目录
作为一名资深的C#开发者,你是否在转向Java时被一些"看似相同实则不同"的语法细节困扰?变量声明方式的差异、运算符行为的微妙变化、控制流语句的细微区别——这些看似简单的基础语法,往往成为C#开发者学习Java路上的第一道坎。
本文将从基本数据类型、变量声明、运算符和控制流语句四个维度,为你详细对比Java与C#的语法差异,每个知识点都配有实战代码示例和踩坑提醒。让你在15分钟内掌握Java语法基础,告别转型初期的语法迷茫!
🔢 基本数据类型:细节决定成败
问题分析:数据类型看似相同,实则暗藏玄机
许多C#开发者初学Java时,看到int、double、boolean这些熟悉的关键字,以为可以无缝切换。然而,在数据范围、默认值、装箱拆箱等方面,两种语言存在重要差异。
解决方案:掌握核心差异点
💡 方案一:整型数据类型对比
Java代码示例:
Javapackage org.example;
public class DataTypeComparison{
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Java中的基本整型
byte b = 127;
short s = 32767;
int i = 2147483647;
long l = 9223372036854775807L; // 注意L后缀
// 字面量表示
int hex = 0xFF; // 十六进制
int binary = 0b1010; // 二进制(Java 7+)
int underScore = 1_000_000; // 下划线分隔(Java 7+)
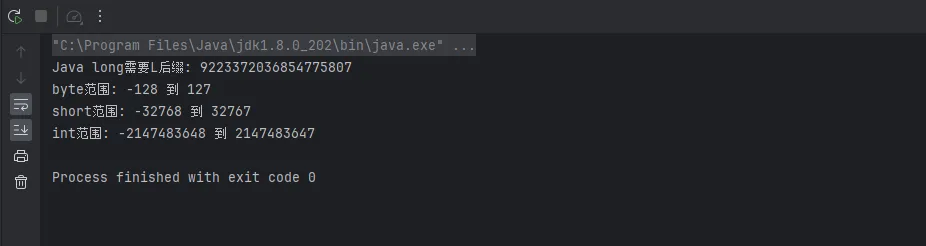
System.out.println("Java long需要L后缀: " + l);
//输出byte最大,最小值
System.out.println("byte范围: " + Byte.MIN_VALUE + " 到 " + Byte.MAX_VALUE);
//输出short最大,最小值
System.out.println("short范围: " + Short.MIN_VALUE + " 到 " + Short.MAX_VALUE);
//输出int最大,最小值
System.out.println("int范围: " + Integer.MIN_VALUE + " 到 " + Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
}
C#对比代码:
C#public class DataTypeComparison
{
public static void Main()
{
// C#中的基本整型
sbyte sb = 127; // -128 ~ 127
byte b = 255; // 0 ~ 255 (无符号)
short s = 32767; // -32768 ~ 32767
ushort us = 65535; // 0 ~ 65535 (无符号)
int i = 2147483647;
uint ui = 4294967295U; // 无符号整型,注意U后缀
long l = 9223372036854775807; // 无需后缀
Console.WriteLine("C#支持更多无符号类型");
}
}
⚠️ 常见坑点提醒:
- Java的
byte是有符号的(-128127),C#的255)byte是无符号的(0 - Java的长整型字面量必须加
L后缀,C#可选 - C#有更丰富的无符号整型,Java基本类型都是有符号的
💡 方案二:浮点型和布尔型对比
Java代码示例:
Javapackage org.example;
public class FloatBooleanDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 浮点型
float f = 3.14f; // 必须有f后缀
double d = 3.14; // 默认是double
// 特殊浮点值
double positiveInf = Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY;
double negativeInf = Double.NEGATIVE_INFINITY;
double nan = Double.NaN;
// 布尔型
boolean flag = true; // 只能是true或false
// boolean result = 1; // 编译错误!不能用数值
// 字符型
char c = 'A'; // 单引号
char unicode = '\u4e2d'; // 中文'中'
System.out.println("Java boolean严格区分: " + flag);
System.out.println("Unicode字符: " + unicode);
}
}

C#对比代码:
C#public class FloatBooleanDemo
{
public static void Main()
{
// 浮点型
float f = 3.14f; // 需要f后缀
double d = 3.14; // 默认是double
decimal dec = 3.14m; // 高精度,Java没有对应类型
// 布尔型
bool flag = true; // C#用bool关键字
// 字符型
char c = 'A';
char unicode = '\u4e2d';
Console.WriteLine($"C#有decimal类型: {dec}");
Console.WriteLine($"Unicode字符: {unicode}");
}
}
⚠️ 常见坑点提醒:
- Java用
boolean,C#用bool - C#有
decimal高精度浮点型,Java没有直接对应 - Java的boolean不能与数值类型转换,更加严格
💡 方案三:默认值和初始化差异
Java代码示例:
Javapackage org.example;
