目录
在工业自动化和上位机开发中,程序需要根据不同的传感器数据、设备状态和工艺参数做出智能决策。今天我们深入解析Python条件语句,这是每个Python开发者必须熟练掌握的核心技能。无论你是刚入门的新手,还是想在工业应用中提升编程技巧的开发者,本文将通过实战案例,让你彻底掌握Python条件语句的精髓,并直接应用到实际项目中。
🎯 问题分析:为什么条件语句如此重要?
💡 工业场景中的决策需求
在工业自动化系统中,我们经常遇到这样的需求:
- 温度超过阈值时触发报警
- 根据不同的产品类型执行不同的加工程序
- 设备故障时自动切换备用系统
- 根据传感器数据调整控制参数
这些都需要程序具备智能决策能力,而Python的条件语句正是实现这种决策逻辑的核心工具。
🔍 条件语句的本质
条件语句本质上是程序的分支控制结构,它让程序能够:
- 判断条件:评估布尔表达式的真假
- 选择执行:根据条件结果选择不同的代码块
- 控制流程:改变程序的执行顺序
💻 解决方案:Python条件语句完整语法
🟢 基础if语句
Python# 基础语法
if 条件表达式:
执行代码块
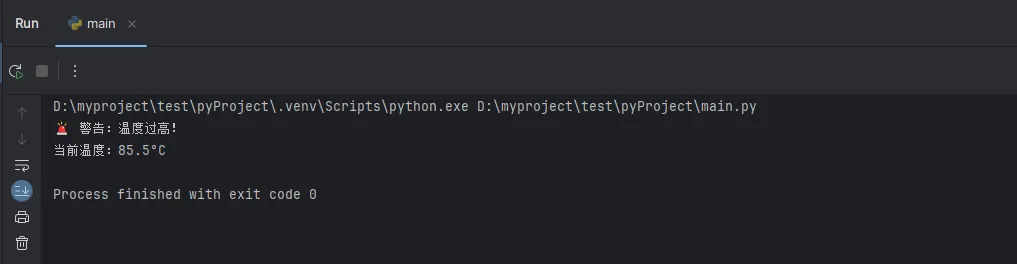
工业实战案例:温度监控
Python# 工业温度监控系统
temperature = 85.5 # 当前温度值
if temperature > 80:
print("🚨 警告:温度过高!")
print(f"当前温度:{temperature}°C")
# 触发冷却系统
cooling_system_active = True
🟡 if-else双分支
Python# if-else语法
if 条件表达式:
条件为真时执行
else:
条件为假时执行
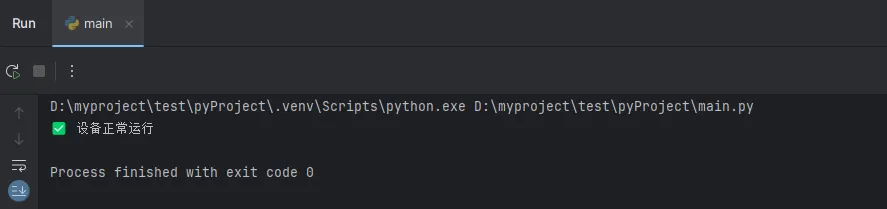
工业实战案例:设备状态检测
Python# 设备运行状态检测
device_status = "running"
uptime = 0
def start_diagnostic_procedure():
print("🔍 开始故障诊断程序")
if device_status == "running":
print("✅ 设备正常运行")
# 记录正常运行时间
uptime += 1
else:
print("❌ 设备异常停机")
# 启动故障诊断程序
start_diagnostic_procedure()
🟠 if-elif-else多分支
Python# 多分支语法
if 条件1:
执行代码块1
elif 条件2:
执行代码块2
elif 条件3:
执行代码块3
else:
默认执行代码块
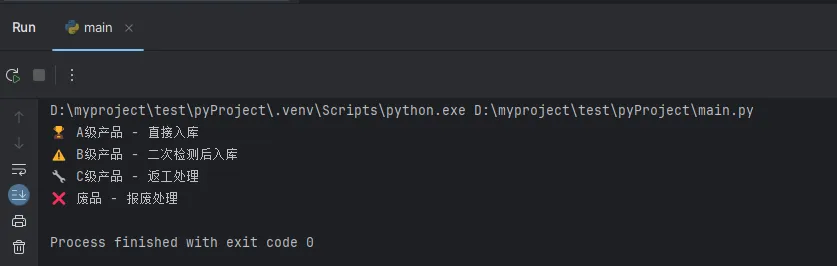
工业实战案例:产品质量分级
Python# 产品质量自动分级系统
def classify_product_quality(defect_count, size_deviation):
"""
根据缺陷数量和尺寸偏差对产品进行质量分级
"""
if defect_count == 0 and size_deviation <= 0.1:
grade = "A级"
action = "直接入库"
