目录
引言
管道模式是一种强大的软件设计模式,它允许我们将复杂的处理任务分解为一系列较小的、独立的步骤。在C#中,这种模式可以带来显著的性能提升和代码可维护性的改善。本文将详细介绍如何在C#中实现管道模式,并探讨其各种变体和优化技巧。
管道模式基础
管道模式的核心思想是将数据处理分为多个阶段,每个阶段接收上一阶段的输出作为输入,并产生新的输出传递给下一阶段。这种方式类似于工厂的装配线,每个工作站都专注于特定的任务。
基本实现
让我们从一个简单的例子开始:
C#public interface IPipelineStep<in TInput, out TOutput>
{
TOutput Process(TInput input);
}
public class Pipeline<TInput>
{
private readonly List<Func<object, object>> _steps = new List<Func<object, object>>();
public Pipeline<TInput> AddStep<TStepInput, TStepOutput>(IPipelineStep<TStepInput, TStepOutput> step)
{
_steps.Add(input => step.Process((TStepInput)input));
return this;
}
public TOutput Execute<TOutput>(TInput input)
{
object current = input;
foreach (var step in _steps)
{
current = step(current);
}
return (TOutput)current;
}
}
使用示例:
C#public class StringToUpperStep : IPipelineStep<string, string>
{
public string Process(string input) => input.ToUpper();
}
public class StringReverseStep : IPipelineStep<string, string>
{
public string Process(string input) => new string(input.Reverse().ToArray());
}
public class StringLengthStep : IPipelineStep<string, int>
{
public int Process(string input) => input.Length;
}
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 使用管道
var pipeline = new Pipeline<string>()
.AddStep(new StringToUpperStep())
.AddStep(new StringReverseStep())
.AddStep(new StringLengthStep());
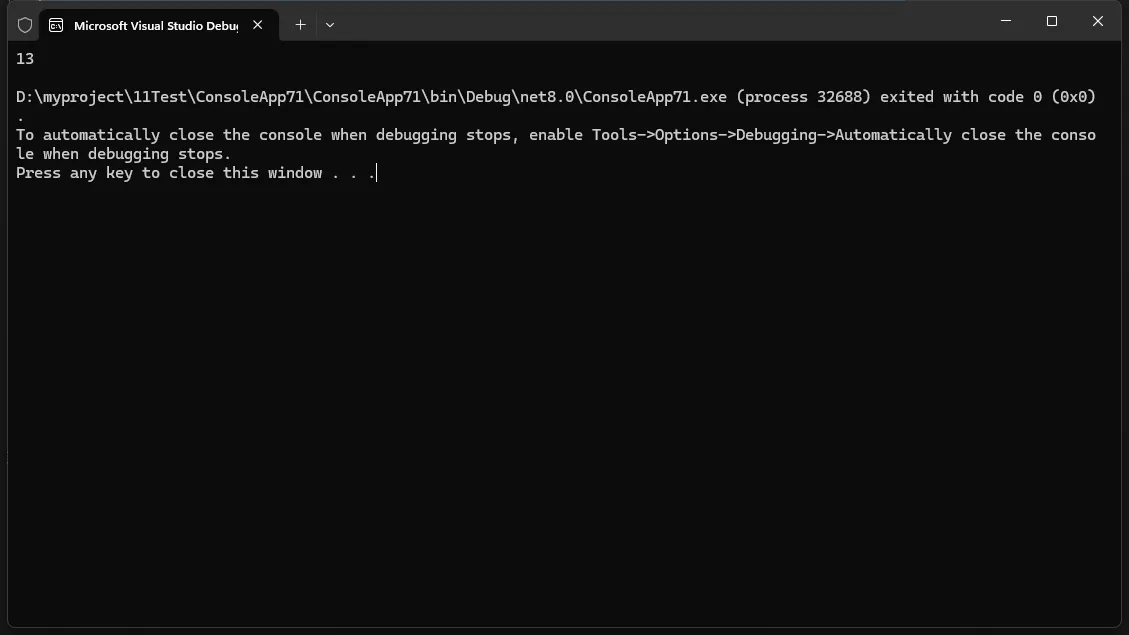
int result = pipeline.Execute<int>("Hello, World!");
Console.WriteLine(result); // 输出: 13
}
}
异步管道
在实际应用中,我们经常需要处理异步操作。下面是一个支持异步处理的管道实现:
C#public interface IAsyncPipelineStep<TInput, TOutput>
{
Task<TOutput> ProcessAsync(TInput input);
}
public class AsyncPipeline<TInput>
{
private readonly List<Func<object, Task<object>>> _steps = new List<Func<object, Task<object>>>();
public AsyncPipeline<TInput> AddStep<TStepInput, TStepOutput>(IAsyncPipelineStep<TStepInput, TStepOutput> step)
{
_steps.Add(async input => await step.ProcessAsync((TStepInput)input));
return this;
}
public async Task<TOutput> ExecuteAsync<TOutput>(TInput input)
{
object current = input;
foreach (var step in _steps)
{
current = await step(current);