public class DefaultValueDemo {
// 类成员变量的默认值
private int intValue; // 0
private double doubleValue; // 0.0
private boolean boolValue; // false
private String stringValue; // null
private int[] arrayValue; // null
public void demonstrateDefaults() {
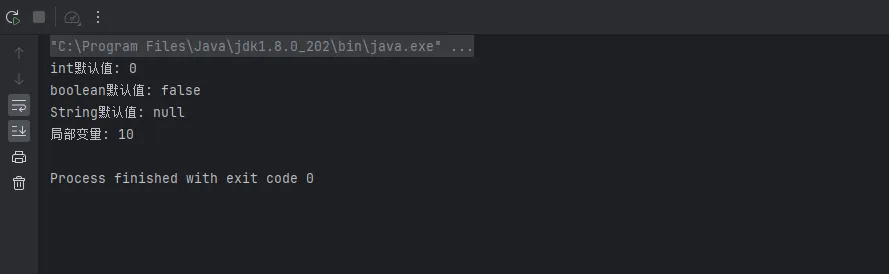
System.out.println("int默认值: " + intValue);
System.out.println("boolean默认值: " + boolValue);
System.out.println("String默认值: " + stringValue);
// 局部变量没有默认值,必须初始化
int localInt;
// System.out.println(localInt); // 编译错误!
localInt = 10; // 必须先赋值
System.out.println("局部变量: " + localInt);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
DefaultValueDemo demo = new DefaultValueDemo();
demo.demonstrateDefaults();
}
}
C#对比代码:
C#public class DefaultValueDemo
{
// 类成员字段的默认值
private int intValue; // 0
private double doubleValue; // 0.0
private bool boolValue; // false
private string stringValue; // null
private int[] arrayValue; // null
public void DemonstrateDefaults()
{
Console.WriteLine($"int默认值: {intValue}");
Console.WriteLine($"bool默认值: {boolValue}");
Console.WriteLine($"string默认值: {stringValue ?? "null"}");
// C#局部变量也必须初始化
int localInt;
// Console.WriteLine(localInt); // 编译错误!
localInt = 10;
Console.WriteLine($"局部变量: {localInt}");
}
}
📝 变量声明:现代化VS传统化
问题分析:声明方式影响代码可读性
C#开发者习惯了var关键字的类型推断和灵活的声明方式,转到Java时可能会感到约束较多。理解两种语言在变量声明上的差异,有助于写出更规范的Java代码。
解决方案:掌握各种声明模式
💡 方案一:类型推断对比
Java代码示例:
Javapackage org.example;
import java.util.*;
public class VariableDeclaration {
public void demonstrateDeclaration() {
// 传统显式声明
String name = "张三";
List<String> names = new ArrayList<>();
Map<String, Integer> scores = new HashMap<>();
// Java 10+ 支持var(局部变量类型推断)
var autoName = "李四"; // 推断为String
var autoList = new ArrayList<String>(); // 推断为ArrayList<String>
var autoMap = new HashMap<String, Integer>(); // 推断类型
// var的限制
// var uninitalized; // 编译错误!必须初始化
// var nullVar = null; // 编译错误!不能推断null
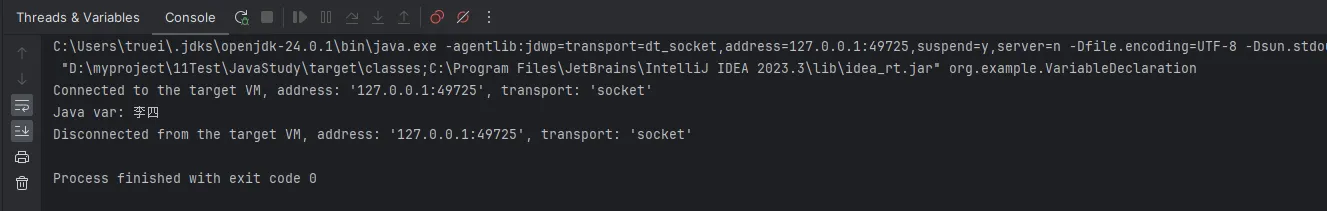
System.out.println("Java var: " + autoName);
// 钻石操作符(Java 7+)
List<String> diamondList = new ArrayList<>(); // 右侧可省略泛型
Map<String, List<Integer>> complexMap = new HashMap<>();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
VariableDeclaration demo = new VariableDeclaration();
demo.demonstrateDeclaration();
}
}
XML<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>17</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>17</maven.compiler.target>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
</properties>
注意调整pom.xml中的source,target
C#对比代码:
C#using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class VariableDeclaration
{
public void DemonstrateDeclaration()
{
// 显式声明
string name = "张三";
List<string> names = new List<string>();
