你有没有想过,为什么有些AI助手回答问题总让人觉得"机械感"爆棚,而有些却能让你感觉像在跟老朋友聊天?
关键在于性格系统设计——这玩意儿远比你想象的重要。
咱们今天要聊的,不是那种简单调用个ChatGPT API就完事儿的玩具项目,而是真正工程化、可扩展、生产级别的聊天机器人架构。上周末打磨了一下这个,我用Semantic Kernel搭了个框架,不仅支持多性格切换、插件动态加载,还能流式响应、自动函数调用。最关键的是——代码结构清晰到新手都能看懂,这个写着写着,我又加上了简单的Excel,文件,指定数据库的一些操作插件,算是一个学习用的例子吧。
这篇文章会带你从零开始,拆解整个系统的核心设计思路,让你看完就能直接上手改造成自己的AI应用。
💡 为什么大部分聊天机器人都"没灵魂"?
痛点一: 硬编码系统提示词,改个性格得重新发布
很多开发者习惯把System Prompt直接写死在代码里:
csharp// ❌ 典型的错误做法
var systemPrompt = "你是一个专业的AI助手... ";
chatHistory.AddSystemMessage(systemPrompt);
这样搞的后果是:老板突然说"客服场景需要更热情点",你得改代码、重新测试、发布——一顿操作猛如虎,实际就改了一句话。
痛点二:插件扩展全靠手动注册,维护成本炸裂
早期我见过最离谱的代码是这样:
csharp// ❌ 每加一个插件就要改一次代码
kernel. Plugins.AddFromObject(new TimePlugin());
kernel.Plugins.AddFromObject(new WeatherPlugin());
kernel.Plugins.AddFromObject(new CalculatorPlugin());
// 新需求来了: 加个Excel操作插件? 继续加代码吧...
这种模式下,产品经理提个需求"能不能让AI帮用户生成Excel报表? ",你要做的事情包括:写插件代码→手动注册→测试→发布。整个流程像回到了石器时代。
痛点三:流式响应和普通响应割裂,用户体验不一致
有些场景需要打字机效果(比如知识问答),有些场景需要快速返回结果(比如数据查询)。但很多系统要么全用流式、要么全不用,没法根据场景动态切换。
运行效果
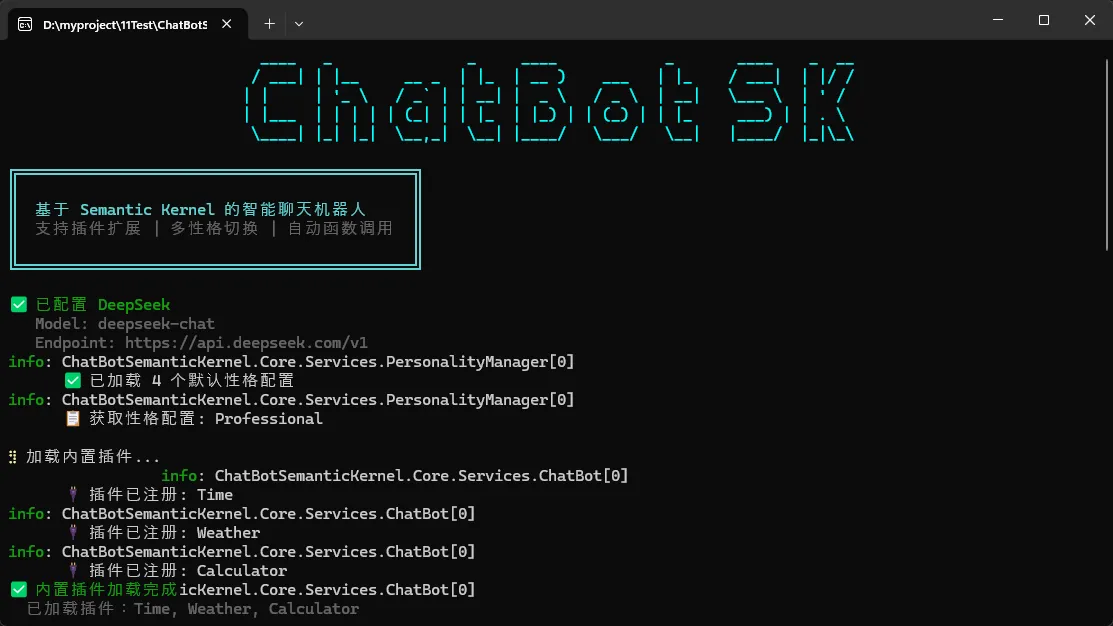
你是否遇到过这样的场景:客户要求在Windows窗体上实现自定义绘图效果,比如绘制统计图表、自定义控件外观,或者实现图片的特殊处理?传统的控件已经无法满足需求,这时候你就需要掌握GDI+ 这个强大的图形绘制技术了。
作为.NET Framework的重要组成部分,GDI+(Graphics Device Interface Plus)为WinForm开发者提供了丰富的2D图形绘制能力。从简单的线条绘制到复杂的图像处理,GDI+都能轻松胜任。本文将从零开始,带你掌握GDI+的核心概念和实战技巧,让你的WinForm应用更加生动精彩!
