目录
什么是表达式树?
表达式树(Expression Trees)是一种以树形数据结构表示代码的方式,其中每个节点都是一个表达式。它允许我们在运行时检查、修改和执行代码。
为什么需要表达式树?
表达式树主要用于以下场景:
- LINQ to SQL/Entity Framework 查询转换
- 动态查询构建
- 元编程
- 代码分析和修改
- 跨平台代码转换
创建表达式树
通过Lambda表达式创建
C#using System.Linq.Expressions;
namespace AppExpressionTrees
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main()
{
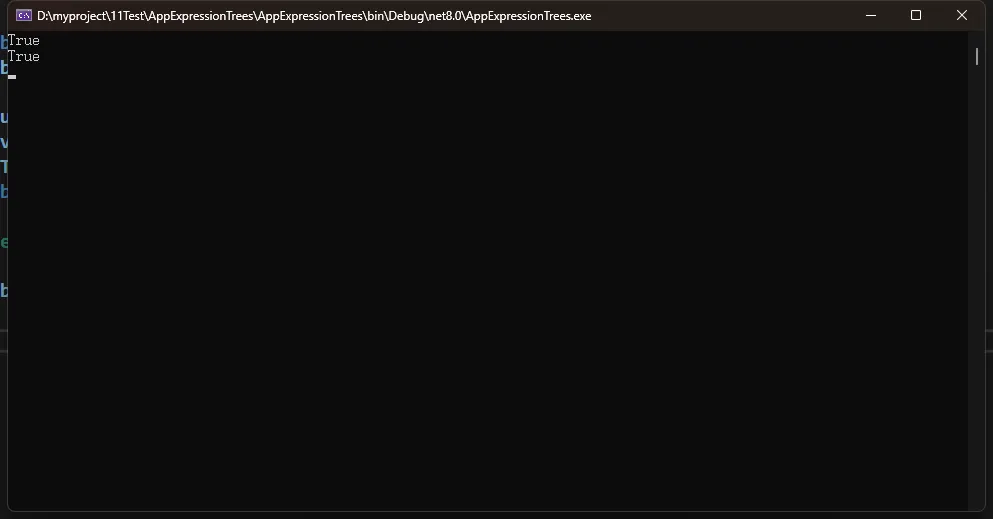
Expression<Func<int, bool>> lambda1 = num => num < 5;
Console.WriteLine(lambda1.Compile().Invoke(4));
ParameterExpression numParam = Expression.Parameter(typeof(int), "num");
ConstantExpression five = Expression.Constant(5);
BinaryExpression lessThan = Expression.LessThan(numParam, five);
Expression<Func<int, bool>> lambda2 = Expression.Lambda<Func<int, bool>>(
lessThan,
new ParameterExpression[] { numParam }
);
Console.WriteLine(lambda2.Compile().Invoke(4));
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
以上两种方式是一回事。
手动构建更复杂的表达式树
C#using System.Linq.Expressions;
namespace AppExpressionTrees
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main()
{
ParameterExpression x = Expression.Parameter(typeof(int), "x");
ParameterExpression y = Expression.Parameter(typeof(int), "y");
BinaryExpression add = Expression.Add(x, y);
Expression<Func<int, int, int>> addExpr =
Expression.Lambda<Func<int, int, int>>(
add,
new ParameterExpression[] { x, y }
);
// 编译并执行
var compiled = addExpr.Compile();
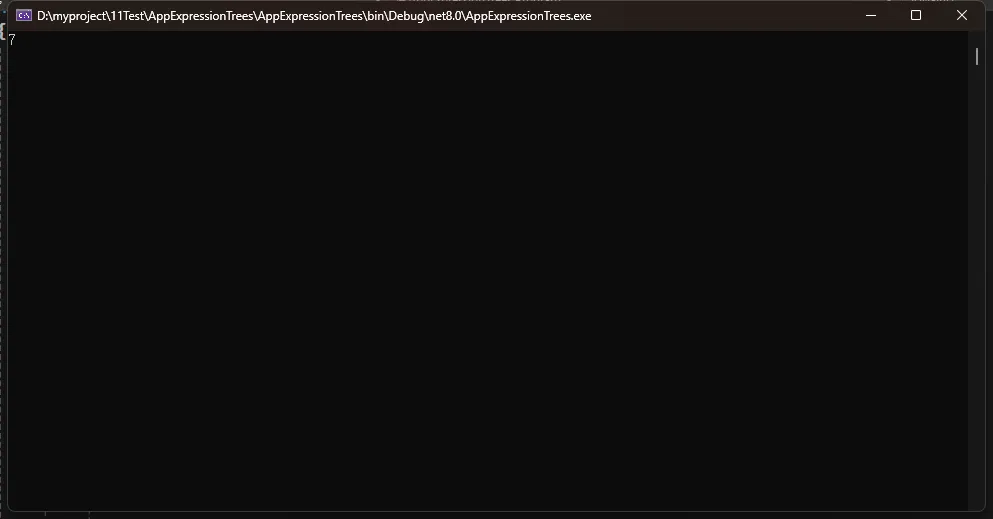
int result = compiled(3, 4);
Console.WriteLine(result);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
常见表达式节点类型
C#using System.Linq.Expressions;
namespace AppExpressionTrees
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main()
{
// 1. 常量表达式
ConstantExpression constant = Expression.Constant(42);
Console.WriteLine(constant.Value);
// 2. 参数表达式
ParameterExpression param = Expression.Parameter(typeof(string), "str");
Console.WriteLine(param.Name);
// 3. 方法调用表达式
MethodCallExpression methodCall = Expression.Call(
typeof(Console).GetMethod("WriteLine", new[] { typeof(string) }),
Expression.Constant("Hello")
);
var compiledLambda = Expression.Lambda<Action>(methodCall).Compile();
compiledLambda.Invoke();
// 4. 条件表达式
Expression condition = Expression.Condition(
Expression.Constant(true),
Expression.Constant("Yes"),
Expression.Constant("No")
);
Console.WriteLine(condition.Reduce().ToString());
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
实际应用示例
动态查询构建器
C#using System;
using System.Linq;
