目录
摘要:本文详细介绍如何在WinForm应用程序中集成NLog日志框架,实现全局异常捕获与记录,提高应用程序稳定性和可维护性。包含完整代码示例和配置说明,适用于.NET开发者。
为什么需要全局异常处理?
在开发WinForm桌面应用程序时,异常处理是确保应用稳定性的关键环节。未处理的异常不仅会导致程序崩溃,还会造成用户体验下降和数据丢失。全局异常处理机制可以:
- 防止应用程序意外崩溃
- 记录异常信息,便于问题定位和修复
- 向用户提供友好的错误提示
- 收集软件运行状态数据,辅助产品改进
NLog作为.NET生态中的优秀日志框架,具有配置灵活、性能优异、扩展性强等特点,是实现全局异常处理的理想工具。
环境准备
创建WinForm项目
首先,创建一个新的WinForm应用程序项目。
安装NLog包
通过NuGet包管理器安装NLog:
PowerShellInstall-Package NLog
或在Visual Studio中右键项目 -> 管理NuGet包 -> 搜索并安装上述包。
三、配置NLog
基础配置
项目中添加NLog.config文件。我们可以根据需求修改配置:
XML<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<nlog xmlns="http://www.nlog-project.org/schemas/NLog.xsd"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.nlog-project.org/schemas/NLog.xsd NLog.xsd"
autoReload="true"
throwExceptions="false"
internalLogLevel="Off">
<!-- 定义日志输出目标 -->
<targets>
<!-- 文件日志,按日期滚动 -->
<target xsi:type="File" name="file"
fileName="${basedir}/logs/${shortdate}.log"
layout="${longdate} | ${level:uppercase=true} | ${logger} | ${message} ${exception:format=tostring}"
archiveFileName="${basedir}/logs/archives/{#}.log"
archiveNumbering="Date"
archiveEvery="Day"
archiveDateFormat="yyyy-MM-dd"
maxArchiveFiles="30" />
<!-- 错误日志单独存储 -->
<target xsi:type="File" name="errorfile"
fileName="${basedir}/logs/errors/${shortdate}.log"
layout="${longdate} | ${level:uppercase=true} | ${logger} | ${message} ${exception:format=tostring}" />
</targets>
<!-- 定义日志规则 -->
<rules>
<!-- 所有日志 -->
<logger name="*" minlevel="Info" writeTo="file" />
<!-- 仅错误日志 -->
<logger name="*" minlevel="Error" writeTo="errorfile" />
</rules>
</nlog>
自定义配置(可选)
根据项目需求,你可以添加更多的输出目标,如:
- 数据库日志
- 邮件通知
- Windows事件日志
- 网络日志等
实现全局异常处理
创建Logger工具类
首先,创建一个Logger工具类,封装NLog的使用:
C#using NLog;
using System;
namespace WinFormNLogDemo
{
public static class LogHelper
{
// 创建NLog实例
private static readonly Logger logger = LogManager.GetCurrentClassLogger();
/// <summary>
/// 记录信息日志
/// </summary>
/// <param name="message">日志消息</param>
public static void Info(string message)
{
logger.Info(message);
}
/// <summary>
/// 记录警告日志
/// </summary>
/// <param name="message">警告消息</param>
public static void Warn(string message)
{
logger.Warn(message);
}
/// <summary>
/// 记录错误日志
/// </summary>
/// <param name="ex">异常对象</param>
/// <param name="message">附加消息</param>
public static void Error(Exception ex, string message = "")
{
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(message))
{
logger.Error(ex);
}
else
{
logger.Error(ex, message);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 记录致命错误日志
/// </summary>
/// <param name="ex">异常对象</param>
/// <param name="message">附加消息</param>
public static void Fatal(Exception ex, string message = "")
{
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(message))
{
logger.Fatal(ex);
}
else
{
logger.Fatal(ex, message);
}
}
}
}
全局异常处理器
接下来,在Program.cs中添加全局异常捕获代码:
C#namespace AppNLog
{
internal static class Program
{
/// <summary>
/// The main entry point for the application.
/// </summary>
[STAThread]
static void Main()
{
// To customize application configuration such as set high DPI settings or default font,
// see https://aka.ms/applicationconfiguration.
