目录
概述
在WPF中,事件处理机制与传统的WinForms有很大的不同。WPF提供了更加灵活和强大的事件处理方式,包括XAML声明式事件绑定和代码后置事件处理两种主要方式。
WPF vs WinForms事件处理对比
主要区别
- 事件绑定方式
- WinForms:主要通过设计器自动生成代码或手动编写代码进行绑定
- WPF:可以在XAML中声明式绑定,也可以在代码后置中绑定
- 事件处理器位置
- WinForms:事件处理器代码通常集中在一个文件中
- WPF:支持分离式编程模型,可以更好地分离界面和逻辑
- 事件路由
- WinForms:简单的直接事件模型
- WPF:支持路由事件(Bubbling、Tunneling、Direct)
WPF事件处理示例
XAML声明式事件绑定
XML<Window x:Class="AppEvent.MainWindow"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:AppEvent"
mc:Ignorable="d"
Title="MainWindow" Height="450" Width="800">
<StackPanel>
<!-- 基本事件绑定 -->
<Button Content="点击我" Click="Button_Click" Margin="10"/>
<!-- 带参数的事件绑定 -->
<Button Content="带参数的按钮"
Click="Button_Click_WithParameter"
Tag="自定义参数"
Margin="10"/>
<!-- 多个事件的绑定 -->
<TextBox Text="输入些内容"
TextChanged="TextBox_TextChanged"
KeyDown="TextBox_KeyDown"
Margin="10"/>
</StackPanel>
</Window>
代码后置事件处理
C#using System.Diagnostics;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows;
using System.Windows.Controls;
using System.Windows.Data;
using System.Windows.Documents;
using System.Windows.Input;
using System.Windows.Media;
using System.Windows.Media.Imaging;
using System.Windows.Navigation;
using System.Windows.Shapes;
namespace AppEvent
{
/// <summary>
/// Interaction logic for MainWindow.xaml
/// </summary>
public partial class MainWindow : Window
{
public MainWindow()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
// 基本事件处理器
private void Button_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
// sender是事件的源对象
Button button = sender as Button;
MessageBox.Show("按钮被点击了!");
}
// 带参数的事件处理器
private void Button_Click_WithParameter(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
Button button = sender as Button;
string parameter = button.Tag.ToString();
MessageBox.Show($"按钮参数:{parameter}");
}
// TextBox文本改变事件
private void TextBox_TextChanged(object sender, TextChangedEventArgs e)
{
TextBox textBox = sender as TextBox;
Debug.WriteLine($"文本已更改:{textBox.Text}");
}
// TextBox按键事件
private void TextBox_KeyDown(object sender, KeyEventArgs e)
{
if (e.Key == Key.Enter)
{
MessageBox.Show("你按下了回车键!");
}
}
}
}
代码方式绑定事件
XML<Window x:Class="AppEvent.Window1"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:AppEvent"
mc:Ignorable="d"
Title="Window1" Height="450" Width="800">
<StackPanel x:Name="rootPanel">
</StackPanel>
</Window>
C#public partial class MainWindow : Window
{
public MainWindow()
{