Dictionary<string, int> scores = new Dictionary<string, int>();
// C#的var(从C# 3.0开始)
var autoName = "李四"; // 推断为string
var autoList = new List<string>(); // 推断为List<string>
var autoDict = new Dictionary<string, int>(); // 推断类型
// C#的var更灵活
var anonymous = new { Name = "匿名", Age = 25 }; // 匿名类型
Console.WriteLine($"C# var: {autoName}");
// C#目标类型new(C# 9.0+)
List<string> targetList = new(); // 更简洁
Dictionary<string, int> targetDict = new();
}
}
💡 方案二:常量和final关键字
Java代码示例:
Javapackage org.example;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class ConstantDemo {
// 编译时常量
public static final String COMPANY_NAME = "科技公司";
public static final int MAX_USERS = 1000;
// 运行时常量
private final String instanceId;
private final List<String> readOnlyList;
public ConstantDemo() {
// final变量可以在构造器中初始化
this.instanceId = generateId();
this.readOnlyList = new ArrayList<>();
// this.readOnlyList = new ArrayList<>(); // 编译错误!不能重新赋值
}
public void demonstrateFinal() {
final int localConstant = 42;
// localConstant = 43; // 编译错误!
final List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("可以修改内容"); // 允许!只是引用不能变
System.out.println("List : " + list);
// list = new ArrayList<>(); // 编译错误!不能重新赋值引用
System.out.println("Java final: " + localConstant);
}
private String generateId() {
return "ID_" + System.currentTimeMillis();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConstantDemo demo = new ConstantDemo();
demo.demonstrateFinal();
System.out.println("Company: " + COMPANY_NAME + ", Max Users: " + MAX_USERS);
}
}

C#对比代码:
C#using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class ConstantDemo
{
// 编译时常量
public const string CompanyName = "科技公司";
public const int MaxUsers = 1000;
// 运行时常量
private readonly string instanceId;
private readonly List<string> readOnlyList;
public ConstantDemo()
{
// readonly可以在构造函数中赋值
this.instanceId = GenerateId();
this.readOnlyList = new List<string>();
}
public void DemonstrateReadonly()
{
const int localConstant = 42; // C#局部const
// C#没有局部readonly,但有ref readonly
var list = new List<string>();
list.Add("可以修改内容");
Console.WriteLine($"C# const: {localConstant}");
}
private string GenerateId()
{
return "ID_" + DateTimeOffset.Now.ToUnixTimeMilliseconds();
}
}
⚠️ 常见坑点提醒:
- Java用
final,C#用const(编译时)和readonly(运行时) - Java的
var需要Java 10+,C#从3.0就支持 - Java的
final对象内容仍可修改,只是引用不可变
⚡ 运算符差异:魔鬼藏在细节里
问题分析:运算符行为的微妙差异
看似相同的运算符,在两种语言中可能有不同的行为,特别是在字符串操作、相等比较、位运算等方面。
💡 方案一:字符串运算符对比
Java代码示例:
Javapackage org.example;
import java.util.Objects;
public class OperatorDemo {
public void demonstrateStringOperators() {
// 字符串连接
String str1 = "Hello";
String str2 = "World";
String result = str1 + " " + str2; // 创建新对象
// 字符串比较 - 重要!