ApplicationConfiguration.Initialize();
// 设置应用程序异常处理
Application.SetUnhandledExceptionMode(UnhandledExceptionMode.CatchException);
// 处理UI线程异常
Application.ThreadException += Application_ThreadException;
// 处理非UI线程异常
AppDomain.CurrentDomain.UnhandledException += CurrentDomain_UnhandledException;
// 启动应用程序
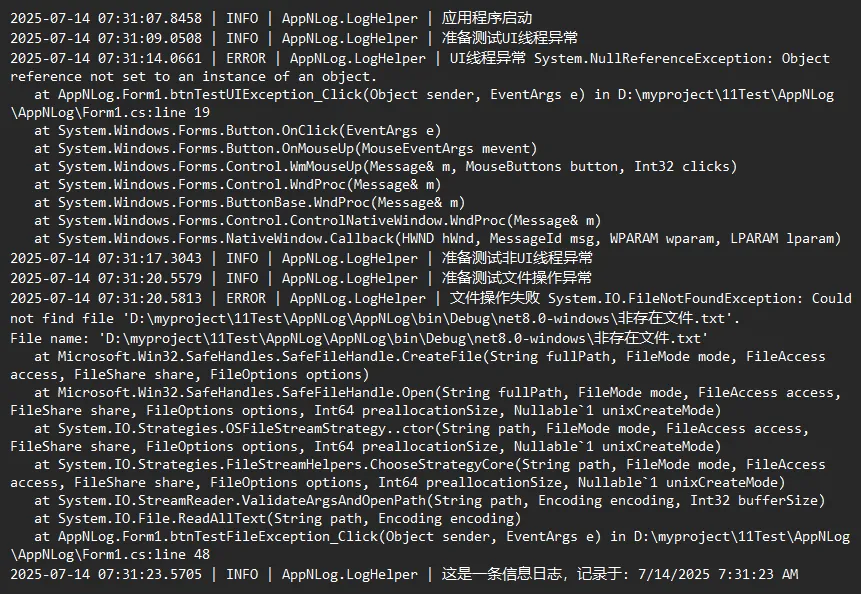
LogHelper.Info("应用程序启动");
Application.Run(new Form1());
}
/// <summary>
/// 处理UI线程异常
/// </summary>
private static void Application_ThreadException(object sender, ThreadExceptionEventArgs e)
{
try
{
// 记录异常日志
LogHelper.Error(e.Exception, "UI线程异常");
// 向用户显示友好错误消息
MessageBox.Show(
"程序遇到了一个问题,已记录异常信息。\n\n" +
"错误信息: " + e.Exception.Message,
"应用程序错误",
MessageBoxButtons.OK,
MessageBoxIcon.Error);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
try
{
LogHelper.Fatal(ex, "处理UI线程异常时发生错误");
}
catch
{
// 如果日志记录也失败,使用消息框作为最后手段
MessageBox.Show("无法记录异常信息: " + ex.Message, "严重错误", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Error);
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 处理非UI线程异常
/// </summary>
private static void CurrentDomain_UnhandledException(object sender, UnhandledExceptionEventArgs e)
{
try
{
Exception ex = e.ExceptionObject as Exception;
// 记录异常日志
if (ex != null)
{
LogHelper.Fatal(ex, "非UI线程异常");
}
else
{
LogHelper.Fatal(new Exception("未知异常类型"),
"发生未知类型的非UI线程异常: " + e.ExceptionObject.ToString());
}
// 如果异常导致应用程序终止,记录这一信息
if (e.IsTerminating)
{
LogHelper.Fatal(new Exception("应用程序即将终止"), "由于未处理的异常,应用程序即将关闭");
MessageBox.Show(
"程序遇到了一个严重问题,必须关闭。\n请联系技术支持获取帮助。",
"应用程序即将关闭",
MessageBoxButtons.OK,
MessageBoxIcon.Error);
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
try
{
LogHelper.Fatal(ex, "处理非UI线程异常时发生错误");
}
catch
{
// 如果日志记录也失败,使用消息框作为最后手段
MessageBox.Show("无法记录异常信息: " + ex.Message, "严重错误", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Error);
}
}
}
}
}
在界面添加测试按钮
接下来,在MainForm中添加几个按钮,用于测试不同类型的异常:
C#namespace AppNLog
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
/// <summary>
/// 测试UI线程异常
/// </summary>
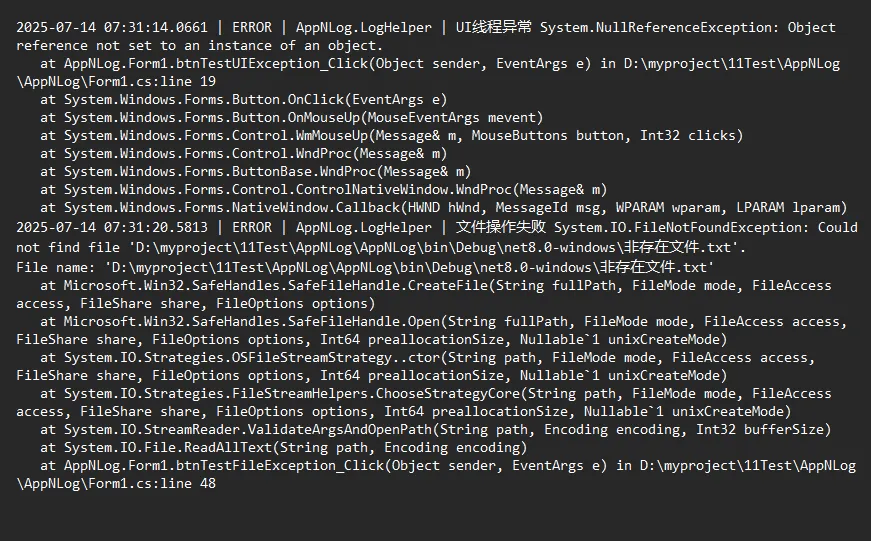
private void btnTestUIException_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
LogHelper.Info("准备测试UI线程异常");
// 故意制造一个异常
string str = null;
int length = str.Length; // 这里会引发NullReferenceException
}
/// <summary>
/// 测试非UI线程异常
/// </summary>
private void btnTestNonUIException_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
LogHelper.Info("准备测试非UI线程异常");
