目录
你是否经常看到资深同事写出的代码简洁优雅,而自己的代码却显得冗长笨拙?其实,高手和新手之间的差距,往往就在于对语言特性的深度掌握。
今天我要分享10个C#中的"隐藏"关键词,这些都是资深开发者日常使用,但初级程序员却很少接触的强大特性。掌握它们,让你的代码立刻提升一个档次!
🎯 问题分析:为什么初级开发者不知道这些关键词?
很多开发者在学习C#时,往往只关注基础语法(if/else、for循环、class定义等),而忽略了这些高级特性。原因主要有:
- 教程覆盖不全:大部分入门教程不会深入讲解这些特性
- 实际应用场景有限:初级项目中很少遇到需要优化的场景
- 缺乏代码审查:没有资深同事指导,很难接触到最佳实践
但是,这些关键词恰恰是区分代码质量的重要标志!
💡 10个必知的隐藏关键词
1️⃣ nameof - 编译时字符串获取
常见痛点:硬编码属性名,重构时容易出错
C#// ❌ 初级写法 - 硬编码字符串
public void ValidateUser(User user)
{
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(user.FirstName))
throw new ArgumentException("FirstName cannot be empty");
}
// ✅ 资深写法 - 使用nameof
public void ValidateUser(User user)
{
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(user.FirstName))
throw new ArgumentException($"{nameof(user.FirstName)} cannot be empty");
}
关键优势:编译时检查,重构安全,代码更易维护,实际业务中偶而可以用到。
2️⃣ default - 智能默认值
常见痛点:泛型方法中需要返回类型默认值时的冗余写法
C#// ❌ 初级写法
public T GetValueOrDefault<T>(Dictionary<string, T> dict, string key)
{
return dict.ContainsKey(key) ? dict[key] : default(T);
}
// ✅ 资深写法 (C# 7.1+)
public T GetValueOrDefault<T>(Dictionary<string, T> dict, string key)
{
return dict.ContainsKey(key) ? dict[key] : default;
}
这个我用的还算比较多的了。
3️⃣ when - 条件模式匹配
常见痛点:复杂的条件判断导致代码可读性差
C#// ❌ 初级写法 - 嵌套if语句
public string GetUserRole(User user)
{
if (user is Admin)
{
var admin = (Admin)user;
if (admin.Level > 5)
return "Super Admin";
else
return "Admin";
}
else if (user is RegularUser)
{
return "User";
}
return "Unknown";
}
C#using System;
namespace AppHideKey
{
// 基类:User
public abstract class User
{
public string Name { get; init; }
public int Level { get; init; } // 某些用户(如 Admin)使用 Level 字段
public bool IsActive { get; init; } // RegularUser 会参考此字段
protected User(string name, int level = 0, bool isActive = true)
{
Name = name;
Level = level;
IsActive = isActive;
}
public override string ToString() =>
$"{GetType().Name}(Name={Name}, Level={Level}, IsActive={IsActive})";
}
// 管理员子类
public class Admin : User
{
public Admin(string name, int level) : base(name, level, isActive: true) { }
}
// 普通用户子类
public class RegularUser : User
{
public RegularUser(string name, bool isActive) : base(name, level: 0, isActive: isActive) { }
}
internal class Program
{
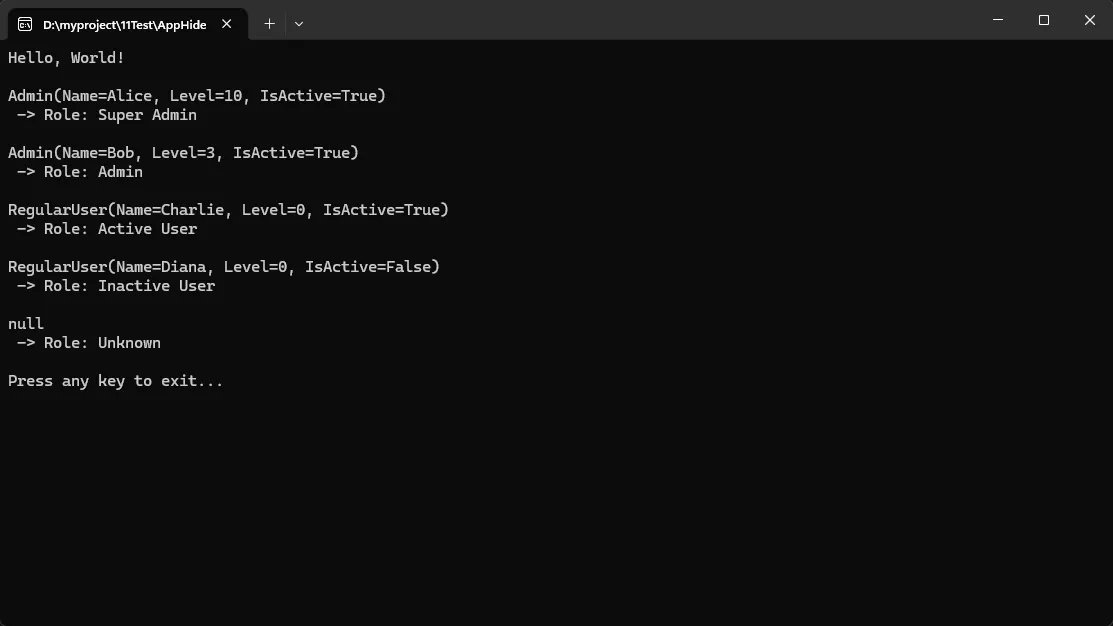
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("Hello, World!");
Console.WriteLine();
var users = new User[]
{
new Admin("Alice", level: 10),
new Admin("Bob", level: 3),
new RegularUser("Charlie", isActive: true),
new RegularUser("Diana", isActive: false),
null // 测试空引用匹配
};
var program = new Program();
foreach (var u in users)
{
// 打印对象并调用 GetUserRole
Console.WriteLine(u?.ToString() ?? "null");
Console.WriteLine(" -> Role: " + program.GetUserRole(u));
Console.WriteLine();
}
// 等待按键(在某些环境中用于暂停)