print(f"🏆 {grade}产品 - {action}")
elif defect_count <= 2 and size_deviation <= 0.3:
grade = "B级"
action = "二次检测后入库"
print(f"⚠️ {grade}产品 - {action}")
elif defect_count <= 5 and size_deviation <= 0.5:
grade = "C级"
action = "返工处理"
print(f"🔧 {grade}产品 - {action}")
else:
grade = "废品"
action = "报废处理"
print(f"❌ {grade} - {action}")
return grade, action
# 测试不同的产品
classify_product_quality(0, 0.05) # A级产品
classify_product_quality(1, 0.2) # B级产品
classify_product_quality(3, 0.4) # C级产品
classify_product_quality(8, 0.8) # 废品
🛠️ 代码实战:高级应用技巧
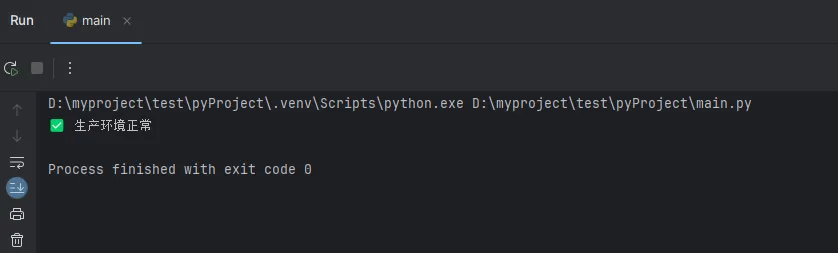
🔥 技巧1:复合条件判断
Python# 使用逻辑运算符组合多个条件
def check_production_conditions(temperature, humidity, pressure):
"""
检查生产环境是否符合要求
"""
if temperature >= 20 and temperature <= 25 and humidity < 60 and pressure > 1000:
return "✅ 生产环境正常"
elif temperature < 20 or temperature > 25:
return "🌡️ 温度超出范围"
elif humidity >= 60:
return "💧 湿度过高"
elif pressure <= 1000:
return "📊 气压不足"
else:
return "❓ 未知状态"
# 实际应用
current_temp = 23
current_humidity = 45
current_pressure = 1013
status = check_production_conditions(current_temp, current_humidity, current_pressure)
print(status)
🔥 技巧2:嵌套条件语句
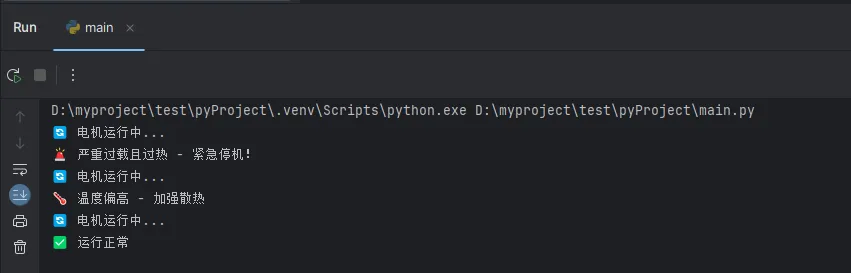
Pythondef motor_control_system(motor_status, load_current, temperature):
"""
电机控制系统 - 多层条件判断
"""
if motor_status == "running":
print("🔄 电机运行中...")
if load_current > 10: # 过载检测
if temperature > 80:
print("🚨 严重过载且过热 - 紧急停机!")