using System.Linq.Expressions;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace AppExpressionTrees
{
public class Product
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public decimal Price { get; set; }
}
public class QueryBuilder
{
public static Expression<Func<T, bool>> BuildFilter<T>(
List<FilterCondition> conditions,
bool isAndOperator = true)
{
if (conditions == null || conditions.Count == 0)
throw new ArgumentException("条件不能为NULL");
var parameter = Expression.Parameter(typeof(T), "x");
Expression combinedExpression = null;
foreach (var condition in conditions)
{
var property = Expression.Property(parameter, condition.PropertyName);
var constant = Expression.Constant(condition.Value);
Expression comparison = condition.Operation.ToLower() switch
{
"equals" => Expression.Equal(property, constant),
"greaterthan" => Expression.GreaterThan(property, constant),
"lessthan" => Expression.LessThan(property, constant),
"contains" => CreateContainsExpression(property, constant),
"startswith" => CreateStartsWithExpression(property, constant),
"endswith" => CreateEndsWithExpression(property, constant),
_ => throw new ArgumentException($"Invalid operation: {condition.Operation}")
};
// 组合条件
if (combinedExpression == null)
{
combinedExpression = comparison;
}
else
{
combinedExpression = isAndOperator
? Expression.AndAlso(combinedExpression, comparison)
: Expression.OrElse(combinedExpression, comparison);
}
}
return Expression.Lambda<Func<T, bool>>(combinedExpression, parameter);
}
// 处理字符串 Contains
private static Expression CreateContainsExpression(Expression property, Expression constant)
{
var containsMethod = typeof(string).GetMethod("Contains", new[] { typeof(string) });
return Expression.Call(property, containsMethod, constant);
}
// 处理字符串 StartsWith
private static Expression CreateStartsWithExpression(Expression property, Expression constant)
{
var startsWithMethod = typeof(string).GetMethod("StartsWith", new[] { typeof(string) });
return Expression.Call(property, startsWithMethod, constant);
}
// 处理字符串 EndsWith
private static Expression CreateEndsWithExpression(Expression property, Expression constant)
{
var endsWithMethod = typeof(string).GetMethod("EndsWith", new[] { typeof(string) });
return Expression.Call(property, endsWithMethod, constant);
}
public static List<T> ApplyFilter<T>(List<T> list, Expression<Func<T, bool>> filter)
{
return list.Where(filter.Compile()).ToList();
}
}
// 新增过滤条件类
public class FilterCondition