Console.WriteLine("Press any key to exit...");
Console.ReadKey();
}
// ✅ 资深写法 - when子句 & 模式匹配
public string GetUserRole(User user) => user switch
{
Admin { Level: > 5 } => "Super Admin",
Admin => "Admin",
RegularUser when user != null && user.IsActive => "Active User",
RegularUser => "Inactive User",
_ => "Unknown"
};
}
}
4️⃣ stackalloc - 栈内存分配
常见痛点:频繁创建小数组导致GC压力
C#// ❌ 初级写法 - 堆分配
public unsafe void ProcessData()
{
int[] buffer = new int[1024]; // 堆分配,会触发GC
// 处理数据...
}
// ✅ 资深写法 - 栈分配
public void ProcessData()
{
Span<int> buffer = stackalloc int[1024]; // 栈分配,无GC压力
// 处理数据...
}
// 🔥 实战应用 - 高性能字符串操作
public string FormatNumber(int number)
{
Span<char> buffer = stackalloc char[32];
if (number.TryFormat(buffer, out int written))
{
return buffer.Slice(0, written).ToString();
}
return number.ToString();
}
5️⃣ ref readonly - 只读引用
常见痛点:大结构体传参时的性能损失
C#// ❌ 初级写法 - 值传递,复制开销大
public void ProcessLargeStruct(LargeStruct data)
{
// data被完整复制了一份
Console.WriteLine(data.Value);
}
// ✅ 资深写法 - 引用传递,只读保护
public void ProcessLargeStruct(in LargeStruct data)
{
// data按引用传递,但不能修改
Console.WriteLine(data.Value);
// data.Value = 100; // 编译错误
}
// 🔥 实战应用 - 返回只读引用
public readonly struct Point
{
public readonly int X, Y;
public static ref readonly Point Origin => ref _origin;
private static readonly Point _origin = new Point(0, 0);
}
6️⃣ fixed - 固定内存指针
常见痛点:与非托管代码交互时的内存管理
C#// 🔥 实战应用 - P/Invoke优化
public unsafe void OptimizedCopy(byte[] source, byte[] destination)
{
fixed (byte* srcPtr = source)
fixed (byte* destPtr = destination)
{
// 直接内存操作,性能最优
NativeMethods.MemoryCopy(destPtr, srcPtr, source.Length);
}
}
// 🎯 高级用法 - Span<T>替代方案
public void ModernCopy(ReadOnlySpan<byte> source, Span<byte> destination)
{
source.CopyTo(destination); // 内部可能使用fixed
}
7️⃣ using - 资源管理利器
常见痛点:忘记释放资源导致内存泄漏
C#// ❌ 初级写法 - 手动管理
public string ReadFile(string path)
{
FileStream fs = null;
StreamReader reader = null;
try
{
fs = new FileStream(path, FileMode.Open);
reader = new StreamReader(fs);
return reader.ReadToEnd();
}
finally
{
reader?.Dispose();
fs?.Dispose();
}
}
// ✅ 资深写法 - using声明 (C# 8.0+)
public string ReadFile(string path)
{
using var fs = new FileStream(path, FileMode.Open);
using var reader = new StreamReader(fs);
return reader.ReadToEnd();
} // 自动释放资源
// 🔥 实战应用 - 自定义资源管理
public readonly struct DatabaseTransaction : IDisposable
{
private readonly IDbTransaction _transaction;
public DatabaseTransaction(IDbConnection connection)
{
_transaction = connection.BeginTransaction();
}
public void Dispose() => _transaction?.Rollback();
}
8️⃣ init - 只写属性
常见痛点:对象初始化后意外修改属性值
C#// ❌ 初级写法 - 可变属性
public class User
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public int Id { get; set; }
}
var user = new User { Name = "John", Id = 1 };
user.Id = 999; // 意外修改!
