目录
在日常C#开发中,你是否遇到过这样的痛点:需要自动化测试复杂的WPF应用?想要开发辅助工具来操作第三方软件?传统的SendMessage和Win32 API让你头疼不已?今天,我将为你详细解析微软官方推荐的自动化解决方案——UI Automation,它不仅能解决上述问题,还能让你的自动化开发事半功倍。
本文将从UI Automation的基础概念出发,深入对比各种自动化技术的优劣,并通过实战代码帮你快速掌握这项强大的技术。无论你是自动化测试工程师还是桌面应用开发者,这篇文章都将成为你的必备收藏。
🎯 什么是UI Automation?
UI Automation是微软.NET Framework 3.0开始引入的官方UI自动化框架,专门用于Windows桌面应用程序的自动化操作和测试。它提供了一套标准化的API来访问和操作各种UI元素,无论是WPF、WinForms、Win32还是Web应用。
核心特点:
- 跨技术栈支持:统一操作WPF、WinForms、Win32等不同技术的应用
- 无障碍访问:内置支持屏幕阅读器等辅助技术
- 事件驱动:可监听UI元素的各种变化事件
- 结构化访问:通过元素树的形式组织UI结构
C#
using UIAutomationClient;
namespace AppUiAutomation
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var automation = new CUIAutomation8();
var rootElement = automation.GetRootElement();
var cal= rootElement.FindFirst(
TreeScope.TreeScope_Children,
automation.CreatePropertyCondition(
UIA_PropertyIds.UIA_NamePropertyId,
"Calculator"
)
);
if (cal != null)
{
Console.WriteLine("找到计算器");
}
}
}
}
注意:在.net下这个引用比较麻烦,使用COMReference
XML<Project Sdk="Microsoft.NET.Sdk">
<PropertyGroup>
<OutputType>Exe</OutputType>
<TargetFramework>net8.0</TargetFramework>
<ImplicitUsings>enable</ImplicitUsings>
<Nullable>enable</Nullable>
</PropertyGroup>
<ItemGroup>
<COMReference Include="UIAutomationClient">
<WrapperTool>tlbimp</WrapperTool>
<VersionMinor>0</VersionMinor>
<VersionMajor>1</VersionMajor>
<Guid>944de083-8fb8-45cf-bcb7-c477acb2f897</Guid>
<Lcid>0</Lcid>
<Isolated>false</Isolated>
<EmbedInteropTypes>false</EmbedInteropTypes>
</COMReference>
<COMReference Include="UIA">
<WrapperTool>tlbimp</WrapperTool>
<VersionMinor>0</VersionMinor>
<VersionMajor>1</VersionMajor>
<Guid>930299ce-9965-4dec-b0f4-a54848d4b667</Guid>
<Lcid>0</Lcid>
<Isolated>false</Isolated>
<EmbedInteropTypes>false</EmbedInteropTypes>
</COMReference>
</ItemGroup>
</Project>
📚 UI Automation的历史与发展
发展历程:
- 2006年:随.NET Framework 3.0首次发布
- 2009年:.NET 4.0增强了性能和稳定性
- 2012年:Windows 8引入UI Automation Core API
- 2015年:UWP应用全面支持UI Automation
- 至今:持续更新,支持最新的Windows特性
UI Automation的设计初衷是为了标准化Windows平台的UI访问方式,解决传统方法的碎片化问题。它不仅服务于自动化测试,更是Windows无障碍访问的技术基础。
⚔️ 技术对比:UI Automation vs 传统方法
让我通过实际代码对比来展示各种技术的差异:
🔴 Win32 API方式
C#// 使用Win32 API查找和点击按钮
[DllImport("user32.dll")]
static extern IntPtr FindWindow(string lpClassName, string lpWindowName);
[DllImport("user32.dll")]
static extern IntPtr FindWindowEx(IntPtr hwndParent, IntPtr hwndChildAfter,
string lpszClass, string lpszWindow);
[DllImport("user32.dll")]
static extern bool PostMessage(IntPtr hWnd, uint Msg, IntPtr wParam, IntPtr lParam);
