在Python桌面应用开发中,Tkinter作为Python内置的GUI库,是许多开发者的首选。然而,很多初学者在创建窗口时,常常遇到这样的困惑:如何精确控制窗口大小?怎样设置个性化的窗口标题?窗口位置能否自定义?本文将通过详细的代码实战,帮你彻底掌握Python Tkinter窗口的基础设置技巧,让你的上位机开发更加专业规范。
无论你是Python开发新手,还是想要提升桌面应用界面美观度的程序员,这些实用的编程技巧都将为你的项目增色不少。让我们从最基础的窗口创建开始,逐步深入到高级定制技巧。
🔍 问题分析
在实际的Python开发项目中,窗口的外观设置直接影响用户体验。常见的需求包括:
基础需求:
- 设置合适的窗口尺寸,避免过大或过小
- 自定义窗口标题,体现应用特色
- 控制窗口在屏幕上的显示位置
进阶需求:
- 限制窗口最大最小尺寸
- 禁止用户调整窗口大小
- 设置窗口图标,提升专业度
这些看似简单的设置,实际上涉及Tkinter的多个重要方法,掌握好了能让你的应用界面更加精致。
💡 解决方案详解
🎯 核心方法概览
Tkinter提供了以下几个关键方法来控制窗口属性:
geometry():设置窗口大小和位置title():设置窗口标题resizable():控制窗口是否可调整大小minsize()** / ****maxsize()**:设置最小最大尺寸iconbitmap():设置窗口图标
让我们通过实际代码来看看这些方法的具体用法。
🔥 代码实战演练
1️⃣ 基础窗口设置
Pythonimport tkinter as tk
def create_basic_window():
"""创建基础窗口示例"""
root = tk.Tk()
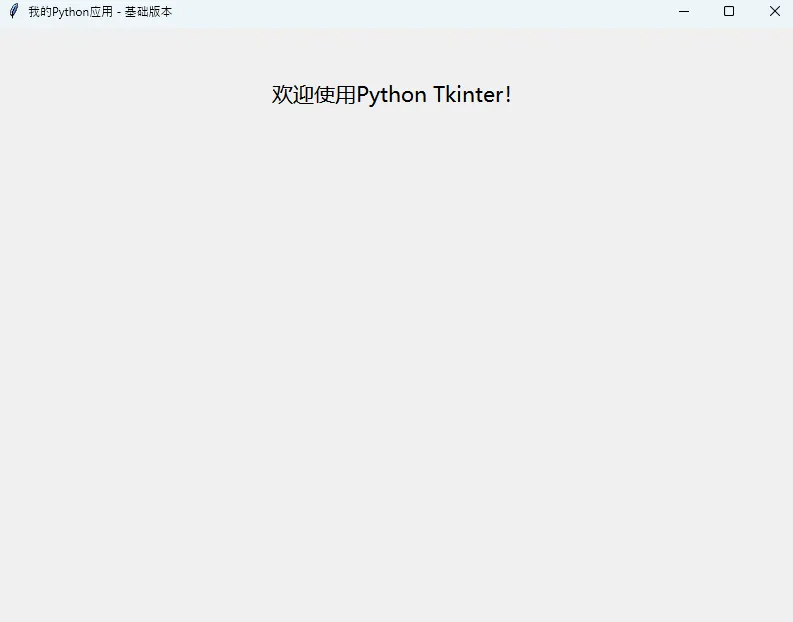
# 设置窗口标题
root.title("我的Python应用 - 基础版本")
# 设置窗口大小:宽x高
root.geometry("800x600")
# 添加一些内容
label = tk.Label(root, text="欢迎使用Python Tkinter!",
font=("微软雅黑", 16))
label.pack(pady=50)
root.mainloop()
# 运行示例
create_basic_window()
在Python开发的世界里,整数(int)看似简单,但却蕴含着强大的功能。无论你是刚入门的新手,还是经验丰富的开发者,都可能在整数处理上遇到困惑:为什么Python的整数可以无限大?二进制、八进制、十六进制到底怎么用?在Windows下做上位机开发时,如何高效处理各种进制的数据?