InitializeComponent();
// 创建控件
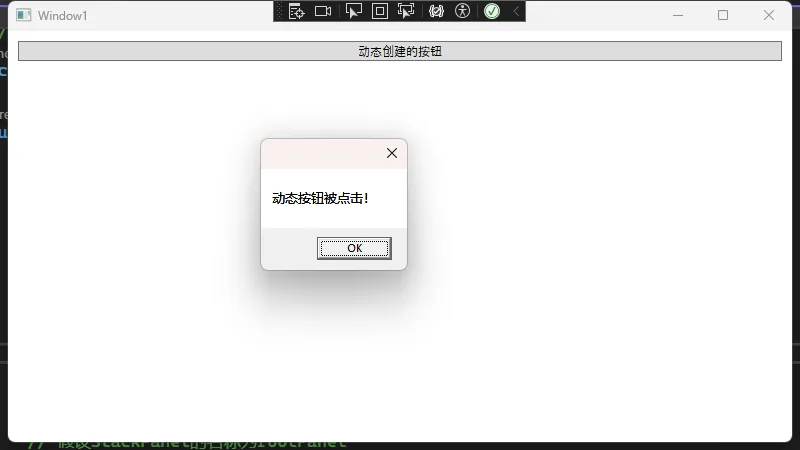
Button dynamicButton = new Button
{
Content = "动态创建的按钮",
Margin = new Thickness(10)
};
// 添加事件处理器
dynamicButton.Click += DynamicButton_Click;
// 假设StackPanel的名称为rootPanel
rootPanel.Children.Add(dynamicButton);
}
private void DynamicButton_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
MessageBox.Show("动态按钮被点击!");
}
}
路由事件示例
冒泡事件(Bubbling)
XML<Window x:Class="AppEvent.Window2"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:AppEvent"
mc:Ignorable="d"
Title="Window2" Height="450" Width="800">
<StackPanel ButtonBase.Click="StackPanel_Click">
<Button Content="按钮1" Click="Button_Click" Margin="10"/>
<Button Content="按钮2" Click="Button_Click" Margin="10"/>
</StackPanel>
</Window>
C#using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows;
using System.Windows.Controls;
using System.Windows.Data;
using System.Windows.Documents;
using System.Windows.Input;
using System.Windows.Media;
using System.Windows.Media.Imaging;
using System.Windows.Shapes;
namespace AppEvent
{
/// <summary>
/// Interaction logic for Window2.xaml
/// </summary>
public partial class Window2 : Window
{
public Window2()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
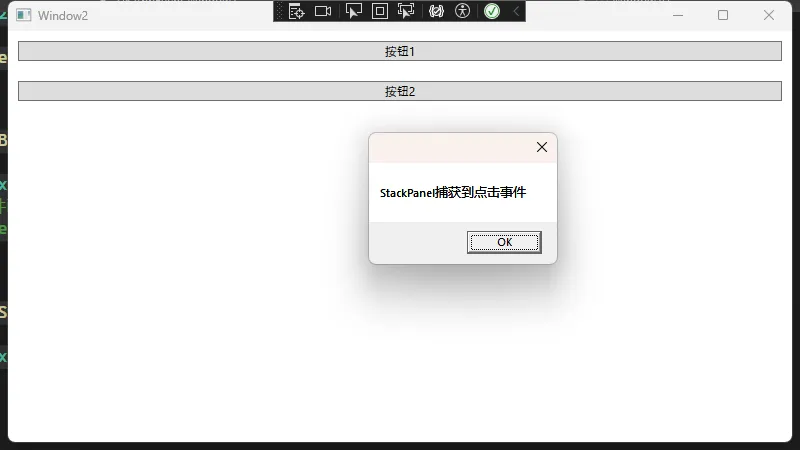
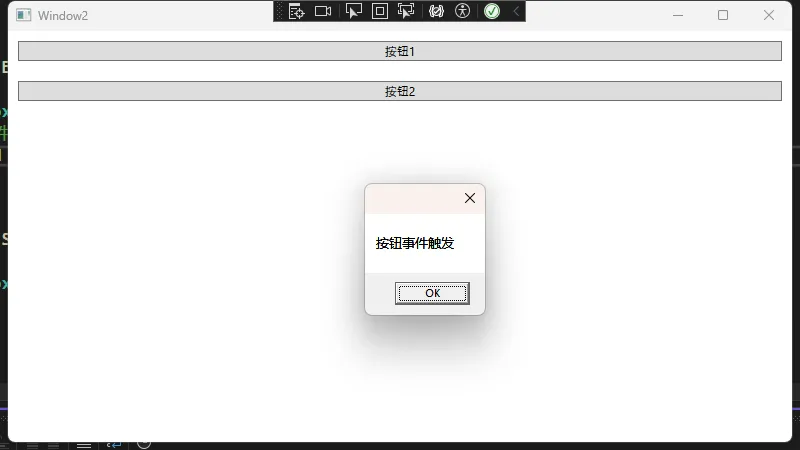
private void Button_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
MessageBox.Show("按钮事件触发");
// 标记事件已处理,阻止事件继续冒泡
//e.Handled = true;
}
private void StackPanel_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
MessageBox.Show("StackPanel捕获到点击事件");
}
}
}
e.Handled = true; 时StackPanel点击事件不会触发
隧道事件(Tunneling)
XML<Window x:Class="AppEvent.Window3"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:AppEvent"
mc:Ignorable="d"
Title="Window3" Height="450" Width="800">
<StackPanel PreviewMouseDown="StackPanel_PreviewMouseDown">
<Button Content="预览事件按钮"
PreviewMouseDown="Button_PreviewMouseDown"
Margin="10"/>
</StackPanel>
</Window>
C#using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows;
using System.Windows.Controls;
using System.Windows.Data;
using System.Windows.Documents;
using System.Windows.Input;
using System.Windows.Media;
using System.Windows.Media.Imaging;
using System.Windows.Shapes;
namespace AppEvent
{
/// <summary>
/// Interaction logic for Window3.xaml
/// </summary>
public partial class Window3 : Window
{