// 复杂的窗口句柄查找过程
IntPtr mainWindow = FindWindow(null, "计算器");
IntPtr button = FindWindowEx(mainWindow, IntPtr.Zero, "Button", "1");
PostMessage(button, 0x0201, IntPtr.Zero, IntPtr.Zero); // 模拟点击
🟡 SendMessage方式
C#// SendMessage方式操作文本框
[DllImport("user32.dll")]
static extern IntPtr SendMessage(IntPtr hWnd, int Msg, IntPtr wParam, string lParam);
IntPtr textBox = FindWindowEx(mainWindow, IntPtr.Zero, "Edit", null);
SendMessage(textBox, 0x000C, IntPtr.Zero, "Hello World"); // WM_SETTEXT
// ❌ 问题:消息常量记忆困难、兼容性问题多
早此年我基本是这么做的
🟢 UI Automation方式
C#// 使用UI Automation的优雅方式
public class CalculatorAutomation
{
private AutomationElement calculatorWindow;
public void Initialize()
{
// 查找计算器窗口
calculatorWindow = AutomationElement.RootElement.FindFirst(
TreeScope.Children,
new PropertyCondition(AutomationElement.NameProperty, "计算器")
);
}
public void ClickButton(string buttonText)
{
var button = calculatorWindow.FindFirst(
TreeScope.Descendants,
new PropertyCondition(AutomationElement.NameProperty, buttonText)
);
if (button != null)
{
var invokePattern = button.GetCurrentPattern(InvokePattern.Pattern) as InvokePattern;
invokePattern?.Invoke();
}
}
public string GetResult()
{
var resultElement = calculatorWindow.FindFirst(
TreeScope.Descendants,
new PropertyCondition(AutomationElement.AutomationIdProperty, "CalculatorResults")
);
return resultElement?.Current.Name ?? "";
}
}
// ✅ 优势:代码清晰、面向对象、易于维护
🏆 UI Automation的核心优势
1. 📈 跨平台兼容性强
C#// 同一套代码可以操作不同技术的应用
public class UniversalAutomation
{
public void OperateAnyApplication(string windowTitle)
{
var window = AutomationElement.RootElement.FindFirst(
TreeScope.Children,
new PropertyCondition(AutomationElement.NameProperty, windowTitle)
);
// 无论是WPF、WinForms还是Win32应用,操作方式一致
var buttons = window.FindAll(
TreeScope.Descendants,
new PropertyCondition(AutomationElement.ControlTypeProperty, ControlType.Button)
);
Console.WriteLine($"找到 {buttons.Count} 个按钮");
}
}
2. 🎭 模式化操作
C#// 不同类型的控件有对应的操作模式
public void DemonstratePatterns(AutomationElement element)
{
// 文本框操作
if (element.TryGetCurrentPattern(ValuePattern.Pattern, out object valuePattern))
{
((ValuePattern)valuePattern).SetValue("输入文本");
}
// 复选框操作
if (element.TryGetCurrentPattern(TogglePattern.Pattern, out object togglePattern))
{
((TogglePattern)togglePattern).Toggle();
}
// 选择项操作
if (element.TryGetCurrentPattern(SelectionItemPattern.Pattern, out object selectionPattern))
{
((SelectionItemPattern)selectionPattern).Select();