本文将带你深入了解Python整数的核心特性,掌握任意精度计算、进制转换等实战技巧,让你在面对复杂的数值计算和数据处理时游刃有余。
🔍 Python整数的独特之处
任意精度:告别整数溢出的烦恼
与C++、Java等语言不同,Python的整数类型支持任意精度,这意味着你永远不用担心整数溢出问题。
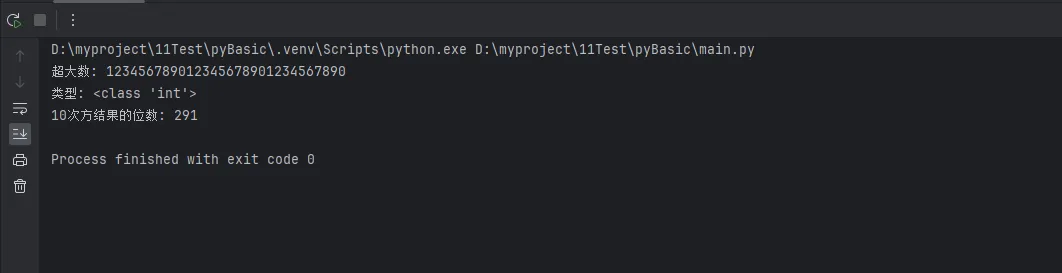
Python# 在其他语言中可能溢出的超大数
big_number = 123456789012345678901234567890
print(f"超大数: {big_number}")
print(f"类型: {type(big_number)}")
# 进行大数运算
result = big_number ** 10
print(f"10次方结果的位数: {len(str(result))}")
作为Python开发者,你是否遇到过这样的困扰:新装的Ubuntu系统不知道如何正确安装Python?多个Python版本冲突导致项目无法运行?虚拟环境配置复杂,总是出现各种奇怪的错误?
本文将从实战角度出发,手把手教你在Ubuntu系统下完成Python的完整安装与配置。无论你是刚入门的新手,还是需要在新服务器上部署环境的资深开发者,这篇文章都能为你提供一套完整、可靠的解决方案。我们将涵盖系统Python管理、多版本Python安装、虚拟环境配置以及常见问题的解决方法。
🔍 问题分析
📊 Ubuntu系统Python现状分析
Ubuntu系统通常预装了Python,但这往往不能满足我们的开发需求:
系统默认Python的局限性:
- Ubuntu 20.04默认Python 3.8,Ubuntu 22.04默认Python 3.10
- 系统Python主要服务于系统工具,不建议直接用于开发
- 缺少pip包管理器和开发工具
- 权限管理复杂,容易污染系统环境
常见的安装配置问题:
- 版本冲突:系统Python与开发Python混用
- 权限问题:使用sudo安装包导致的权限混乱
- 路径配置:多个Python版本PATH配置错误
- 依赖缺失:编译安装时缺少必要的系统依赖
💡 解决方案
🛠️ 三种主流安装方案对比
| 方案 | 优势 | 劣势 | 适用场景 |
|---|---|---|---|
| apt包管理器 | 简单快速,系统集成好 | 版本相对较旧 | 生产环境,稳定性优先 |
| 源码编译 | 版本最新,可自定义 | 复杂,依赖多 | 特殊需求,性能优化 |
| pyenv管理 | 多版本管理,灵活 | 学习成本高 | 开发环境,多项目 |
🎯 推荐方案选择策略
- 新手开发者:apt + 虚拟环境
- 多项目开发:pyenv + 虚拟环境
- 生产部署:Docker + 官方镜像
- 特殊需求:源码编译
🚀 代码实战
📦 使用apt包管理器安装(推荐)
🔧 更新系统并安装基础依赖
Bash# 更新包列表
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y
# 安装编译和开发必需的系统依赖
sudo apt install -y software-properties-common \
build-essential \
curl \
wget \
git \
vim \
tree
在Python开发的路上,你是否遇到过这样的困扰:不同项目需要不同版本的Python和第三方库,全局安装各种包导致版本冲突,或者团队协作时环境配置不一致?这些问题都指向一个核心需求——环境管理。
今天我们来聊聊Python界的"瑞士军刀"——Anaconda。作为一个在Windows下摸爬滚打多年的Python开发者,我深知配置一个干净、高效的开发环境有多重要。本文将从实战角度出发,手把手教你用Anaconda打造专业的Python开发环境,让你告别环境配置的各种坑。
无论你是刚入门的Python小白,还是想要规范化开发流程的老司机,这篇文章都将为你提供实用、易懂、可操作的完整解决方案。
🤔 问题分析:为什么选择Anaconda?