// ✅ 资深写法 - init访问器 (C# 9.0+)
public class User
{
public string Name { get; init; }
public int Id { get; init; }
}
var user = new User { Name = "John", Id = 1 };
// user.Id = 999; // 编译错误
// 🔥 实战应用 - 记录类型
public record UserInfo(string Name, int Id, DateTime CreatedAt)
{
public string DisplayName { get; init; } = Name.ToUpper();
}
9️⃣ record - 数据类型简化
常见痛点:大量样板代码用于数据传输对象
C#// ❌ 初级写法 - 传统类
public class PersonDto
{
public string FirstName { get; set; }
public string LastName { get; set; }
public override bool Equals(object obj) { /* 冗长实现 */ }
public override int GetHashCode() { /* 冗长实现 */ }
public override string ToString() { /* 冗长实现 */ }
}
// ✅ 资深写法 - 记录类型
public record PersonDto(string FirstName, string LastName);
// 🔥 实战应用 - API响应对象
public record ApiResponse<T>(
bool Success,
T Data,
string Message = "",
int StatusCode = 200
)
{
public static ApiResponse<T> Ok(T data) => new(true, data);
public static ApiResponse<T> Error(string message) => new(false, default(T), message, 400);
}
🔟 partial - 代码分离
常见痛点:自动生成代码与手写代码混在一起
C#// 🔥 实战应用 - 源代码生成器配合
// User.generated.cs (自动生成)
public partial class User
{
partial void OnPropertyChanged(string propertyName);
private string _name;
public string Name
{
get => _name;
set
{
_name = value;
OnPropertyChanged(nameof(Name));
}
}
}
// User.cs (手写代码)
public partial class User : INotifyPropertyChanged
{
public event PropertyChangedEventHandler PropertyChanged;
partial void OnPropertyChanged(string propertyName)
{
PropertyChanged?.Invoke(this, new PropertyChangedEventArgs(propertyName));
}
// 其他业务逻辑...
}
这个的好处太多了。
⚠️ 常见坑点提醒
- stackalloc注意事项:只能在unsafe上下文或Span中使用,栈空间有限
- fixed使用限制:需要unsafe上下文,注意内存安全
- init访问器版本要求:需要C# 9.0+和.NET 5+
- record类型限制:引用类型默认行为与值类型不同
🎯 总结:从初级到资深的进阶之路
通过掌握这10个隐藏关键词,你将能够:
✅ 写出更安全的代码:使用nameof、init避免运行时错误
✅ 提升代码性能:使用stackalloc、ref readonly优化内存使用
✅ 增强代码可读性:使用when、record简化复杂逻辑
记住,优秀的代码不仅要能运行,更要易维护、高性能、可扩展。这些关键词正是帮助你达到这个目标的利器!
💬 互动时间:
- 你在项目中使用过哪些高级C#特性?遇到过什么坑?
- 还有哪些C#隐藏特性想了解?留言告诉我!
觉得这篇文章有用?请分享给更多需要进阶的C#开发者朋友! 🚀
关注我,获取更多C#进阶技巧和最佳实践!
#CSharp #编程技巧 #软件开发 #性能优化
本文作者:技术老小子
本文链接:
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!