}
return (TOutput)current;
}
// 添加这个属性以便外部访问步骤数量
public int StepCount => _steps.Count;
}
使用示例:
C#internal class Program
{
public class AsyncStringToUpperStep : IAsyncPipelineStep<string, string>
{
public async Task<string> ProcessAsync(string input)
{
await Task.Delay(100); // 模拟异步操作
return input.ToUpper();
}
}
public class AsyncStringReverseStep : IAsyncPipelineStep<string, string>
{
public async Task<string> ProcessAsync(string input)
{
await Task.Delay(100); // 模拟异步操作
return new string(input.Reverse().ToArray());
}
}
static async Task Main(string[] args)
{
// 使用异步管道
var asyncPipeline = new AsyncPipeline<string>()
.AddStep(new AsyncStringToUpperStep())
.AddStep(new AsyncStringReverseStep());
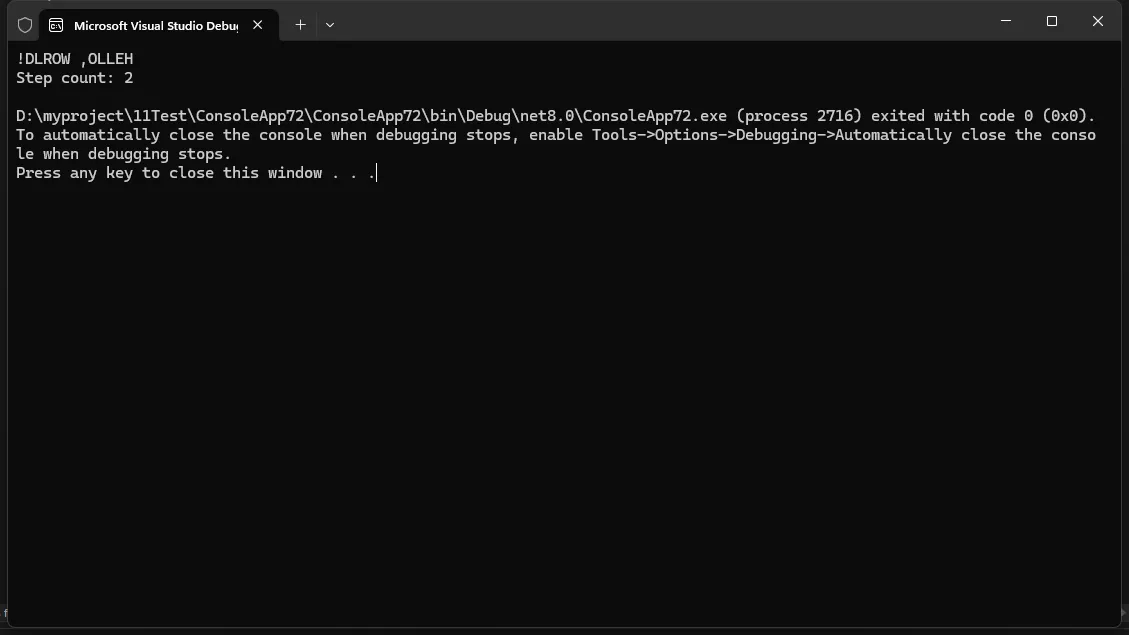
string result = await asyncPipeline.ExecuteAsync<string>("Hello, World!");
Console.WriteLine(result); // 输出: !DLROW ,OLLEH
Console.WriteLine($"Step count: {asyncPipeline.StepCount}"); // 输出: Step count: 2
}
}
并行处理
对于某些场景,我们可能希望并行执行管道中的某些步骤。以下是一个支持并行处理的管道实现:
C#public class ParallelPipeline<TInput, TOutput>
{
private readonly List<Func<TInput, Task<TOutput>>> _steps = new List<Func<TInput, Task<TOutput>>>();
public ParallelPipeline<TInput, TOutput> AddStep(Func<TInput, Task<TOutput>> step)
{
_steps.Add(step);
return this;
}
public async Task<IEnumerable<TOutput>> ExecuteAsync(IEnumerable<TInput> inputs)
{
var tasks = inputs.Select(input =>
Task.WhenAll(_steps.Select(step => step(input)))
);
var results = await Task.WhenAll(tasks);
return results.SelectMany(r => r);
}
}
使用示例:
C#var parallelPipeline = new ParallelPipeline<string, string>()
.AddStep(async input =>
{
await Task.Delay(100);
return input.ToUpper();
})
.AddStep(async input =>
{
await Task.Delay(100);
return new string(input.Reverse().ToArray());
});
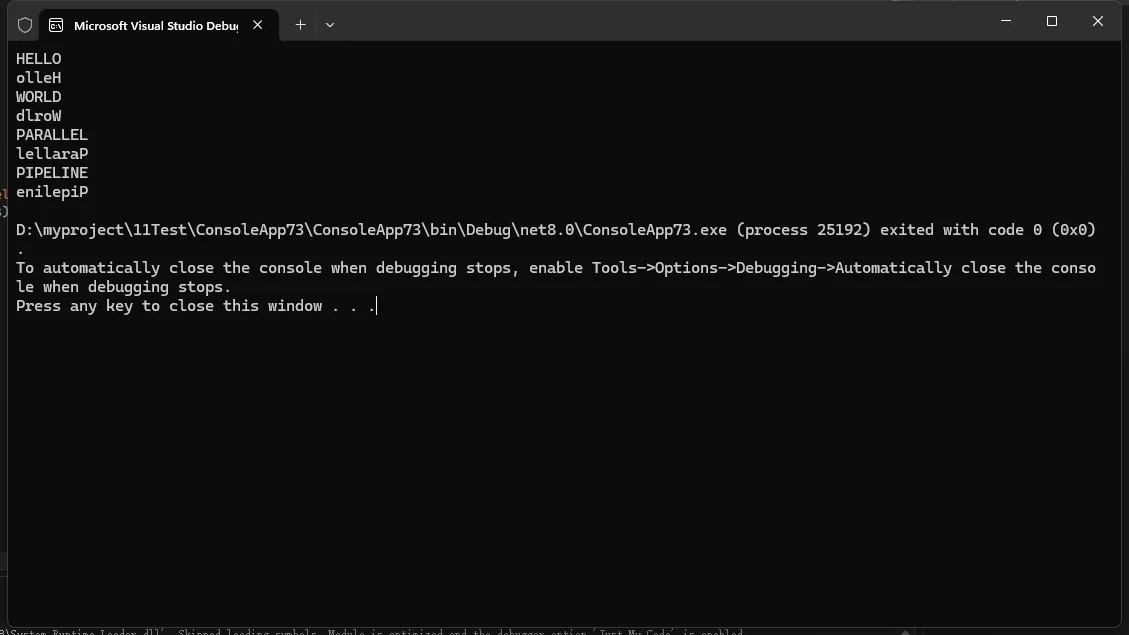
var inputs = new[] { "Hello", "World", "Parallel", "Pipeline" };
var results = await parallelPipeline.ExecuteAsync(inputs);
foreach (var result in results)
{
Console.WriteLine(result);
}
使用BlockingCollection实现线程安全的管道
对于需要在多个线程间传递数据的场景,我们可以使用BlockingCollection<T>来实现一个线程安全的管道:
C#public class ThreadSafePipeline<TInput>