String a = new String("test");
String b = new String("test");
String c = "test";
String d = "test";
System.out.println("== 比较引用:");
System.out.println("a == b: " + (a == b));
System.out.println("c == d: " + (c == d));
System.out.println("equals 比较内容:");
System.out.println("a.equals(b): " + a.equals(b));
// 空值安全比较
String nullStr = null;
// System.out.println(nullStr.equals("test"));
System.out.println("test".equals(nullStr));
System.out.println(Objects.equals(nullStr, "test")); // false 更安全
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
OperatorDemo demo = new OperatorDemo();
demo.demonstrateStringOperators();
}
}

这块估计是大我刚用Java的C#程序员最容易不出的地方,毕竟C#中比较简单。
C#对比代码:
C#using System;
public class OperatorDemo
{
public void DemonstrateStringOperators()
{
// 字符串连接
string str1 = "Hello";
string str2 = "World";
string result = str1 + " " + str2; // C#也创建新对象
// 字符串比较
string a = new string("test".ToCharArray());
string b = new string("test".ToCharArray());
string c = "test";
string d = "test";
Console.WriteLine("== 比较:");
Console.WriteLine($"a == b: {a == b}"); // true! C#重载了==
Console.WriteLine($"c == d: {c == d}"); // true
Console.WriteLine("Equals 比较:");
Console.WriteLine($"a.Equals(b): {a.Equals(b)}"); // true
// 空值安全
string nullStr = null;
Console.WriteLine($"安全比较: {string.Equals(nullStr, "test")}"); // false
}
}
💡 方案二:数值运算符差异
Java代码示例:
Javapackage org.example;
public class NumericOperators {
public void demonstrateNumericOps() {
// 整数除法
int a = 7;
int b = 3;
System.out.println("7 / 3 = " + (a / b));
System.out.println("7.0 / 3 = " + (7.0 / 3));
// 取模运算
System.out.println("7 % 3 = " + (a % b));
System.out.println("7 % -3 = " + (7 % -3));
System.out.println("-7 % 3 = " + (-7 % 3));
// 位运算
int x = 12; // 1100
int y = 10; // 1010
System.out.println("12 & 10 = " + (x & y));
System.out.println("12 | 10 = " + (x | y));
System.out.println("12 ^ 10 = " + (x ^ y));
System.out.println("~12 = " + (~x));
// 移位运算
System.out.println("12 << 2 = " + (x << 2)); // 48 左移
System.out.println("12 >> 2 = " + (x >> 2)); // 3 算术右移
System.out.println("-12 >>> 2 = " + (-12 >>> 2)); // 无符号右移
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
NumericOperators demo = new NumericOperators();
demo.demonstrateNumericOps();
}
}

C#对比代码:
C#using System;
public class NumericOperators
{
public void DemonstrateNumericOps()
{
// 整数除法
int a = 7;
int b = 3;
Console.WriteLine($"7 / 3 = {a / b}"); // 2 整数除法
Console.WriteLine($"7.0 / 3 = {7.0 / 3}"); // 2.333...
// 取模运算(行为相同)
Console.WriteLine($"7 % 3 = {a % b}"); // 1
Console.WriteLine($"7 % -3 = {7 % -3}"); // 1
Console.WriteLine($"-7 % 3 = {-7 % 3}"); // -1
// 位运算
int x = 12; // 1100
int y = 10; // 1010
Console.WriteLine($"12 & 10 = {x & y}"); // 8 (1000)
Console.WriteLine($"12 | 10 = {x | y}"); // 14 (1110)
Console.WriteLine($"12 ^ 10 = {x ^ y}"); // 6 (0110)
Console.WriteLine($"~12 = {~x}"); // -13
// 移位运算
Console.WriteLine($"12 << 2 = {x << 2}"); // 48 左移
Console.WriteLine($"12 >> 2 = {x >> 2}"); // 3 算术右移
// C#检查溢出
try
{
checked
{
int max = int.MaxValue;
int overflow = max + 1; // 抛出OverflowException
}
}
catch (OverflowException ex)
{
Console.WriteLine("C#可以检查整数溢出");
}
}
}
⚠️ 常见坑点提醒:
- Java字符串比较必须用
equals(),C#可以用== - Java有无符号右移
>>>,C#没有 - C#有
checked/unchecked上下文检查整数溢出,Java默认不检查
🔄 控制流语句:结构化思维的体现
问题分析:控制流语法的演进差异
两种语言的控制流语句在基本结构上相似,但在一些现代化特性上有所不同,比如增强for循环、switch表达式等。
💡 方案一:循环语句对比
Java代码示例:
Javapackage org.example;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