// 在新线程中抛出异常
Task.Run(() =>
{
// 故意制造一个异常
int[] numbers = new int[5];
int value = numbers[10]; // 这里会引发IndexOutOfRangeException
});
}
/// <summary>
/// 测试文件操作异常
/// </summary>
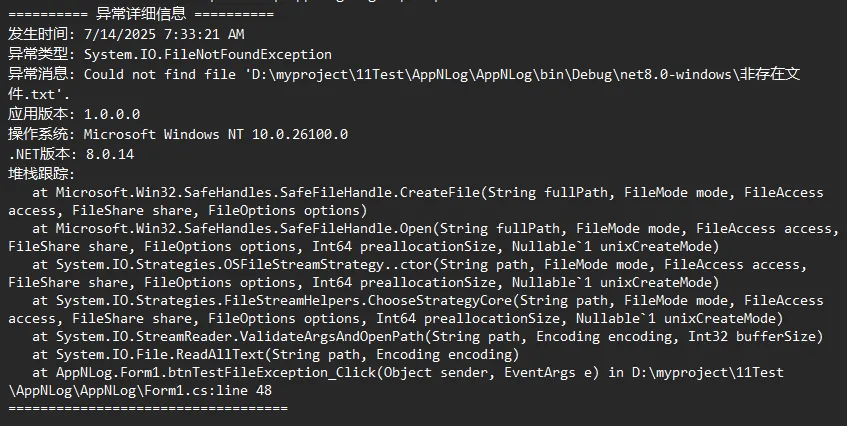
private void btnTestFileException_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
LogHelper.Info("准备测试文件操作异常");
try
{
// 尝试读取一个不存在的文件
string content = File.ReadAllText("非存在文件.txt");
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
// 局部异常处理示例
LogHelper.Error(ex, "文件操作失败");
MessageBox.Show("无法读取文件,详情请查看日志。", "文件错误", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Warning);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 记录普通日志
/// </summary>
private void btnLogInfo_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
LogHelper.Info("这是一条信息日志,记录于: " + DateTime.Now.ToString());
MessageBox.Show("日志已记录", "信息", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Information);
}
}
}
高级功能实现
异常信息扩展
为了更好地记录异常发生时的上下文环境,我们可以扩展异常信息:
C#using NLog;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Reflection;
using System.Text;
namespace WinFormNLogDemo
{
public static class ExceptionExtensions
{
/// <summary>
/// 获取详细的异常信息,包括内部异常、堆栈跟踪等
/// </summary>
public static string GetDetailedErrorMessage(this Exception ex)
{
if (ex == null) return string.Empty;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.AppendLine("========== 异常详细信息 ==========");
sb.AppendLine($"发生时间: {DateTime.Now}");
sb.AppendLine($"异常类型: {ex.GetType().FullName}");
sb.AppendLine($"异常消息: {ex.Message}");
// 获取应用程序版本信息
sb.AppendLine($"应用版本: {Assembly.GetExecutingAssembly().GetName().Version}");
// 记录操作系统信息
sb.AppendLine($"操作系统: {Environment.OSVersion}");
sb.AppendLine($".NET版本: {Environment.Version}");
// 堆栈跟踪
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(ex.StackTrace))
{
sb.AppendLine("堆栈跟踪:");
sb.AppendLine(ex.StackTrace);
}
// 内部异常
if (ex.InnerException != null)
{
sb.AppendLine("内部异常:");
sb.AppendLine(GetInnerExceptionDetails(ex.InnerException));
}
sb.AppendLine("===================================");
return sb.ToString();
}
/// <summary>
/// 递归获取内部异常信息
/// </summary>
private static string GetInnerExceptionDetails(Exception exception, int level = 1)
{
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.AppendLine($"[内部异常级别 {level}]");
sb.AppendLine($"类型: {exception.GetType().FullName}");
sb.AppendLine($"消息: {exception.Message}");
