrateRecordWithConstructor();
// 演示继承的Record
DemonstrateInheritedRecord();
}
static void DemonstrateBasicRecord()
{
// 创建Person record的实例
var person1 = new Person { Name = "Alice", Age = 30 };
// 访问Record的属性
Console.WriteLine($"Name: {person1.Name}, Age: {person1.Age}");
// Record自动实现的ToString()方法
Console.WriteLine($"ToString(): {person1}"); // 输出: Person { Name = Alice, Age = 30 }
}
static void DemonstrateRecordEquality()
{
// 创建两个具有相同值的Record实例
var person1 = new Person { Name = "Bob", Age = 25 };
var person2 = new Person { Name = "Bob", Age = 25 };
// Record类型的相等性比较(基于值)
Console.WriteLine($"Are equal? {person1 == person2}"); // 输出: True
Console.WriteLine($"Equals(): {person1.Equals(person2)}"); // 输出: True
}
static void DemonstrateImmutabilityAndWith()
{
var person1 = new Person { Name = "Charlie", Age = 35 };
// 使用with表达式创建修改后的副本
var person2 = person1 with { Age = 36 };
Console.WriteLine($"Original: {person1}"); // 原始对象保持不变
Console.WriteLine($"Modified: {person2}"); // 新对象包含修改后的值
}
static void DemonstrateRecordWithConstructor()
{
// 使用构造函数创建Employee实例
var employee = new Employee("David", 40, "IT");
Console.WriteLine(employee);
// 使用with表达式
var promotedEmployee = employee with { Department = "Management" };
Console.WriteLine(promotedEmployee);
}
static void DemonstrateInheritedRecord()
{
// 创建Manager记录的实例
var manager = new Manager("Eve", 45, "Sales", 5);
Console.WriteLine(manager);
// 使用with表达式
var seniorManager = manager with { TeamSize = 10 };
Console.WriteLine(seniorManager);
}
}
// 基本的Record定义
public record Person
{
// init-only属性
public string Name { get; init; }
public int Age { get; init; }
}
// 带构造函数的Record
public record Employee
{
// 只读属性
public string Name { get; init; }
public int Age { get; init; }
public string Department { get; init; }
// 构造函数
public Employee(string name, int age, string department)
{
Name = name;
Age = age;
Department = department;
}
}
// 继承的Record
public record Manager : Employee
{
public int TeamSize { get; init; }
// 构造函数,调用基类构造函数
public Manager(string name, int age, string department, int teamSize)
: base(name, age, department)
{
TeamSize = teamSize;
}
}
// 使用主构造函数语法的Record(更简洁的语法)
public record Student(string Name, int Age, string StudentId);
// 带有附加成员的Record
public record Course(string Name, string Code)
{
// 额外的属性
public bool IsActive { get; init; } = true;
// 方法
public string GetFullDescription() => $"{Code}: {Name} ({(IsActive ? "Active" : "Inactive")})";
}
// 使用sealed修饰符防止继承的Record
public sealed record Grade(string SubjectName, char LetterGrade);
// 抽象Record
public abstract record Vehicle
{
public string Brand { get; init; }
public abstract string GetVehicleType();
}
// 实现抽象Record
public record Car : Vehicle
{
public int Doors { get; init; }
public override string GetVehicleType() => "Car";
}
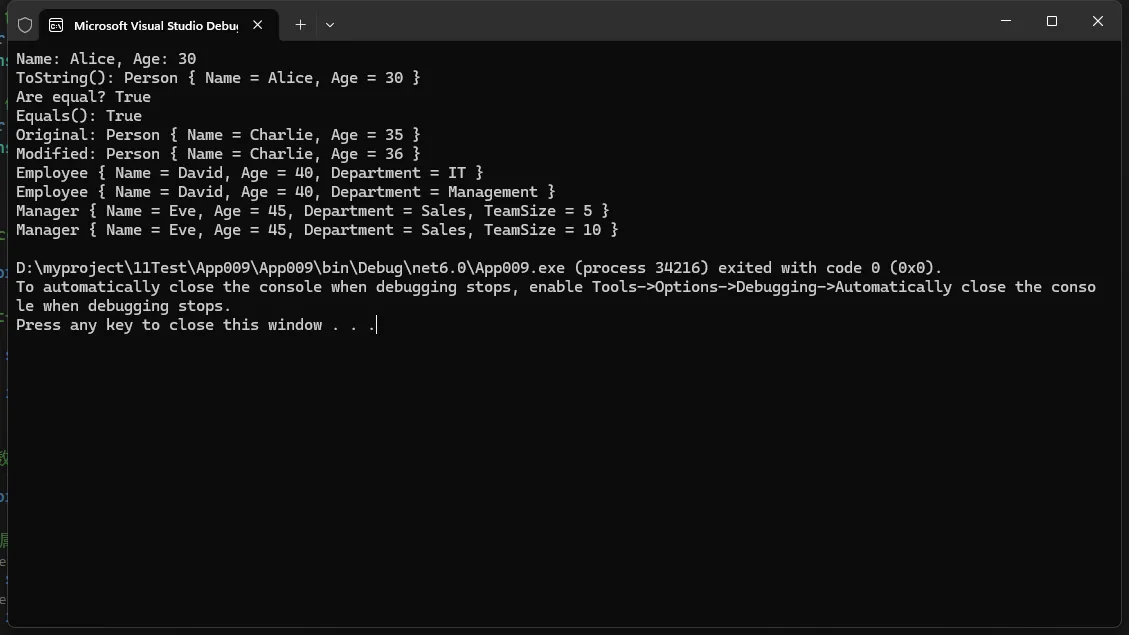
在这个例子中,我们定义了一个名为 Person 的 Record 类型,它有两个属性 Name 和 Age。使用 init 访问器可以确保这些属性在实例创建后不可修改。通过创建 Record 类的实例并访问其成员,我们可以看到 Record 类型的简洁性和不可变性。
请注意,Record 类型在 C# 9 中引入,需要使用 .NET 5 或更新的版本才能使用。
3.5 引用类型特点
- 内存分配:引用类型的变量存储的是对象的引用(内存地址),而不是对象本身。对象的实际数据存储在堆内存中,而引用存储在栈内存中。
- 对象生命周期:引用类型的对象在堆内存中分配,并且在不再被引用时,会由垃圾回收器自动回收。
- 对象赋值:引用类型的变量之间的赋值操作会复制引用,而不是复制对象本身。这意味着当一个引用类型的变量修改了对象的状态,其他引用该对象的变量也会反映出这一修改。
- 空引用:引用类型的变量可以存储空引用(null),表示它不引用任何对象。
- 类、接口和委托:在 C# 中,类、接口和委托都属于引用类型,它们在内存中的行为和特性都符合引用类型的特点。
4. 常量声明
在 C# 中,可以使用 const 关键字声明常量,一旦赋值,常量的值就不能再修改。
C#const int MaxValue = 100;
readonly int x=99;
5. 变量初始化
在声明变量时,可以选择是否对变量进行初始化。未初始化的变量将具有默认值。
C#int count; // 未初始化,默认值为 0
string message = "Hello"; // 初始化字符串变量
6. 总结
本课程详细介绍了 C# 中的变量声明和常见数据类型,包括基本数据类型、引用类型、常量和变量的声明规则等内容。通过学习本课程,你将能够熟练地声明变量并选择合适的数据类型来存储不同类型的数据,为后续的 C# 编程打下坚实的基础。
本文作者:技术老小子
本文链接:
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!