public class ControlFlowDemo {
public void demonstrateLoops() {
List<String> languages = Arrays.asList("Java", "C#", "Python", "Go");
// 传统for循环
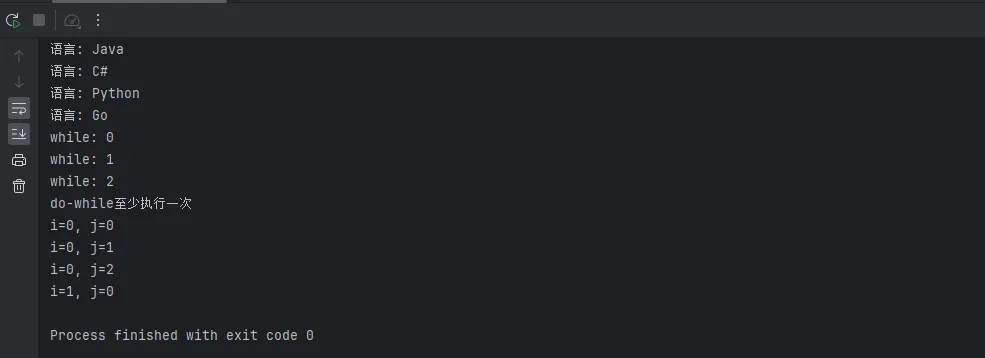
for (int i = 0; i < languages.size(); i++) {
System.out.println("索引 " + i + ": " + languages.get(i));
}
// 增强for循环 (foreach)
for (String lang : languages) {
System.out.println("语言: " + lang);
if (lang.equals("C#")) {
continue; // 跳过本次循环
}
}
// while和do-while
int count = 0;
while (count < 3) {
System.out.println("while: " + count++);
}
do {
System.out.println("do-while至少执行一次");
} while (false);
// 嵌套循环与标签
outer: for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
if (i == 1 && j == 1) {
break outer; // 跳出外层循环
}
System.out.println("i=" + i + ", j=" + j);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ControlFlowDemo demo = new ControlFlowDemo();
demo.demonstrateLoops();
}
}
这块基本一样
C#对比代码:
C#using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class ControlFlowDemo
{
public void DemonstrateLoops()
{
var languages = new List<string> { "Java", "C#", "Python", "Go" };
// 传统for循环
for (int i = 0; i < languages.Count; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine($"索引 {i}: {languages[i]}");
}
// foreach循环
foreach (string lang in languages)
{
Console.WriteLine($"语言: {lang}");
if (lang == "C#")
{
continue; // 跳过本次循环
}
}
// while和do-while
int count = 0;
while (count < 3)
{
Console.WriteLine($"while: {count++}");
}
do
{
Console.WriteLine("do-while至少执行一次");
} while (false);
// 嵌套循环与goto(不推荐)
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++)
{
if (i == 1 && j == 1)
{
goto OuterBreak; // C#有goto,但不推荐
}
Console.WriteLine($"i={i}, j={j}");
}
}
OuterBreak:
Console.WriteLine("跳出嵌套循环");
}
}
💡 方案二:条件语句和模式匹配
Java代码示例:
Javapackage org.example;
public class ConditionalDemo {
public void demonstrateConditionals() {
// if-else语句
int score = 85;
String grade;
if (score >= 90) {
grade = "A";
} else if (score >= 80) {
grade = "B";
} else if (score >= 70) {
grade = "C";
} else {
grade = "D";
}
System.out.println("成绩等级: " + grade);
// 三元运算符
String result = score >= 60 ? "及格" : "不及格";
System.out.println("结果: " + result);
// 传统switch
int dayOfWeek = 3;
String dayName;
switch (dayOfWeek) {
case 1:
dayName = "周一";
break;
case 2:
dayName = "周二";
break;
case 3:
dayName = "周三";
break;
default:
dayName = "其他";
break;
}
System.out.println("今天是: " + dayName);
// Java 14+ Switch表达式
String modernDayName = switch (dayOfWeek) {
case 1 -> "周一";
case 2 -> "周二";
case 3 -> "周三";
case 4, 5 -> "工作日"; // 多个case
default -> "周末";
};
System.out.println("现代switch: " + modernDayName);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConditionalDemo demo = new ConditionalDemo();
demo.demonstrateConditionals();
}
}

C#对比代码:
C#using System;
public class ConditionalDemo
{
public void DemonstrateConditionals()
{
// if-else语句
int score = 85;
string grade;
if (score >= 90)
{
grade = "A";
}
else if (score >= 80)
{
grade = "B";
}
else if (score >= 70)
{
grade = "C";
}
else
{
grade = "D";
}
Console.WriteLine($"成绩等级: {grade}");
// 三元运算符
string result = score >= 60 ? "及格" : "不及格";
Console.WriteLine($"结果: {result}");
// 传统switch
int dayOfWeek = 3;
string dayName;
switch (dayOfWeek)
{
case 1:
dayName = "周一";
break;
case 2:
dayName = "周二";
break;
case 3:
dayName = "周三";
break;
default:
dayName = "其他";
break;
}
Console.WriteLine($"今天是: {dayName}");
// C# 8.0+ Switch表达式
string modernDayName = dayOfWeek switch