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(exception.StackTrace))
{
sb.AppendLine("堆栈跟踪:");
sb.AppendLine(exception.StackTrace);
}
if (exception.InnerException != null)
{
sb.AppendLine(GetInnerExceptionDetails(exception.InnerException, level + 1));
}
return sb.ToString();
}
}
}
然后,修改LogHelper类使用这个扩展方法:
C#/// <summary>
/// 记录错误日志(增强版)
/// </summary>
public static void ErrorDetailed(Exception ex, string message = "")
{
string detailedMessage = ex.GetDetailedErrorMessage();
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(message))
{
logger.Error(detailedMessage);
}
else
{
logger.Error($"{message}\n{detailedMessage}");
}
}
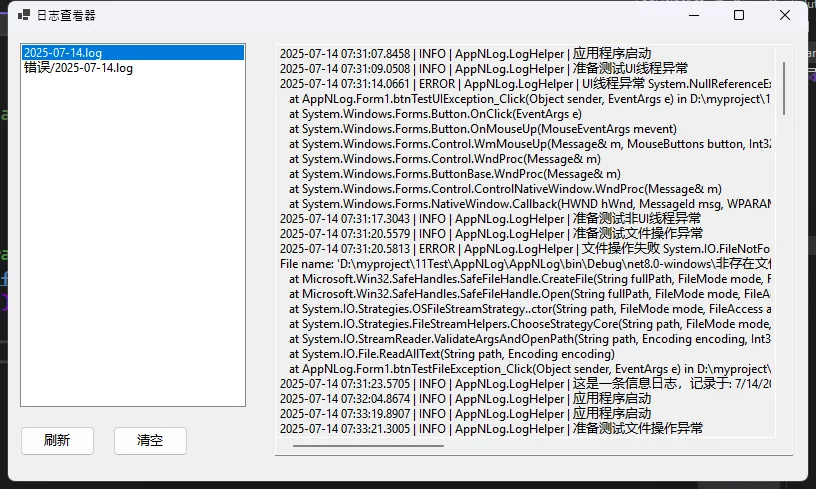
日志查看器集成
为了方便在应用程序内部查看日志,可以添加一个简单的日志查看器:
C#using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace AppNLog
{
public partial class FrmLogViewer : Form
{
private string logDirectory;
public FrmLogViewer()
{
InitializeComponent();
logDirectory = Path.Combine(AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirectory, "logs");
}
/// <summary>
/// 加载日志文件列表
/// </summary>
private void LoadLogFiles()
{
try
{
listBoxLogFiles.Items.Clear();
if (!Directory.Exists(logDirectory))
{
MessageBox.Show("日志目录不存在", "提示", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Information);
return;
}
string[] logFiles = Directory.GetFiles(logDirectory, "*.log");
foreach (string file in logFiles)
{
listBoxLogFiles.Items.Add(Path.GetFileName(file));
}
// 加载错误日志
string errorDirectory = Path.Combine(logDirectory, "errors");
if (Directory.Exists(errorDirectory))
{
string[] errorFiles = Directory.GetFiles(errorDirectory, "*.log");
foreach (string file in errorFiles)
{
listBoxLogFiles.Items.Add("错误/" + Path.GetFileName(file));
}
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
LogHelper.Error(ex, "加载日志文件列表时出错");
MessageBox.Show("无法加载日志文件列表: " + ex.Message, "错误", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Error);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 选择日志文件
/// </summary>
private void listBoxLogFiles_SelectedIndexChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
try
{
if (listBoxLogFiles.SelectedItem == null) return;
string selectedFile = listBoxLogFiles.SelectedItem.ToString();
string filePath;
if (selectedFile.StartsWith("错误/"))
{
filePath = Path.Combine(logDirectory, "errors", selectedFile.Substring(3));
}
else
{
filePath = Path.Combine(logDirectory, selectedFile);
}
if (File.Exists(filePath))
{
txtLogContent.Text = File.ReadAllText(filePath);
