目录
你是否在开发WinForm应用时遇到过这样的困扰:按钮点击没反应?多个控件事件处理重复代码?事件绑定写法混乱?
别担心! 作为一名资深C#开发者,我见过太多因为事件处理不当导致的项目延期和用户体验问题。今天就来分享3种实战级的事件处理程序写法,让你的WinForm应用响应如飞!
🎯 核心问题分析
在WinForm开发中,事件处理是用户交互的核心。很多开发者在处理事件时容易遇到以下痛点:
- 响应迟缓:事件绑定方式不正确,导致用户操作无反应
- 代码冗余:多个相似控件重复编写相同逻辑
- 维护困难:事件处理程序分散,难以统一管理
这些问题不仅影响开发效率,更直接影响用户体验。让我们逐一击破!
💡 方案一:经典命名方法 - 稳定可靠的基础写法
对于初学者和需要调试的复杂逻辑,命名方法是最佳选择。
C#namespace AppWinformEvent3
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
private Button myButton;
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
// 初始化按钮并设置其属性
myButton = new Button
{
Text = "点击我",
Location = new System.Drawing.Point(100, 100),
Size = new System.Drawing.Size(100, 30)
};
// 注册点击事件处理程序
myButton.Click += MyButtonClickHandler;
// 将按钮添加到窗体控件集合中
Controls.Add(myButton);
// 设置窗体属性
Text = "事件处理示例";
Size = new System.Drawing.Size(300, 200);
}
// 点击事件处理程序
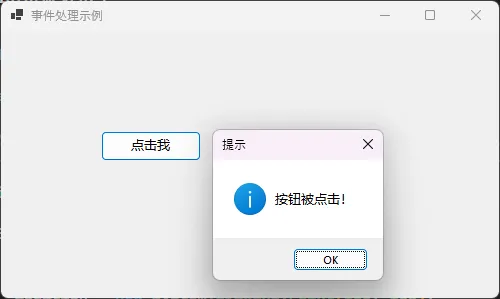
private void MyButtonClickHandler(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
MessageBox.Show("按钮被点击!", "提示", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Information);
}
}
}
🔥 实战技巧:
- 事件处理方法命名遵循
控件名称+事件类型+Handler模式 - 使用
sender参数可以获取触发事件的控件引用 - 记得设置MessageBox的图标和按钮类型,提升用户体验
- 实际业务中,事件注册代码IDE会自动生成在Desginer.cs文件中
🎯 方案二:共用事件处理 - 一招解决多控件问题
当多个控件需要执行相似逻辑时,共用事件处理程序是最优解。
C#using System;
using System.Windows.Forms;
public class MultiControlForm : Form
{
private Button button1;
private Button button2;
private Button button3;
public MultiControlForm()
{
InitializeButtons();
RegisterEvents();
SetupForm();
}
private void InitializeButtons()
{
button1 = new Button
{
Text = "保存",
Location = new System.Drawing.Point(50, 50),
Size = new System.Drawing.Size(80, 30),
Tag = "save" // 使用Tag属性存储操作类型
};
button2 = new Button
{
Text = "删除",
Location = new System.Drawing.Point(50, 100),
Size = new System.Drawing.Size(80, 30),
Tag = "delete"
};
button3 = new Button
{
Text = "刷新",
Location = new System.Drawing.Point(50, 150),
Size = new System.Drawing.Size(80, 30),
Tag = "refresh"
};
}
private void RegisterEvents()
{
// 所有按钮共用同一个事件处理程序
button1.Click += CommonClickHandler;
button2.Click += CommonClickHandler;
button3.Click += CommonClickHandler;
}
private void SetupForm()
{
Controls.AddRange(new Control[] { button1, button2, button3 });
Text = "多控件事件处理";
