目录
在这篇文章中,我们将学习如何在C#中实现一个简单的自定义脚本语言。这将包括解析脚本、执行命令以及实现基本的控制结构。我们将逐步构建这个示例,最终创建一个小型的脚本引擎。
定义语法
我们的自定义脚本语言将支持以下基本功能:
- 变量定义 (
let x = 10) - 数值输出 (
print(x))
词法分析
首先,我们需要对输入的脚本进行词法分析,将其转换为标记(token)。这可以通过一个简单的状态机来实现。
C#using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace Appcscs
{
public enum TokenType
{
Number,
Identifier,
Print,
Let,
Equals,
Semicolon,
If,
LeftBrace,
RightBrace,
LeftParen,
RightParen,
Plus,
Minus,
EOF
}
public class Token
{
public TokenType Type { get; }
public string Value { get; }
public Token(TokenType type, string value)
{
Type = type;
Value = value;
}
}
public class Lexer
{
private readonly string _input;
private int _position;
public Lexer(string input)
{
_input = input;
_position = 0;
}
private char CurrentChar => _position < _input.Length ? _input[_position] : '\0';
public List<Token> Tokenize()
{
var tokens = new List<Token>();
while (CurrentChar != '\0')
{
if (char.IsWhiteSpace(CurrentChar))
{
_position++;
continue;
}
if (char.IsDigit(CurrentChar))
{
var num = ReadNumber();
tokens.Add(new Token(TokenType.Number, num));
continue;
}
if (char.IsLetter(CurrentChar))
{
var id = ReadIdentifier();
tokens.Add(CreateToken(id));
continue;
}
switch (CurrentChar)
{
case '=':
tokens.Add(new Token(TokenType.Equals, "="));
_position++;
break;
case ';':
tokens.Add(new Token(TokenType.Semicolon, ";"));
_position++;
break;
case '{':
tokens.Add(new Token(TokenType.LeftBrace, "{"));
_position++;
break;
case '}':
tokens.Add(new Token(TokenType.RightBrace, "}"));
_position++;
break;
case '+':
tokens.Add(new Token(TokenType.Plus, "+"));
_position++;
break;
case '-':
tokens.Add(new Token(TokenType.Minus, "-"));
_position++;
break;
case '(':
tokens.Add(new Token(TokenType.LeftParen, "("));
_position++;
break;
case ')':
tokens.Add(new Token(TokenType.RightParen, ")"));
_position++;
break;
default:
throw new Exception($"未知字符: {CurrentChar}");
}
}
tokens.Add(new Token(TokenType.EOF, ""));
return tokens;
}
private string ReadNumber()
{
var start = _position;
while (char.IsDigit(CurrentChar))
_position++;
return _input.Substring(start, _position - start);
}
private string ReadIdentifier()
{
var start = _position;
while (char.IsLetter(CurrentChar))
_position++;
return _input.Substring(start, _position - start);
}
private Token CreateToken(string id)
{
return id switch
{
"print" => new Token(TokenType.Print, id),
"let" => new Token(TokenType.Let, id),
"if" => new Token(TokenType.If, id),
_ => new Token(TokenType.Identifier, id),
};
}
}
}
解析器
接下来,我们将实现一个解析器,它将从词法分析器生成的标记中构建一个抽象语法树(AST)。
C#using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace Appcscs
{
public abstract class ASTNode { }
public class NumberNode : ASTNode
{
public string Value { get; }
public NumberNode(string value) => Value = value;
}
public class VariableNode : ASTNode
{
public string Name { get; }
public VariableNode(string name) => Name = name;
}
public class PrintNode : ASTNode
{
public ASTNode Expression { get; }
public PrintNode(ASTNode expression) => Expression = expression;
}
public class LetNode : ASTNode
{
public string Variable { get; }
public ASTNode Value { get; }