}
}
3. 🔊 事件监听机制
C#public class UIEventListener
{
public void StartListening()
{
// 监听窗口打开事件
Automation.AddAutomationEventHandler(
WindowPattern.WindowOpenedEvent,
AutomationElement.RootElement,
TreeScope.Children,
OnWindowOpened
);
// 监听焦点变化
Automation.AddAutomationFocusChangedEventHandler(OnFocusChanged);
}
private void OnWindowOpened(object sender, AutomationEventArgs e)
{
var element = sender as AutomationElement;
Console.WriteLine($"新窗口打开: {element?.Current.Name}");
}
private void OnFocusChanged(object sender, AutomationFocusChangedEventArgs e)
{
var element = sender as AutomationElement;
Console.WriteLine($"焦点切换到: {element?.Current.Name}");
}
}
⚠️ UI Automation的局限性
1. 🐌 性能考虑
C#// ❌ 低效的查找方式
public AutomationElement SlowFind()
{
// 每次都从根元素开始查找,性能差
return AutomationElement.RootElement.FindFirst(
TreeScope.Descendants, // 搜索所有后代元素
new PropertyCondition(AutomationElement.NameProperty, "按钮1")
);
}
// ✅ 优化后的查找方式
public class OptimizedAutomation
{
private AutomationElement cachedParent;
public AutomationElement FastFind()
{
// 缓存父级元素,减少搜索范围
if (cachedParent == null)
{
cachedParent = AutomationElement.RootElement.FindFirst(
TreeScope.Children,
new PropertyCondition(AutomationElement.NameProperty, "主窗口")
);
}
// 在较小范围内查找
return cachedParent?.FindFirst(
TreeScope.Children,
new PropertyCondition(AutomationElement.NameProperty, "按钮1")
);
}
}
2. 🚫 技术限制
C#// 某些场景下UI Automation可能无效
public void CheckLimitations()
{
try
{
// 游戏界面通常无法识别
var gameWindow = AutomationElement.RootElement.FindFirst(
TreeScope.Children,
new PropertyCondition(AutomationElement.NameProperty, "游戏窗口")
);
if (gameWindow != null)
{
// 可能无法获取游戏内的UI元素
var gameButtons = gameWindow.FindAll(TreeScope.Descendants, Condition.TrueCondition);
Console.WriteLine($"游戏UI元素数量: {gameButtons.Count}");
}
}
catch (ElementNotAvailableException ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"元素不可用: {ex.Message}");
// 此时可考虑使用图像识别等替代方案
}
}
🛠️ 实战应用场景
场景1:自动化测试框架
C#using System;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.Threading;
using UIAutomationClient;
public class ImprovedTestFramework
{
private Process targetApp;
private CUIAutomation8 automation;
public ImprovedTestFramework()
{
automation = new CUIAutomation8();
}
public bool StartTargetApplication(string appPath)
{
try
{
targetApp = Process.Start(appPath);
Thread.Sleep(2000); // 等待应用启动
return targetApp != null && !targetApp.HasExited;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"启动目标应用失败: {ex.Message}");
