目录
在Windows Forms(WinForm)开发中,常用Label控件来显示只读文本;当我们转向WPF进行开发时,用于显示文本的常用控件则是TextBlock。TextBlock是WPF中非常轻量且灵活的文本呈现控件,相比Label而言,TextBlock有更丰富的格式化功能和更好的性能表现。本文将从WinForm到WPF的转型角度,为您介绍TextBlock在WPF中的应用场景和典型用法。
WinForm与WPF之比较
WinForm中的文本显示控件
在WinForm中,如果要在界面上展示文本内容,通常使用以下控件:
Label:用于显示只读文本,几乎无格式化选项,可更改字体、颜色等基本属性TextBox:可编辑的文本控件,允许用户输入
WPF中的文本显示控件
WPF中可以使用以下控件来显示文本:
TextBlock:轻量级文本显示控件,支持丰富的文本格式化(如Run、Span等)Label:WPF中也提供了Label控件,但更多是兼容WinForm的用法;Label通常会包含一个ContentPresenter来显示内容
在实际WPF开发中,推荐使用TextBlock实现只读文本的显示,因为它具有更好的可扩展性和渲染性能。
TextBlock的基础应用
在WPF中,使用TextBlock最简单的方式就是直接将要显示的文本通过Text属性绑定到控件上。下面是一个演示示例,包括在XAML中的用法和后端C#代码。
基本示例
C#<Window x:Class="AppTextBlock.MainWindow"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:AppTextBlock"
mc:Ignorable="d"
Title="MainWindow" Height="450" Width="800">
<StackPanel Margin="20">
<!-- 使用TextBlock显示静态文本 -->
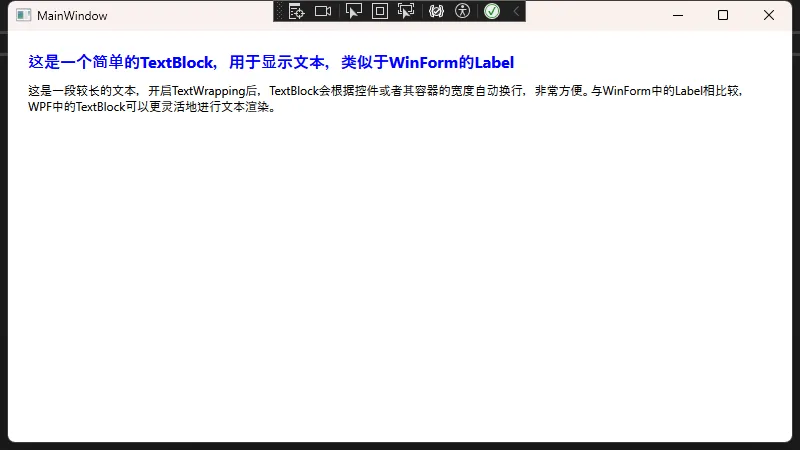
<TextBlock Text="这是一个简单的TextBlock,用于显示文本,类似于WinForm的Label"
FontSize="16"
FontWeight="Bold"
Foreground="Blue"/>
<!-- 多行文本示例 -->
<TextBlock TextWrapping="Wrap"
Margin="0,10,0,0">
这是一段较长的文本,开启TextWrapping后,TextBlock会根据控件或者其容器的宽度自动换行,非常方便。与WinForm中的Label相比较,WPF中的TextBlock可以更灵活地进行文本渲染。
</TextBlock>
</StackPanel>
</Window>
核心要点
TextBlock是一个轻量级控件,渲染性能好TextWrapping="Wrap"可以让文本根据控件宽度自动换行
TextBlock的高级用法
混合使用Run标签
和WinForm中的Label只能在一个文本元素中展示单一格式不同,WPF中TextBlock可以结合Run标签来实现多段文字的不同格式。
XML<Window x:Class="AppTextBlock.Window1"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:AppTextBlock"
mc:Ignorable="d"
Title="Window1" Height="450" Width="800">
<StackPanel>
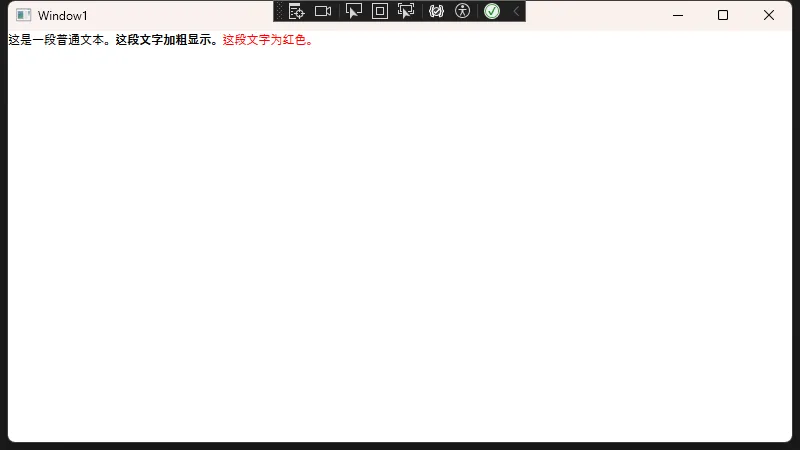
<TextBlock>
<!-- 普通文本 -->
<Run Text="这是一段普通文本。" />
<!-- 加粗文本 -->
<Run Text="这段文字加粗显示。" FontWeight="Bold" />
<!-- 彩色文本 -->
<Run Text="这段文字为红色。" Foreground="Red" />
</TextBlock>
</StackPanel>
</Window>
文本换行与行高
XML<Window x:Class="AppTextBlock.Window2"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:AppTextBlock"
mc:Ignorable="d"
Title="Window2" Height="450" Width="800">
<Grid>
<TextBlock TextWrapping="Wrap"
LineHeight="30"
LineStackingStrategy="BlockLineHeight">