return "emergency_stop"
else:
print("⚠️ 过载警告 - 降低负载")
return "reduce_load"
else:
if temperature > 70:
print("🌡️ 温度偏高 - 加强散热")
return "increase_cooling"
else:
print("✅ 运行正常")
return "normal"
else:
print("⏸️ 电机停止状态")
return "stopped"
# 测试不同场景
result1 = motor_control_system("running", 12, 85) # 紧急情况
result2 = motor_control_system("running", 8, 75) # 温度偏高
result3 = motor_control_system("running", 6, 60) # 正常运行
🔥 技巧3:三元运算符(简化条件表达式)
Python# 简化的条件表达式
# 语法:值1 if 条件 else 值2
# 传统写法
def get_status_traditional(value):
if value > 50:
return "高"
else:
return "低"
# 三元运算符写法
def get_status_simple(value):
return "高" if value > 50 else "低"
# 实际应用:传感器数据处理
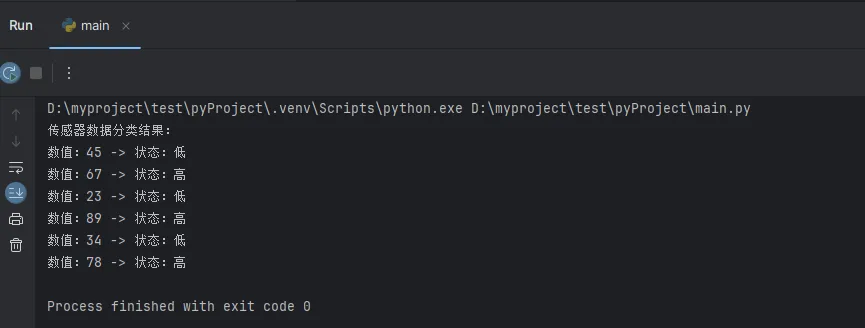
sensor_readings = [45, 67, 23, 89, 34, 78]
# 快速分类传感器读数
classified_data = [("高" if reading > 50 else "低", reading)
for reading in sensor_readings]
print("传感器数据分类结果:")
for status, value in classified_data:
print(f"数值:{value} -> 状态:{status}")
🔥 技巧4:字典替代多重elif
Python# 使用字典优化多重elif结构
class ProductionLineController:
def __init__(self):
# 状态码对应的处理函数映射
self.status_handlers = {
0: self.handle_normal,
1: self.handle_warning,
2: self.handle_error,
3: self.handle_critical,
4: self.handle_maintenance
}
# 状态描述
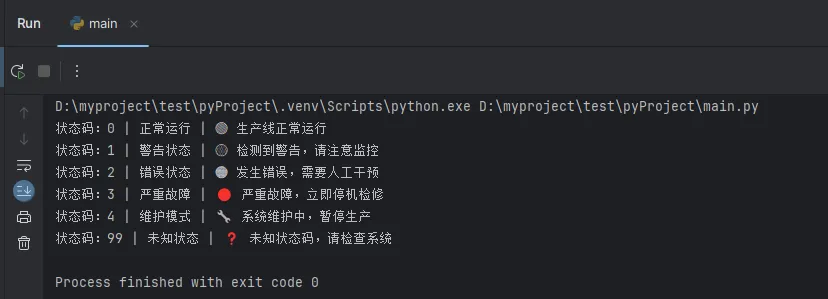
self.status_descriptions = {
0: "正常运行",
1: "警告状态",
2: "错误状态",
3: "严重故障",
4: "维护模式"
}
def handle_normal(self):
return "🟢 生产线正常运行"
def handle_warning(self):
return "🟡 检测到警告,请注意监控"
def handle_error(self):
return "🟠 发生错误,需要人工干预"
def handle_critical(self):
return "🔴 严重故障,立即停机检修"
def handle_maintenance(self):
return "🔧 系统维护中,暂停生产"
def process_status(self, status_code):
"""
处理状态码 - 使用字典替代多重elif
"""
# 获取状态描述
description = self.status_descriptions.get(status_code, "未知状态")
# 获取处理函数并执行
handler = self.status_handlers.get(status_code, self.handle_unknown)
result = handler()
return f"状态码:{status_code} | {description} | {result}"
def handle_unknown(self):
return "❓ 未知状态码,请检查系统"
# 使用示例
controller = ProductionLineController()
# 测试不同状态码
test_codes = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 99]
for code in test_codes:
print(controller.process_status(code))
🔥 技巧5:条件语句与异常处理结合
Pythonimport logging
def safe_device_operation(device_id, operation_type, parameters):
"""
安全的设备操作函数 - 结合条件判断和异常处理
"""
try:
# 参数验证
if not device_id:
raise ValueError("设备ID不能为空")
if operation_type not in ["start", "stop", "reset", "configure"]:
raise ValueError(f"不支持的操作类型:{operation_type}")
# 根据操作类型执行不同逻辑
if operation_type == "start":
if parameters.get("temperature", 0) > 100:
logging.warning("⚠️ 启动温度过高,执行预冷却")
return {"status": "pending", "message": "预冷却中..."}
else:
logging.info("✅ 设备启动成功")
return {"status": "success", "message": "设备已启动"}
elif operation_type == "stop":
if parameters.get("force_stop", False):
logging.warning("🚨 强制停机执行")
return {"status": "success", "message": "设备已强制停止"}