return false;
}
}
public void CloseTargetApplication()
{
try
{
if (targetApp != null && !targetApp.HasExited)
{
targetApp.CloseMainWindow();
targetApp.WaitForExit(5000);
if (!targetApp.HasExited)
{
targetApp.Kill();
}
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"关闭目标应用失败: {ex.Message}");
}
}
public bool LoginTest(string username, string password)
{
try
{
Console.WriteLine("开始登录测试...");
var loginWindow = WaitForWindow("登录窗口", TimeSpan.FromSeconds(10));
if (loginWindow == null)
{
Console.WriteLine("未找到登录窗口");
return false;
}
Console.WriteLine("找到登录窗口");
// 输入用户名
if (!SetTextValue(loginWindow, "用户名", username))
{
Console.WriteLine("设置用户名失败");
return false;
}
// 输入密码 - 特殊处理PasswordBox
if (!SetPasswordValue(loginWindow, "密码", password))
{
Console.WriteLine("设置密码失败");
return false;
}
// 点击登录按钮
if (!ClickButton(loginWindow, "登录"))
{
Console.WriteLine("点击登录按钮失败");
return false;
}
// 等待一下让登录处理完成
Thread.Sleep(1500);
// 验证登录结果 - 检查是否出现主界面
var mainWindow = WaitForWindow("主界面", TimeSpan.FromSeconds(8));
bool loginSuccess = mainWindow != null;
Console.WriteLine($"登录测试结果: {(loginSuccess ? "成功" : "失败")}");
return loginSuccess;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"登录测试失败: {ex.Message}");
return false;
}
}
private bool SetPasswordValue(IUIAutomationElement parent, string controlName, string value)
{
try
{
// 查找PasswordBox控件 - 先通过Name属性查找
var nameCondition = automation.CreatePropertyCondition(
UIA_PropertyIds.UIA_NamePropertyId,
controlName);
var passwordControl = parent.FindFirst(
TreeScope.TreeScope_Descendants,
nameCondition);
if (passwordControl == null)
{
// 尝试通过控件类型查找PasswordBox
var classCondition = automation.CreatePropertyCondition(
UIA_PropertyIds.UIA_ClassNamePropertyId,
"PasswordBox");
var passwordControls = parent.FindAll(
TreeScope.TreeScope_Descendants,
classCondition);
if (passwordControls.Length > 0)
{
passwordControl = passwordControls.GetElement(0);
}
}
if (passwordControl == null)
{
Console.WriteLine($"未找到密码控件: {controlName}");
return false;
}
// 设置焦点并输入密码
passwordControl.SetFocus();
Thread.Sleep(200);
// 清空现有内容并输入密码
SendKeys("^a"); // Ctrl+A 全选
Thread.Sleep(100);
SendKeys("{DELETE}"); // 删除
Thread.Sleep(100);
SendKeys(value); // 输入新值
Console.WriteLine($"设置密码成功: {controlName}");
return true;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"设置密码失败 {controlName}: {ex.Message}");
return false;
}
}
private IUIAutomationElement WaitForWindow(string windowName, TimeSpan timeout)