{
public string PropertyName { get; set; }
public string Operation { get; set; }
public object Value { get; set; }
}
internal class Program
{
static void Main()
{
// 创建测试数据
var products = new List<Product>
{
new Product { Id = 1, Name = "Laptop Product", Price = 120.50m },
new Product { Id = 2, Name = "Smartphone", Price = 80.00m },
new Product { Id = 3, Name = "Tablet Product", Price = 200.75m },
new Product { Id = 4, Name = "Headphones", Price = 50.25m },
new Product { Id = 5, Name = "Smart Watch Product", Price = 150.00m }
};
// 单个条件 - 价格大于100
var priceFilter = QueryBuilder.BuildFilter<Product>(new List<FilterCondition>
{
new FilterCondition
{
PropertyName = "Price",
Operation = "greaterthan",
Value = 100m
}
});
var expensiveProducts = QueryBuilder.ApplyFilter(products, priceFilter);
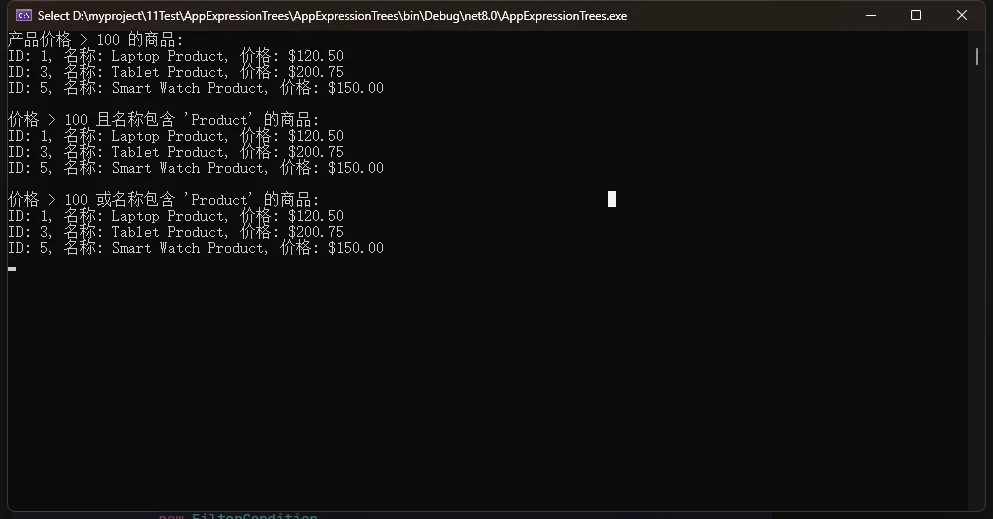
Console.WriteLine("产品价格 > 100 的商品:");
PrintProducts(expensiveProducts);
// 多个条件 AND 操作 - 价格大于100且名称包含"Product"
var multiAndFilter = QueryBuilder.BuildFilter<Product>(new List<FilterCondition>
{
new FilterCondition
{
PropertyName = "Price",
Operation = "greaterthan",
Value = 100m
},
new FilterCondition
{
PropertyName = "Name",
Operation = "contains",
Value = "Product"
}
});
var expensiveProductsWithName = QueryBuilder.ApplyFilter(products, multiAndFilter);
Console.WriteLine("\n价格 > 100 且名称包含 'Product' 的商品:");
PrintProducts(expensiveProductsWithName);
// 多个条件 OR 操作 - 价格大于100或名称包含"Product"
var multiOrFilter = QueryBuilder.BuildFilter<Product>(new List<FilterCondition>
{
new FilterCondition
{
PropertyName = "Price",
Operation = "greaterthan",
Value = 100m
},
new FilterCondition
{
PropertyName = "Name",
Operation = "contains",
Value = "Product"
}
}, isAndOperator: false);
var productsMatchingEitherCondition = QueryBuilder.ApplyFilter(products, multiOrFilter);
Console.WriteLine("\n价格 > 100 或名称包含 'Product' 的商品:");
PrintProducts(productsMatchingEitherCondition);
Console.ReadKey();
}
// 打印产品列表
static void PrintProducts(List<Product> products)
{
if (products == null || products.Count == 0)
{
Console.WriteLine("没有找到匹配的产品");
return;
}
foreach (var product in products)
{
Console.WriteLine($"ID: {product.Id}, 名称: {product.Name}, 价格: {product.Price:C}");
}
}
}
}
总结
表达式树是C#中一个强大的特性,它让我们能够在运行时操作代码。虽然有一些限制,但在特定场景下(如ORM、动态查询、代码生成等)非常有用。掌握表达式树的使用可以帮助我们编写更灵活、更强大的应用程序。
记住要注意性能影响,适当使用缓存,并始终进行异常处理。在实际应用中,表达式树最常用于构建查询、创建动态代理和实现元编程模式。
本文作者:技术老小子
本文链接:
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!
目录