public LetNode(string variable, ASTNode value)
{
Variable = variable;
Value = value;
}
}
public class Parser
{
private readonly List<Token> _tokens;
private int _position;
public Parser(List<Token> tokens)
{
_tokens = tokens;
_position = 0;
}
private Token CurrentToken => _tokens[_position];
public List<ASTNode> Parse()
{
var nodes = new List<ASTNode>();
while (CurrentToken.Type != TokenType.EOF)
{
nodes.Add(ParseStatement());
}
return nodes;
}
private ASTNode ParseStatement()
{
if (CurrentToken.Type == TokenType.Let)
{
_position++; // Eat 'let'
var varName = CurrentToken.Value;
_position++; // Eat identifier
Consume(TokenType.Equals);
var value = ParseExpression();
Consume(TokenType.Semicolon);
return new LetNode(varName, value);
}
else if (CurrentToken.Type == TokenType.Print)
{
_position++; // Eat 'print'
var expr = ParseExpression();
Consume(TokenType.Semicolon);
return new PrintNode(expr);
}
throw new Exception("未知语句");
}
private ASTNode ParseExpression()
{
if (CurrentToken.Type == TokenType.Number)
{
var value = CurrentToken.Value;
_position++;
return new NumberNode(value);
}
else if (CurrentToken.Type == TokenType.Identifier)
{
var name = CurrentToken.Value;
_position++;
return new VariableNode(name);
}
else if (CurrentToken.Type == TokenType.LeftParen)
{
_position++;
var expr = ParseExpression();
Consume(TokenType.RightParen);
return expr;
}
throw new Exception("未知表达式");
}
private void Consume(TokenType type)
{
if (CurrentToken.Type == type)
_position++;
else
throw new Exception($"期望 {type},但得到了 {CurrentToken.Type}");
}
}
}
执行器
最后,我们将实现一个执行器,用于执行解析器生成的AST。
C#using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace Appcscs
{
public class Interpreter
{
private readonly Dictionary<string, string> _variables = new();
public void Interpret(List<ASTNode> nodes)
{
foreach (var node in nodes)
{
Execute(node);
}
}
private void Execute(ASTNode node)
{
switch (node)
{
case PrintNode printNode:
ExecutePrint(printNode);
break;
case LetNode letNode:
ExecuteLet(letNode);
break;
default:
throw new Exception("未知节点");
}
}
private void ExecutePrint(PrintNode node)
{
var value = Evaluate(node.Expression);
Console.WriteLine(value);
}
private void ExecuteLet(LetNode node)
{
var value = Evaluate(node.Value);
_variables[node.Variable] = value;
}
private string Evaluate(ASTNode node)
{
switch (node)
{
case NumberNode numberNode:
return numberNode.Value;
case VariableNode variableNode:
if (_variables.TryGetValue(variableNode.Name, out var value))
return value;
throw new Exception($"未定义变量 {variableNode.Name}");
default:
throw new Exception("未知表达式");
}
}
}
}
整合
现在我们将所有部分整合到一起,创建一个简单的脚本引擎。
C#class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var input = @"
let x = 10;
print(x);
let y = 20;
print(y);
";
var lexer = new Lexer(input);
var tokens = lexer.Tokenize();
var parser = new Parser(tokens);
var ast = parser.Parse();
var interpreter = new Interpreter();
interpreter.Interpret(ast);
}
}
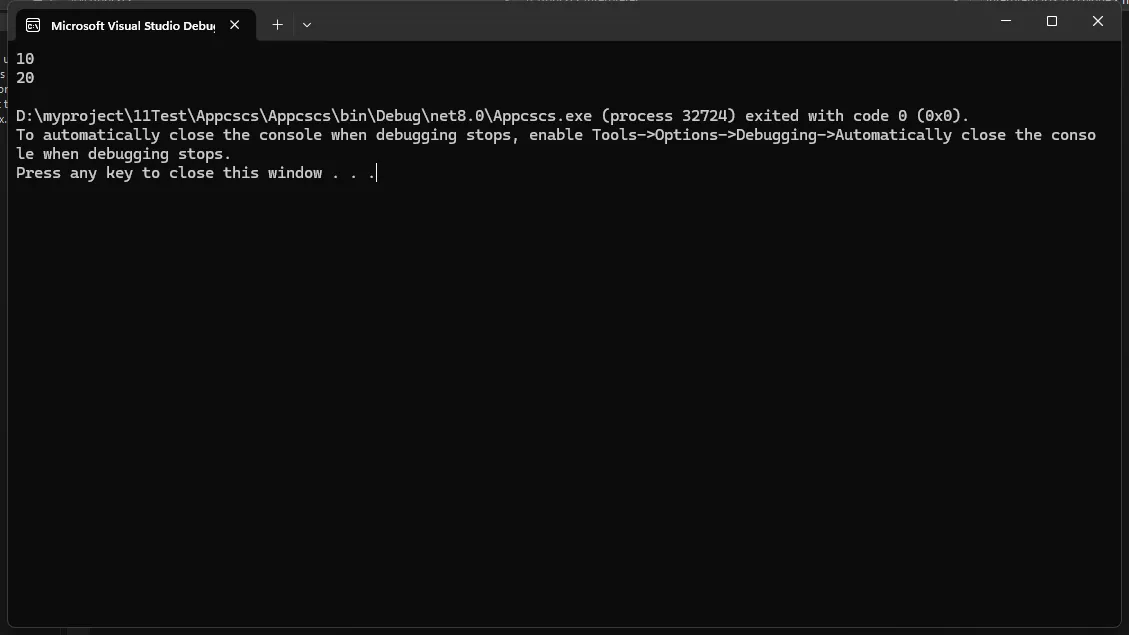
总结
通过以上步骤,我们在C#中实现了一个简单的自定义脚本语言。虽然这个示例非常基础,但它展示了如何构建一个从词法分析、语法解析到执行的完整流程。你可以在此基础上扩展更多功能,如更多的数据类型、控制流等。
本文作者:技术老小子
本文链接:
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!
目录