}
else
{
txtLogContent.Text = "日志文件不存在或已被删除";
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
LogHelper.Error(ex, "读取日志文件内容时出错");
txtLogContent.Text = "无法读取日志文件: " + ex.Message;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 刷新日志文件列表
/// </summary>
private void btnRefresh_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
LoadLogFiles();
}
/// <summary>
/// 清空所选日志内容
/// </summary>
private void btnClear_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
txtLogContent.Clear();
}
private void FrmLogViewer_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
LoadLogFiles();
}
}
}
应用程序退出时记录日志
确保在应用程序退出时记录相关信息:
C#// 在MainForm中添加
private void MainForm_FormClosing(object sender, FormClosingEventArgs e)
{
LogHelper.Info("应用程序正常关闭");
}
应用场景与最佳实践
常见应用场景
全局异常处理在以下场景特别有用:
- 企业级应用:需要高稳定性和可维护性
- 分布式部署的客户端:便于收集用户端异常信息
- 数据处理应用:确保数据处理过程中的异常被捕获和记录
- 长时间运行的应用:提高应用程序的持续可用性
最佳实践
- 分层记录:按照不同级别记录日志(Debug, Info, Warning, Error, Fatal)
- 结构化日志:使用结构化格式,便于后续分析
- 关联信息:记录用户ID、操作ID等关联信息
- 定期清理:设置日志轮转和清理策略,避免磁盘空间占用过大
- 异常分析:定期分析日志,发现并解决常见问题
- 性能考虑:日志记录操作应尽量异步化,避免影响主线程性能
常见问题与解决方案
日志文件权限问题
问题:应用程序没有写入日志目录的权限。
解决方案:
- 确保应用程序有写入权限
- 使用User目录下的路径存储日志
- 在安装程序中正确设置权限
C#// 使用用户目录存储日志
string logPath = Path.Combine(
Environment.GetFolderPath(Environment.SpecialFolder.LocalApplicationData),
"YourAppName",
"logs"
);
// 确保目录存在
if (!Directory.Exists(logPath))
{
Directory.CreateDirectory(logPath);
}
日志内容过大
问题:日志文件增长过快,占用过多磁盘空间。
解决方案:
- 使用日志分级策略,只记录必要的信息
- 设置日志文件大小上限和轮转策略
- 实现自动清理历史日志的功能
XML<!-- NLog配置示例:限制文件大小和数量 -->
<target xsi:type="File" name="file"
fileName="${basedir}/logs/${shortdate}.log"
archiveFileName="${basedir}/logs/archives/{#}.log"
archiveNumbering="Date"
archiveEvery="Day"
archiveDateFormat="yyyy-MM-dd"
maxArchiveFiles="30"
archiveAboveSize="10485760" <!-- 10MB -->
concurrentWrites="true"
keepFileOpen="false" />
性能问题
问题:日志记录影响应用程序性能。
解决方案:
- 使用异步日志记录
- 优化日志配置,减少I/O操作
- 批量写入日志,而不是频繁的单条写入
XML<!-- NLog异步处理配置 -->
<targets async="true">
<!-- 日志目标配置 -->
</targets>
总结
通过本文的介绍,我们学习了如何在WinForm应用程序中使用NLog实现全局异常处理,主要包括:
- NLog的安装与配置
- 全局异常处理器的实现
- 自定义日志工具类
- 异常信息的扩展与增强
- 内置日志查看器的实现
- 应用场景与最佳实践
实现全局异常处理不仅能提高应用程序的稳定性和可维护性,还能为用户提供更好的使用体验。在实际项目中,可以根据具体需求对本文提供的示例进行扩展和定制。
相关信息
通过网盘分享的文件:AppNLog.zip 链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1VMR756Ip-h6r-ajSN7IRLA?pwd=net8 提取码: net8 --来自百度网盘超级会员v9的分享:::
本文作者:技术老小子
本文链接:
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!