{
private readonly BlockingCollection<TInput> _inputQueue = new BlockingCollection<TInput>();
private readonly BlockingCollection<object> _outputQueue = new BlockingCollection<object>();
private readonly List<Func<object, object>> _steps = new List<Func<object, object>>();
private readonly CancellationTokenSource _cts = new CancellationTokenSource();
public ThreadSafePipeline<TInput> AddStep<TStepInput, TStepOutput>(Func<TStepInput, TStepOutput> step)
{
_steps.Add(input => step((TStepInput)input));
return this;
}
public void Start(int workerCount = 1)
{
for (int i = 0; i < workerCount; i++)
{
Task.Run(() => ProcessItems(_cts.Token));
}
}
public void Stop()
{
_cts.Cancel();
_inputQueue.CompleteAdding();
}
public void AddInput(TInput input)
{
_inputQueue.Add(input);
}
public TOutput GetOutput<TOutput>()
{
return (TOutput)_outputQueue.Take();
}
private void ProcessItems(CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
foreach (var input in _inputQueue.GetConsumingEnumerable(cancellationToken))
{
object result = input;
foreach (var step in _steps)
{
result = step(result);
}
_outputQueue.Add(result);
}
}
public int StepCount => _steps.Count;
}
使用示例:
C#static void Main(string[] args)
{
var threadSafePipeline = new ThreadSafePipeline<string>()
.AddStep<string, string>(s => s.ToUpper())
.AddStep<string, string>(s => new string(s.Reverse().ToArray()))
.AddStep<string, int>(s => s.Length);
Console.WriteLine($"Step count: {threadSafePipeline.StepCount}"); // 输出: Step count: 3
threadSafePipeline.Start(workerCount: 2);
// 添加输入
threadSafePipeline.AddInput("Hello");
threadSafePipeline.AddInput("World");
threadSafePipeline.AddInput("Pipeline");
// 获取输出
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(threadSafePipeline.GetOutput<int>());
}
threadSafePipeline.Stop();
}
结论
管道模式是一种强大的设计模式,可以帮助我们构建灵活、可扩展的数据处理系统。在C#中,我们可以利用语言的特性和.NET框架提供的工具来实现各种类型的管道,包括同步、异步、并行和线程安全的版本。
通过使用管道模式,我们可以:
- 提高代码的模块化和可重用性
- 简化复杂的数据处理流程
- 提高系统的性能和可扩展性
- 更容易地实现并行处理
在实际应用中,选择合适的管道实现取决于具体的需求,如处理的数据类型、性能要求、并发需求等。通过本文提供的示例,您应该能够根据自己的需求选择或调整合适的管道实现。
本文作者:技术老小子
本文链接:
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!
目录