💡 什么是GDI+?为什么要学它?
🔍 问题分析
很多C#开发者在面临以下场景时会感到困扰:
- 自定义控件外观:系统控件样式单一,无法满足UI设计需求
- 动态图表绘制:需要根据数据实时生成图表和统计图
- 图像处理需求:对图片进行缩放、裁剪、滤镜等操作
- 游戏开发基础:简单2D游戏的图形渲染
传统的控件拖拽式开发已经无法满足这些个性化需求,这时候掌握GDI+就显得尤为重要。
🎨 GDI+核心优势
GDI+ 是微软为.NET平台专门设计的图形API,相比传统GDI具有以下优势:
- 面向对象设计:更符合C#编程习惯
- 抗锯齿支持:图形更加平滑美观
- 丰富的绘制功能:支持渐变、纹理、Alpha混合
- 图像格式支持:原生支持PNG、JPEG、GIF等多种格式
🚀 GDI+基础概念详解
📐 Graphics类:绘图的核心
Graphics类是GDI+的核心,它代表了一个绘图表面。获取Graphics对象的三种常见方式:
c#// 在Paint事件中获取
private void Form1_Paint(object sender, PaintEventArgs e)
{
Graphics g = e.Graphics;
// 在这里进行绘制操作
}
c#// 通过控件创建
Graphics g = this.CreateGraphics();
// 使用完后记得释放资源
g.Dispose();
c#// 通过图像创建(用于离线绘制)
Bitmap bitmap = new Bitmap(800, 600);
Graphics g = Graphics.FromImage(bitmap);
// 绘制完成后保存图像
bitmap.Save("output.png");
g.Dispose();
bitmap.Dispose();
作为一名C#开发者,你是否遇到过这样的困扰:项目需求频繁变更,每次新增功能都要重新编译整个系统? 客户要求灵活定制功能,但传统的单体架构让你束手无策?
今天我们就来解决这个痛点!通过MEF(Managed Extensibility Framework)插件化架构,让你的应用像积木一样灵活组装,新功能即插即用,无需重启系统。本文将通过一个完整的工业数据采集应用,带你掌握插件化开发的核心技巧。
🤔 为什么需要插件化架构?
传统开发的三大痛点
1. 紧耦合问题
c#// ❌ 传统方式:硬编码依赖
public class DataProcessor
{
public void Process(string data)
{
// 直接依赖具体实现
var textProcessor = new TextProcessor();
var numberProcessor = new NumberProcessor();
// 新增处理器需要修改这里
}
}
2. 扩展性差
- 每次新增功能都要修改主程序
- 部署时必须重启整个系统
- 无法根据客户需求灵活组装功能
3. 维护成本高
- 功能模块相互影响
- 测试复杂度随功能增加而指数增长
- 代码复用性差
插件化架构的优势
✅ 松耦合:主程序与插件通过接口通信
✅ 热插拔:运行时动态加载/卸载插件
✅ 高扩展:新功能独立开发,无需修改主程序
✅ 易维护:插件独立测试,故障隔离
🚀 MEF核心概念速通
三大核心机制
1. Export(导出)- 插件声明自己
c#[Export(typeof(IPlugin))] // 我是一个插件
[ExportMetadata("Name", "数据验证器")] // 我的元数据
public class DataValidatorPlugin : IPlugin
{
// 插件实现
}
2. Import(导入)- 主程序发现插件
c#[ImportMany(typeof(IPlugin))]
private IEnumerable<Lazy<IPlugin>>? _plugins; // 自动注入所有插件
3. Composition(组合)- 自动装配
c#var container = new CompositionContainer(catalog);
container.ComposeParts(this); // 魔法发生的地方
💡 记住这个黄金法则:Export声明能力,Import表达需求,Composition自动匹配!