{
var endTime = DateTime.Now.Add(timeout);
while (DateTime.Now < endTime)
{
var rootElement = automation.GetRootElement();
var condition = automation.CreatePropertyCondition(
UIA_PropertyIds.UIA_NamePropertyId,
windowName);
var window = rootElement.FindFirst(
TreeScope.TreeScope_Children,
condition);
if (window != null)
{
Console.WriteLine($"找到窗口: {windowName}");
return window;
}
Thread.Sleep(500);
}
Console.WriteLine($"超时未找到窗口: {windowName}");
return null;
}
private bool SetTextValue(IUIAutomationElement parent, string controlName, string value)
{
try
{
// 通过Name属性查找文本控件
var nameCondition = automation.CreatePropertyCondition(
UIA_PropertyIds.UIA_NamePropertyId,
controlName);
var textControl = parent.FindFirst(
TreeScope.TreeScope_Descendants,
nameCondition);
if (textControl == null)
{
Console.WriteLine($"未找到文本控件: {controlName}");
return false;
}
// 尝试使用ValuePattern设置文本
try
{
var valuePattern = (IUIAutomationValuePattern)textControl.GetCurrentPattern(UIA_PatternIds.UIA_ValuePatternId);
if (valuePattern != null)
{
valuePattern.SetValue(value);
Console.WriteLine($"通过ValuePattern设置文本: {controlName} = {value}");
return true;
}
}
catch
{
// ValuePattern不可用,继续使用SendKeys
}
// 使用SendKeys方式
textControl.SetFocus();
Thread.Sleep(200);
SendKeys("^a"); // Ctrl+A 全选
Thread.Sleep(100);
SendKeys("{DELETE}"); // 删除
Thread.Sleep(100);
SendKeys(value); // 输入新值
Console.WriteLine($"通过SendKeys设置文本: {controlName} = {value}");
return true;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"设置文本值失败 {controlName}: {ex.Message}");
return false;
}
}
private bool ClickButton(IUIAutomationElement parent, string buttonName)
{
try
{
// 创建组合条件:控件类型为Button且Name为指定值
var buttonTypeCondition = automation.CreatePropertyCondition(
UIA_PropertyIds.UIA_ControlTypePropertyId,
UIA_ControlTypeIds.UIA_ButtonControlTypeId);
var buttonNameCondition = automation.CreatePropertyCondition(
UIA_PropertyIds.UIA_NamePropertyId,
buttonName);
var andCondition = automation.CreateAndCondition(buttonTypeCondition, buttonNameCondition);
var button = parent.FindFirst(
TreeScope.TreeScope_Descendants,
andCondition);
if (button == null)
{
Console.WriteLine($"未找到按钮: {buttonName}");
return false;
}
// 检查按钮是否可用 - 修复布尔值检查
int isEnabled = button.CurrentIsEnabled;
if (isEnabled == 0) // 0表示false,非0表示true
{
Console.WriteLine($"按钮不可用: {buttonName}");
return false;
}
// 尝试使用InvokePattern点击按钮
try
{
var invokePattern = (IUIAutomationInvokePattern)button.GetCurrentPattern(UIA_PatternIds.UIA_InvokePatternId);