Size = new System.Drawing.Size(250, 300);
}
// 共用的点击事件处理程序
private void CommonClickHandler(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (sender is Button clickedButton)
{
string operation = clickedButton.Tag?.ToString() ?? "unknown";
switch (operation)
{
case "save":
HandleSave();
break;
case "delete":
HandleDelete();
break;
case "refresh":
HandleRefresh();
break;
default:
MessageBox.Show($"未知操作:{clickedButton.Text}");
break;
}
}
}
private void HandleSave()
{
MessageBox.Show("执行保存操作", "操作提示");
}
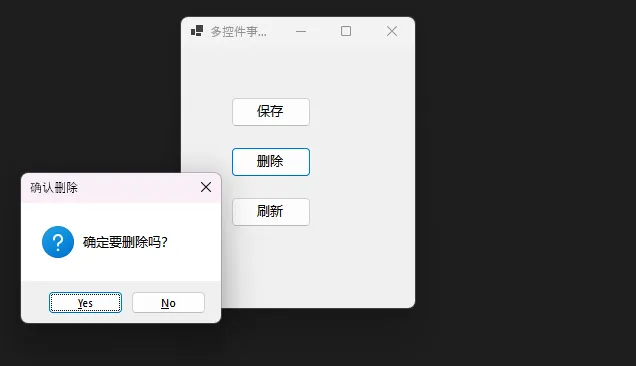
private void HandleDelete()
{
var result = MessageBox.Show("确定要删除吗?", "确认删除",
MessageBoxButtons.YesNo, MessageBoxIcon.Question);
if (result == DialogResult.Yes)
{
MessageBox.Show("删除成功!", "操作结果");
}
}
private void HandleRefresh()
{
MessageBox.Show("数据已刷新", "操作提示");
}
}
 🔥 性能优化技巧:
🔥 性能优化技巧:
- 使用
Tag属性存储控件的业务标识,避免硬编码,这是一个好东西,实际业务中存放不少东西,这个可以保存任何类型的变量,它是Object。 is操作符比as更安全,能避免空引用异常- 将具体业务逻辑抽取到独立方法中,便于单元测试
⚡ 方案三:Lambda表达式 - 简洁高效的现代写法
对于简单的事件处理逻辑,Lambda表达式是最佳选择。
C#namespace AppWinformEvent3
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
private Button button1;
private Button button2;
private TextBox statusText;
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
button1 = new Button
{
Text = "快速操作",
Location = new System.Drawing.Point(20, 20),
Size = new System.Drawing.Size(100, 35)
};
button2 = new Button
{
Text = "异步处理",
Location = new System.Drawing.Point(140, 20),
Size = new System.Drawing.Size(100, 35)
};
statusText = new TextBox
{
Location = new System.Drawing.Point(20, 70),
Size = new System.Drawing.Size(220, 100),
Multiline = true,
ScrollBars = ScrollBars.Vertical,
ReadOnly = true
};
SetupEventHandlers();
ConfigureForm();
}
private void SetupEventHandlers()
{
// 简单逻辑直接使用Lambda表达式
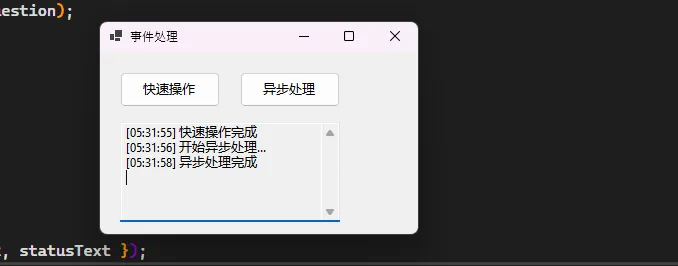
button1.Click += (sender, e) =>
{
statusText.AppendText($"[{DateTime.Now:HH:mm:ss}] 快速操作完成{Environment.NewLine}");
};
// 复杂逻辑可以调用其他方法
button2.Click += async (sender, e) =>
{
button2.Enabled = false;
statusText.AppendText($"[{DateTime.Now:HH:mm:ss}] 开始异步处理...{Environment.NewLine}");
try
{
await SimulateAsyncOperation();
statusText.AppendText($"[{DateTime.Now:HH:mm:ss}] 异步处理完成{Environment.NewLine}");