{
1 => "周一",
2 => "周二",
3 => "周三",
4 or 5 => "工作日", // 多个case
_ => "周末"
};
Console.WriteLine($"现代switch: {modernDayName}");
// C#模式匹配
object obj = "Hello";
string typeMessage = obj switch
{
string s when s.Length > 5 => $"长字符串: {s}",
string s => $"短字符串: {s}",
int i when i > 0 => $"正整数: {i}",
int i => $"非正整数: {i}",
_ => "其他类型"
};
Console.WriteLine($"模式匹配: {typeMessage}");
}
}
⚠️ 常见坑点提醒:
- Java用
:增强for循环,C#用in - Java 14+才支持switch表达式,C# 8.0就支持
- C#的模式匹配更强大,支持类型匹配和条件
💡 方案三:异常处理对比
Java代码示例:
Javapackage org.example;
import java.io.*;
public class ExceptionDemo {
public void demonstrateExceptions() {
// try-catch-finally
try {
int result = riskyOperation();
System.out.println("结果: " + result);
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("算术异常: " + e.getMessage());
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
System.out.println("参数异常: " + e.getMessage());
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("其他异常: " + e.getMessage());
} finally {
System.out.println("finally块总是执行");
}
// try-with-resources (Java 7+)
try (BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("test.txt"))) {
String line = reader.readLine();
System.out.println("读取内容: " + line);
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("IO异常: " + e.getMessage());
} // 自动关闭资源,无需finally
// 多重资源
try (FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("input.txt");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("output.txt")) {
// 使用资源
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("处理多个资源");
}
}
public int riskyOperation() throws ArithmeticException {
return 10 / 0; // 抛出异常
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExceptionDemo demo = new ExceptionDemo();
demo.demonstrateExceptions();
}
}
这块基本一样的,只是c#中用using自动关闭资源
C#对比代码:
C#using System;
using System.IO;
public class ExceptionDemo
{
public void DemonstrateExceptions()
{
// try-catch-finally
try
{
int result = RiskyOperation();
Console.WriteLine($"结果: {result}");
}
catch (DivideByZeroException ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"除零异常: {ex.Message}");
}
catch (ArgumentException ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"参数异常: {ex.Message}");
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"其他异常: {ex.Message}");
}
finally
{
Console.WriteLine("finally块总是执行");
}
// using语句(相当于try-with-resources)
using (var reader = new StreamReader("test.txt"))
{
string line = reader.ReadLine();
Console.WriteLine($"读取内容: {line}");
} // 自动Dispose
// C# 8.0+ using声明
using var fileStream = new FileStream("data.txt", FileMode.Open);
// 文件在作用域结束时自动关闭
// 多重using
using (var input = new FileStream("input.txt", FileMode.Open))
using (var output = new FileStream("output.txt", FileMode.Create))
{
// 使用资源
}
}
public int RiskyOperation()
{
return 10 / 0; // 抛出异常
}
}
🎯 总结:掌握差异,顺利转型
通过以上详细对比,我们可以看出Java与C#在语法基础层面既有相似性,也存在重要差异:
💡 三个核心要点
- 数据类型要谨慎:Java的基本类型都是有符号的,字符串比较必须用equals(),而C#提供了更丰富的类型系统和运算符重载。
- 现代化特性有差异:Java的var需要10+版本,switch表达式需要14+版本;而C#在这些特性上起步更早,模式匹配功能更强大。
- 资源管理方式不同:Java使用try-with-resources,C#使用using语句,都能实现自动资源管理,但语法略有不同。
收藏级代码模板:
- Java字符串安全比较:
Objects.equals(str1, str2) - C#模式匹配:
obj switch { Type t when condition => result, _ => default }
作为C#开发者转向Java,关键是要理解差异背后的设计思想,而不是死记硬背语法规则。两种语言都在不断演进,保持学习的心态,关注最新特性的发展趋势。
💬 互动时间:你在C#转Java的过程中,哪个语法差异让你印象最深?在实际项目中遇到过哪些"踩坑"经历?欢迎在评论区分享你的转型心得!
觉得这篇对比分析有用,请转发给更多正在转型路上的同行朋友! 🚀
本文作者:技术老小子
本文链接:
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!