if (invokePattern != null)
{
invokePattern.Invoke();
Console.WriteLine($"点击按钮成功: {buttonName}");
return true;
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"InvokePattern失败: {ex.Message}");
}
// 如果InvokePattern失败,尝试鼠标点击
try
{
tagPOINT clickablePoint;
button.GetClickablePoint(out clickablePoint);
SetCursorPos(clickablePoint.x, clickablePoint.y);
Thread.Sleep(100);
mouse_event(MOUSEEVENTF_LEFTDOWN | MOUSEEVENTF_LEFTUP, 0, 0, 0, UIntPtr.Zero);
Console.WriteLine($"通过鼠标点击按钮: {buttonName}");
return true;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"鼠标点击失败: {ex.Message}");
}
Console.WriteLine($"无法点击按钮: {buttonName}");
return false;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"点击按钮失败 {buttonName}: {ex.Message}");
return false;
}
}
// 简单的SendKeys实现,使用Windows API
private void SendKeys(string keys)
{
foreach (char c in keys)
{
if (c == '^')
{
// 处理Ctrl键组合,这里简化处理
continue;
}
else if (keys.StartsWith("^a"))
{
// Ctrl+A
keybd_event(VK_CONTROL, 0, 0, UIntPtr.Zero);
keybd_event(VK_A, 0, 0, UIntPtr.Zero);
keybd_event(VK_A, 0, KEYEVENTF_KEYUP, UIntPtr.Zero);
keybd_event(VK_CONTROL, 0, KEYEVENTF_KEYUP, UIntPtr.Zero);
return;
}
else if (keys == "{DELETE}")
{
keybd_event(VK_DELETE, 0, 0, UIntPtr.Zero);
keybd_event(VK_DELETE, 0, KEYEVENTF_KEYUP, UIntPtr.Zero);
return;
}
else
{
// 普通字符输入
short vk = VkKeyScan(c);
byte virtualKey = (byte)(vk & 0xFF);
keybd_event(virtualKey, 0, 0, UIntPtr.Zero);
keybd_event(virtualKey, 0, KEYEVENTF_KEYUP, UIntPtr.Zero);
}
}
}
// Windows API声明
[System.Runtime.InteropServices.DllImport("user32.dll")]
private static extern bool SetCursorPos(int x, int y);
[System.Runtime.InteropServices.DllImport("user32.dll")]
private static extern void mouse_event(uint dwFlags, int dx, int dy, uint dwData, UIntPtr dwExtraInfo);
[System.Runtime.InteropServices.DllImport("user32.dll")]
private static extern void keybd_event(byte bVk, byte bScan, uint dwFlags, UIntPtr dwExtraInfo);
[System.Runtime.InteropServices.DllImport("user32.dll")]
private static extern short VkKeyScan(char ch);
private const uint MOUSEEVENTF_LEFTDOWN = 0x0002;
private const uint MOUSEEVENTF_LEFTUP = 0x0004;
private const uint KEYEVENTF_KEYUP = 0x0002;
// 虚拟键码
private const byte VK_CONTROL = 0x11;
private const byte VK_A = 0x41;
private const byte VK_DELETE = 0x2E;
// 测试套件
public void RunAllTests(string targetAppPath)
{
Console.WriteLine("=== UI自动化测试开始 ===");
int passedTests = 0;
int totalTests = 0;