<!-- 使用LineBreak手动换行 -->
第一行内容<LineBreak/>
第二行内容<LineBreak/>
第三行内容
</TextBlock>
</Grid>
</Window>
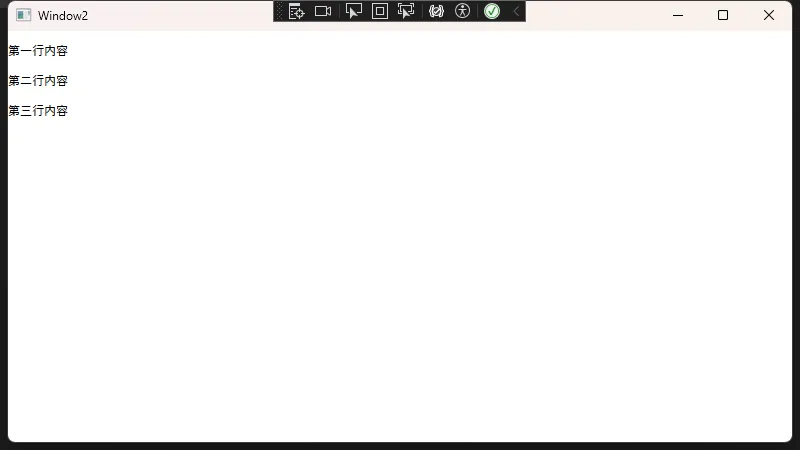
TextWrapping="Wrap":自动换行LineHeight="30":行高设置为30LineStackingStrategy="BlockLineHeight":以行高为基准进行堆叠
数据绑定示例
在WPF的MVVM模式下,TextBlock可以通过Binding来与ViewModel中的属性关联,从而实现数据驱动的视图更新。下面是一个简单的示例。
ViewModel代码
C#using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace AppTextBlock
{
public class MainViewModel : INotifyPropertyChanged
{
private string _displayText;
public string DisplayText
{
get => _displayText;
set
{
_displayText = value;
OnPropertyChanged(nameof(DisplayText));
}
}
public MainViewModel()
{
// 构造函数中初始化数据
DisplayText = "Hello,WPF的TextBlock!";
}
public event PropertyChangedEventHandler PropertyChanged;
protected virtual void OnPropertyChanged(string propertyName)
{
PropertyChanged?.Invoke(this, new PropertyChangedEventArgs(propertyName));
}
}
}
绑定到TextBlock
XML<Window x:Class="AppTextBlock.Window3"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:AppTextBlock"
mc:Ignorable="d"
Title="Window3" Height="450" Width="800">
<Window.DataContext>
<local:MainViewModel/>
</Window.DataContext>
<Grid>
<StackPanel VerticalAlignment="Center" HorizontalAlignment="Center">
<TextBlock Text="{Binding DisplayText}"
FontSize="18"
FontWeight="Bold"
Foreground="Purple"/>
</StackPanel>
</Grid>
</Window>
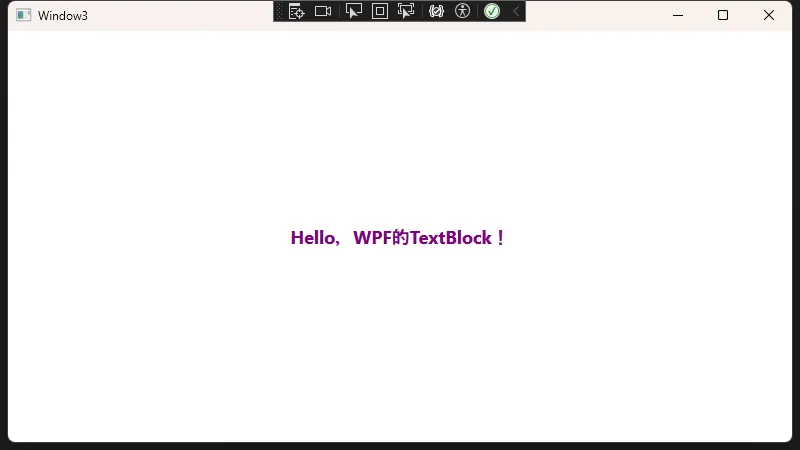
这样在程序运行时,如果MainViewModel的DisplayText属性更新,UI上TextBlock显示的文本将会自动刷新。
TextBlock vs. WinForm的Label
| 特性/属性 | WinForm中的Label | WPF中的TextBlock |
|---|---|---|
| 只读文本显示 | 是 | 是 |
| 文本格式化 | 基本字体设置 | 灵活支持Run等标签 |
| 支持数据绑定 | 需手动处理(或使用第三方框架) | 原生支持数据绑定 |
| 自动换行 | 使用AutoSize或设置大小 | TextWrapping更灵活 |
| 性能及渲染 | 一般,GDI+渲染 | 优秀,使用DirectX渲染 |
| 设计器支持 | WinForm拖拽设计器 | Visual Studio / Blend 设计器 |
结束语
从WinForm转型到WPF中,TextBlock是显示只读文本的理想选择。与WinForm中常用的Label控件相比,TextBlock不仅性能更好,而且支持更丰富的格式化选择。同时WPF本身的MVVM数据绑定模式也让界面逻辑与数据逻辑更好地分离,实现真正的组件化与模块化开发。
在实际项目中,如果需要显示的文本内容很复杂,或者需要结合Run、Span等子元素实现多样式展示,TextBlock都是很好的选择。希望本文能帮助您快速上手WPF的TextBlock控件!
本文作者:技术老小子
本文链接:
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!