传统Python环境配置的痛点
在没有Anaconda之前,Windows下的Python开发环境配置堪称"玄学":
- 依赖地狱:pip install 各种包,版本冲突层出不穷
- 路径混乱:多个Python版本共存,PATH环境变量一团糟
- 团队协作困难:每个人的环境都不一样,代码在我这里能跑,在你那里就报错
- 科学计算库安装困难:numpy、matplotlib等底层依赖复杂,编译报错是家常便饭
Anaconda的核心优势
Markdown🎯 Anaconda = Python + 包管理器(conda) + 虚拟环境 + 科学计算库集合
- 一站式解决方案:集成了数据科学常用的库
- 虚拟环境管理:轻松创建隔离的开发环境
- 跨平台支持:Windows、macOS、Linux一套命令走天下
- 包依赖智能解决:conda会自动处理复杂的依赖关系
你是否曾经羡慕过那些在后台静默运行的任务——自动备份、定时报告、数据同步——它们就像时钟一样精准运转?作为Windows下的Python开发者,我们常常需要处理各种定时任务,虽然市面上有Celery、APScheduler等成熟工具,但有时我们需要的仅仅是一个轻量级、纯Python的解决方案。今天,我将带你从零开始构建一个功能完整的任务调度器,让你彻底理解调度机制的本质,并掌握在上位机开发中的实际应用技巧。
🎯 为什么要自己造轮子?
实际场景分析
在Windows环境下的Python开发中,我们经常遇到这些需求:
- 设备数据采集:每隔30秒读取传感器数据
- 日志清理:每天凌晨2点清理过期日志文件
- 数据库备份:每周日进行数据库自动备份
- 系统监控:实时监控CPU和内存使用率
传统方案的痛点:
- Cron:Windows支持不友好,配置复杂
- Celery:需要Redis/RabbitMQ,部署重量级
- APScheduler:功能强大但学习成本高
自定义调度器的优势:
- ✅ 零依赖,纯Python实现
- ✅ 代码可控,便于定制化
- ✅ 轻量级,适合嵌入式场景
- ✅ 易于调试和维护
🔍 深入理解调度机制核心
时间精度 vs 系统开销
很多初学者认为任务调度就是time.sleep()的循环使用,这是一个严重的误区。真正的调度器需要考虑:
Pythonimport time
import datetime
# ❌ 错误的实现方式
def bad_scheduler():
while True:
time.sleep(60) # 固定睡眠60秒
run_task() # 任务执行时间会累积误差
Python# ✅ 正确的实现方式
import time
def good_scheduler():
next_run = time.time()
while True:
current_time = time.time()
if current_time >= next_run:
run_task()
next_run += 1 # 基于固定间隔计算下次执行
time.sleep(0.1) # 短暂休眠,降低CPU占用
def run_task():
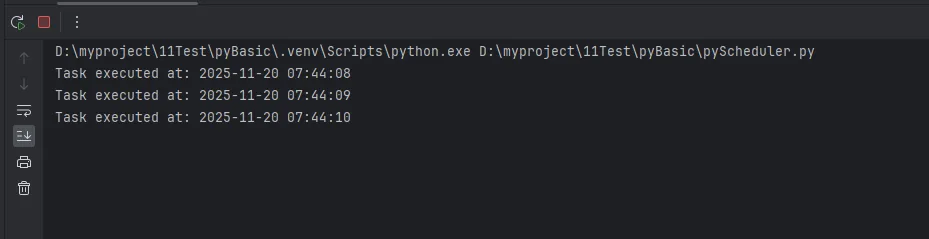
print("Task executed at:", time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", time.localtime()))
if __name__ == "__main__":
good_scheduler()