public Window3()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void StackPanel_PreviewMouseDown(object sender, MouseButtonEventArgs e)
{
MessageBox.Show("StackPanel预览事件触发");
// 可以阻止事件继续传播
//e.Handled = true;
}
private void Button_PreviewMouseDown(object sender, MouseButtonEventArgs e)
{
MessageBox.Show("按钮预览事件触发");
}
}
}
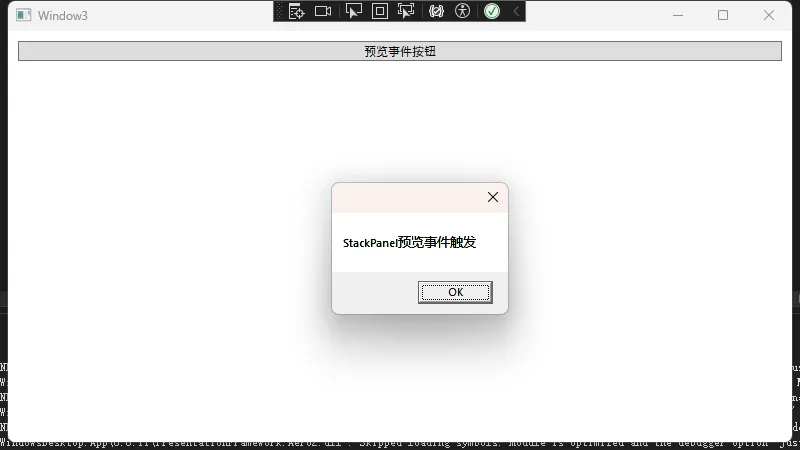
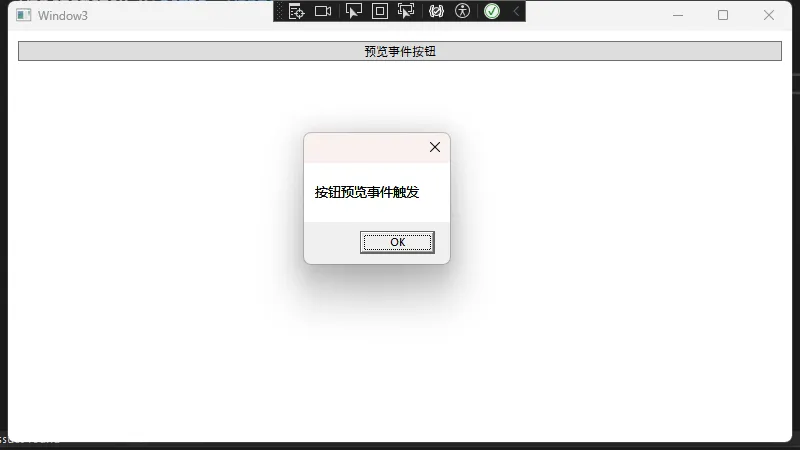
点击按钮先触发StackPanel_PreviewMouseDown,再到Button_PreviewMouseDown
事件处理最佳实践
使用命令替代事件
在WPF中,对于用户交互,推荐使用命令(Commands)而不是事件:
XML<Window x:Class="AppEvent.Window4"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
Title="Window4" Height="450" Width="800">
<Window.CommandBindings>
<CommandBinding Command="ApplicationCommands.Save"
Executed="SaveCommand_Executed"
CanExecute="SaveCommand_CanExecute"/>
</Window.CommandBindings>
<StackPanel>
<TextBox x:Name="txtInput" Margin="10"/>
<Button Command="ApplicationCommands.Save"
Content="保存"
Margin="10"/>
<Button Content="强制更新命令状态"
Click="UpdateCommandState_Click"
Margin="10"/>
</StackPanel>
</Window>
C#using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows;
using System.Windows.Controls;
using System.Windows.Data;
using System.Windows.Documents;
using System.Windows.Input;
using System.Windows.Media;
using System.Windows.Media.Imaging;
using System.Windows.Shapes;
namespace AppEvent
{
public partial class Window4 : Window
{
public Window4()
{
InitializeComponent();
// 监听TextBox的文本变化
txtInput.TextChanged += TxtInput_TextChanged;
}
private void SaveCommand_Executed(object sender, ExecutedRoutedEventArgs e)
{
MessageBox.Show($"保存文本:{txtInput.Text}");
}
private void SaveCommand_CanExecute(object sender, CanExecuteRoutedEventArgs e)
{
// 只有当TextBox有内容时才允许保存
e.CanExecute = !string.IsNullOrEmpty(txtInput.Text);
// 可以在这里添加调试信息来观察触发时机
Debug.WriteLine("CanExecute被调用 - " + DateTime.Now.ToString("HH:mm:ss.fff"));
}
private void TxtInput_TextChanged(object sender, TextChangedEventArgs e)
{
// 方法1:文本变化时手动触发命令状态更新
CommandManager.InvalidateRequerySuggested();
}
private void UpdateCommandState_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
// 方法2:通过按钮手动触发命令状态更新
CommandManager.InvalidateRequerySuggested();
}
}
}
总结
WPF的事件处理机制显著优于WinForms,它不仅支持声明式事件绑定,还提供了强大的路由事件系统,同时实现了更好的关注点分离并支持命令模式,使事件处理更加灵活。在开发实践中,应当优先考虑使用命令代替事件,合理运用路由事件特性,同时要注意事件处理对性能的影响,做好异常处理,并始终确保代码的清晰度和可维护性。
本文作者:技术老小子
本文链接:
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!
目录