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
statusText.AppendText($"[{DateTime.Now:HH:mm:ss}] 错误: {ex.Message}{Environment.NewLine}");
}
finally
{
button2.Enabled = true;
}
};
// 窗体关闭确认
FormClosing += (sender, e) =>
{
var result = MessageBox.Show("确定要关闭应用程序吗?", "确认关闭",
MessageBoxButtons.YesNo, MessageBoxIcon.Question);
if (result == DialogResult.No)
{
e.Cancel = true;
}
};
}
private void ConfigureForm()
{
Controls.AddRange(new Control[] { button1, button2, statusText });
Text = "事件处理";
Size = new System.Drawing.Size(280, 220);
StartPosition = FormStartPosition.CenterScreen;
}
private async System.Threading.Tasks.Task SimulateAsyncOperation()
{
// 模拟异步操作
await System.Threading.Tasks.Task.Delay(2000);
}
}
}
 ⚡ Lambda表达式最佳实践:
⚡ Lambda表达式最佳实践:
- 简单逻辑(1-3行)直接写在Lambda中
- 复杂逻辑调用独立方法,保持代码整洁
- 异步操作使用
async/await模式,避免UI阻塞 - 异常处理要完整,防止程序崩溃
🛠️ 常见坑点与解决方案
坑点1:内存泄漏
C#// ❌ 错误写法 - 可能导致内存泄漏
someControl.SomeEvent += (s, e) => { this.DoSomething(); };
// ✅ 正确写法 - 及时取消订阅
private void Form_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
someControl.SomeEvent += HandleSomeEvent;
}
private void Form_FormClosed(object sender, FormClosedEventArgs e)
{
someControl.SomeEvent -= HandleSomeEvent; // 取消订阅
}
坑点2:跨线程操作UI
C#// ❌ 错误写法 - 跨线程异常
private void BackgroundWork()
{
// 在后台线程中直接操作UI会抛异常
statusLabel.Text = "处理完成";
}
// ✅ 正确写法 - 使用Invoke
private void BackgroundWork()
{
if (statusLabel.InvokeRequired)
{
statusLabel.Invoke((Action)(() => statusLabel.Text = "处理完成"));
}
else
{
statusLabel.Text = "处理完成";
}
}
📊 性能对比分析
| 方法类型 | 编译开销 | 运行性能 | 内存占用 | 调试友好度 | 适用场景 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 命名方法 | 低 | 最高 | 低 | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | 复杂业务逻辑 |
| 共用处理程序 | 低 | 高 | 最低 | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | 多控件相似操作 |
| Lambda表达式 | 中 | 高 | 中 | ⭐⭐⭐ | 简单快捷操作 |
🎯 总结与实战建议
通过本文的深入讲解,我们掌握了C#开发中三种核心的事件处理模式:
- 命名方法:适合复杂逻辑,调试友好,是企业级应用的首选
- 共用处理程序:解决多控件重复代码问题,显著提升开发效率
- Lambda表达式:现代化写法,代码简洁,适合快速开发
金句总结:
- "好的事件处理程序,让用户感受到的是即时响应,而不是漫长等待"
- "代码的优雅不在于炫技,而在于解决实际问题时的清晰与高效"
- "选择合适的事件处理模式,比盲目追求新语法更重要"
现在轮到你了!在实际项目中,你更偏向使用哪种事件处理方式?遇到过哪些让你头疼的事件处理难题?
欢迎在评论区分享你的经验,让我们一起成长!觉得有用的话,请转发给更多C#开发同行~ 🚀
💡 想学更多C#开发技巧?关注我们,每周分享实战干货!
本文作者:技术老小子
本文链接:
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!
目录