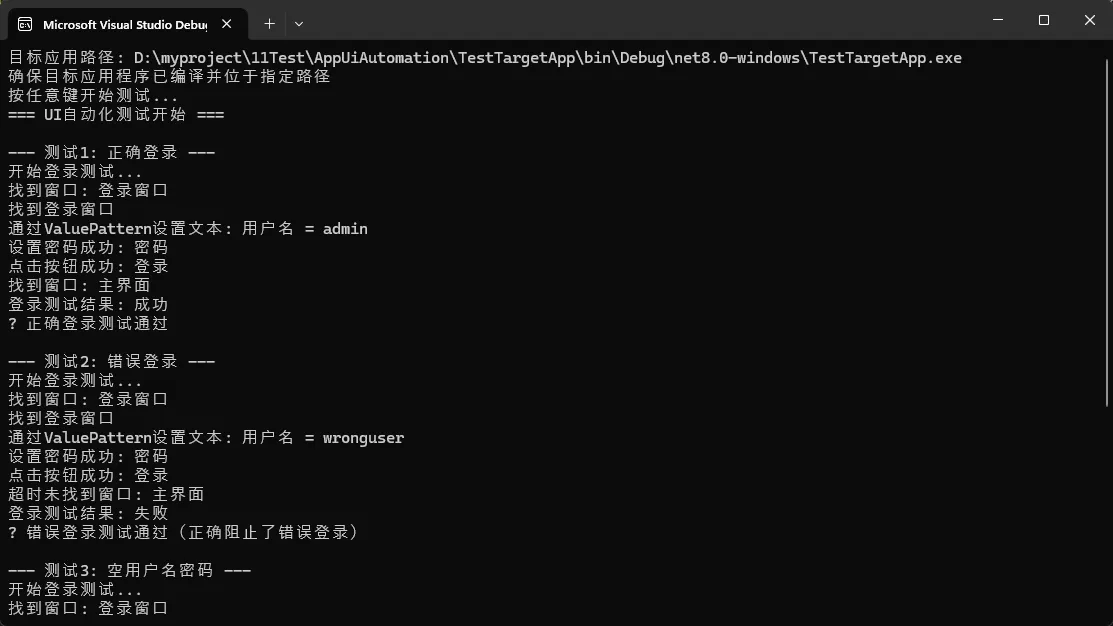
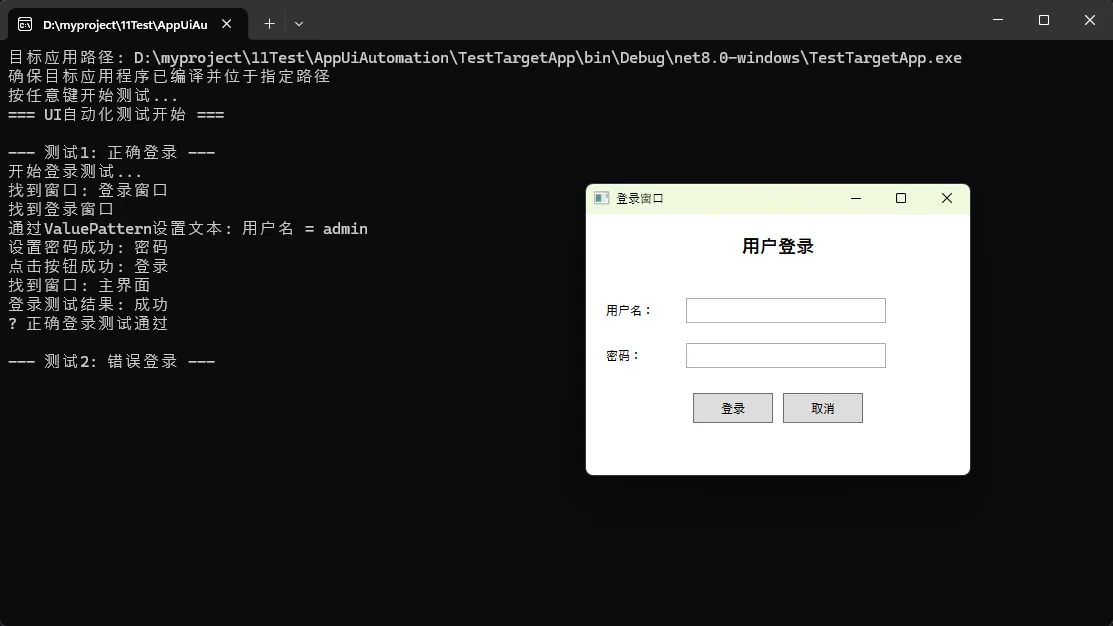
// 测试1: 正确的登录信息
Console.WriteLine("\n--- 测试1: 正确登录 ---");
if (StartTargetApplication(targetAppPath))
{
totalTests++;
if (LoginTest("admin", "password123"))
{
passedTests++;
Console.WriteLine("✓ 正确登录测试通过");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("✗ 正确登录测试失败");
}
CloseTargetApplication();
Thread.Sleep(1000);
}
// 测试2: 错误的登录信息
Console.WriteLine("\n--- 测试2: 错误登录 ---");
if (StartTargetApplication(targetAppPath))
{
totalTests++;
if (!LoginTest("wronguser", "wrongpass"))
{
passedTests++;
Console.WriteLine("✓ 错误登录测试通过(正确阻止了错误登录)");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("✗ 错误登录测试失败(不应该允许错误登录)");
}
CloseTargetApplication();
Thread.Sleep(1000);
}
// 测试3: 空用户名密码
Console.WriteLine("\n--- 测试3: 空用户名密码 ---");
if (StartTargetApplication(targetAppPath))
{
totalTests++;
if (!LoginTest("", ""))
{
passedTests++;
Console.WriteLine("✓ 空用户名密码测试通过");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("✗ 空用户名密码测试失败");
}
CloseTargetApplication();
}
Console.WriteLine($"\n=== 测试完成: {passedTests}/{totalTests} 通过 ===");
}
}
// 程序入口
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var testFramework = new ImprovedTestFramework();
// 请将此路径替换为您的目标应用程序的实际路径
string targetAppPath = @"D:\myproject\11Test\AppUiAutomation\TestTargetApp\bin\Debug\net8.0-windows\TestTargetApp.exe";
if (args.Length > 0)
{
targetAppPath = args[0];
}
Console.WriteLine($"目标应用路径: {targetAppPath}");
Console.WriteLine("确保目标应用程序已编译并位于指定路径");
Console.WriteLine("按任意键开始测试...");
Console.ReadKey();
testFramework.RunAllTests(targetAppPath);
Console.WriteLine("\n按任意键退出...");
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
💡 金句总结
- "UI Automation不仅是自动化工具,更是Windows无障碍访问的技术基石"
- "选择UI Automation = 选择微软官方标准 + 长期技术支持"
- "从Win32 API到UI Automation,是从手工作坊到工业化生产的跨越"
🎯 核心要点总结
通过本文的深入解析,我们可以得出三个关键结论:
- 技术选择明智:UI Automation作为微软官方推荐的自动化框架,在跨平台兼容性和长期维护性方面具有明显优势,是现代C#自动化开发的首选方案。
- 学习曲线友好:相比复杂的Win32 API和SendMessage机制,UI Automation提供了更加面向对象和直观的编程接口,大大降低了自动化开发的技术门槛。
- 应用前景广阔:随着Windows生态系统的不断发展,UI Automation将在自动化测试、辅助工具开发、无障碍访问等领域发挥越来越重要的作用。
💬 互动话题:
- 你在项目中使用过哪些自动化技术?遇到过什么样的技术难题?
- 对于UI Automation的性能优化,你有什么独特的经验分享?
如果这篇文章帮你解决了自动化开发中的困惑,请转发给更多需要的同行,让我们一起推动C#自动化技术的发展!
相关信息
通过网盘分享的文件:AppUiAutomationTestFramework.zip 链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1iGsTZW9pl3nJa33LP9FZbw?pwd=mpda 提取码: mpda --来自百度网盘超级会员v9的分享
本文作者:技术老小子
本文链接:
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!