else:
logging.info("⏸️ 正常停机")
return {"status": "success", "message": "设备已正常停止"}
elif operation_type == "reset":
if parameters.get("backup_data", True):
logging.info("💾 数据备份完成,执行重置")
return {"status": "success", "message": "设备已重置"}
else:
logging.warning("⚠️ 跳过数据备份,直接重置")
return {"status": "success", "message": "设备已重置(无备份)"}
elif operation_type == "configure":
config_valid = all([
parameters.get("speed", 0) > 0,
parameters.get("pressure", 0) > 0,
parameters.get("temperature", 0) > 0
])
if config_valid:
logging.info("⚙️ 配置参数有效,应用成功")
return {"status": "success", "message": "配置已应用"}
else:
logging.error("❌ 配置参数无效")
return {"status": "error", "message": "配置参数验证失败"}
except ValueError as e:
logging.error(f"参数错误:{e}")
return {"status": "error", "message": str(e)}
except Exception as e:
logging.error(f"系统错误:{e}")
return {"status": "error", "message": "系统内部错误"}
# 测试不同场景
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO, format='%(levelname)s: %(message)s')
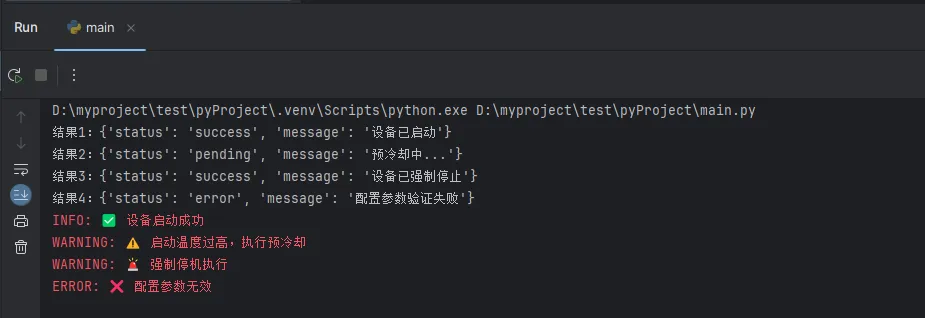
# 正常启动
result1 = safe_device_operation("MOTOR_01", "start", {"temperature": 25})
print(f"结果1:{result1}")
# 高温启动
result2 = safe_device_operation("MOTOR_01", "start", {"temperature": 120})
print(f"结果2:{result2}")
# 强制停机
result3 = safe_device_operation("MOTOR_01", "stop", {"force_stop": True})
print(f"结果3:{result3}")
# 配置错误
result4 = safe_device_operation("MOTOR_01", "configure", {"speed": 0, "pressure": 50})
print(f"结果4:{result4}")
📊 最佳实践与性能优化
🎯 最佳实践清单
- 条件顺序优化:将最可能为真的条件放在前面
- 避免深度嵌套:超过3层嵌套考虑重构
- 使用括号明确优先级:复杂条件表达式要加括号
- 合理使用短路求值:利用
and和or的短路特性 - 保持代码可读性:复杂条件提取为变量或函数
⚡ 性能优化示例
Python# 优化前:低效的条件判断
def process_sensor_data_slow(data_list):
results = []
for data in data_list:
# 每次都重新计算复杂条件
if (data["temperature"] > 50 and data["temperature"] < 100 and
data["pressure"] > 1000 and data["pressure"] < 2000 and
data["humidity"] < 80 and len(data["errors"]) == 0):
results.append("正常")
else:
results.append("异常")
return results
# 优化后:高效的条件判断
def process_sensor_data_fast(data_list):
results = []
for data in data_list:
# 提取条件变量,提高可读性和性能
temp_ok = 50 < data["temperature"] < 100
pressure_ok = 1000 < data["pressure"] < 2000
humidity_ok = data["humidity"] < 80
no_errors = len(data["errors"]) == 0
# 使用短路求值,最可能失败的条件放前面
if no_errors and temp_ok and pressure_ok and humidity_ok:
results.append("正常")
else:
results.append("异常")
return results
🎯 总结与实战建议
通过本文的深入讲解,我们掌握了Python条件语句的三个核心要点:
- 🎯 语法掌握:从基础if到复杂的多分支条件语句,每种语法都有其适用场景
- 💡 实战技巧:三元运算符、字典映射、异常处理结合等高级技巧能显著提升代码质量
- ⚡ 性能优化:合理的条件顺序和代码结构能提升程序执行效率
在工业自动化和上位机开发中,条件语句是实现智能决策的基础。建议你立即在自己的项目中应用这些技巧,从简单的传感器数据判断开始,逐步构建复杂的工业控制逻辑。
记住:好的条件语句不仅要功能正确,更要具备良好的可读性和可维护性。这样才能在团队协作和项目迭代中发挥最大价值。
现在就开始你的Python工业应用之旅吧!如果你在实践中遇到问题,欢迎在评论区交流讨论。
💡 想了解更多Python工业应用技巧?关注我们,获取最新的实战教程和项目案例!
本文作者:技术老小子
本文链接:
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!
目录