🛠️ 实战项目:工业数据采集系统
让我们通过一个真实的工业场景来掌握MEF。这个系统需要支持多种数据处理插件:文本处理、数值计算、数据验证、实时采集等。
📁 项目结构设计
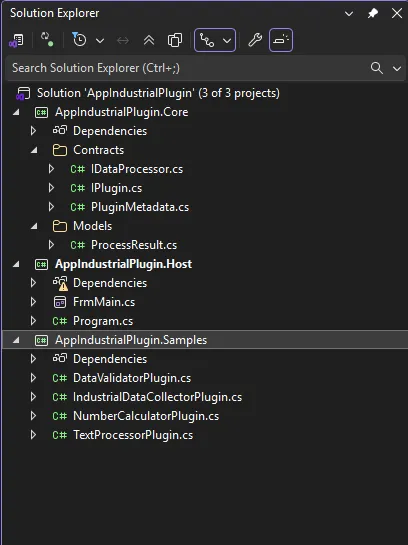
你是否曾经为生产计划的混乱而头疼?库存积压和缺料风险让你夜不能寐?作为一名C#开发者,我将带你用代码构建一套完整的MRP(物料需求计划)系统。这不仅仅是一个技术演示,更是一个能够真正解决制造业痛点的实战项目。在这篇文章中,我们将使用C#和Spectre.Console框架,从BOM结构设计到实时库存预警,一步步搭建一个功能完备的智能制造系统,当然这里只是给一个设计逻辑与最小实例。
🎯 制造业的数字化痛点
在传统制造企业中,生产计划往往面临三大核心难题:
📊 库存预测不准确:无法精确预知何时会缺料,导致生产中断或库存积压
⏰ 信息滞后严重:Excel表格满天飞,数据更新不及时,决策总是慢半拍
🔗 部门协同困难:生产、采购、仓储各自为战,缺乏统一的数据视图
这些问题的本质是缺乏一个实时、智能的物料需求计划系统。而C#凭借其强大的面向对象特性和丰富的生态系统,恰好是构建此类系统的理想选择。
💡 MRP系统架构设计
🏗️ 核心模块划分
一个完整的MRP系统应该包含以下核心模块:
c#// MRP预测记录 - 系统的数据核心
public class MRPForecastRecord
{
public string MaterialCode { get; set; } // 物料编码
public DateTime ForecastTime { get; set; } // 预测时间
public decimal DemandQuantity { get; set; } // 需求数量
public decimal ProjectedStock { get; set; } // 预测库存
public decimal ASNQuantity { get; set; } // ASN到货数量
public string Status { get; set; } // 库存状态
}
// 简化的BOM结构 - 生产配方管理
public class SimpleBOM
{
public string ProductCode { get; set; } = "PROD001";
public Dictionary<string, decimal> MaterialUsage { get; set; } = new Dictionary<string, decimal>
{
{ "MAT001", 1.5m }, // 每个产品需要1.5KG原料001
{ "MAT002", 0.8m }, // 每个产品需要0.8M原料002
{ "MAT003", 2.0m } // 每个产品需要2.0PCS原料003
};
}
你是否还在为复杂的工业图形绘制而头疼?传统的GDI+绘图库性能差、效果单一,而Web前端方案又无法满足桌面应用的需求。今天,我将带你用C#和SkiaSharp构建一个功能完整的工业管线绘制系统,不仅支持实时交互编辑,还能展示流体动画效果。
这不是纸上谈兵的Demo,而是一个可以直接用于生产环境的完整解决方案!从基础绘制到高级交互,从性能优化到用户体验,我们将一步步解析每个关键技术点。
🎯 解决的核心问题
传统绘图方案的痛点
在工业软件开发中,我们经常遇到这些难题:
- GDI+性能瓶颈:复杂图形卡顿严重
- 交互体验差:拖拽、编辑功能实现困难
- 动画效果单一:难以实现流体流动等动态效果
- 跨平台支持弱:Windows专有API限制
SkiaSharp的优势
SkiaSharp作为Google Skia的C#封装,完美解决了这些问题:
- 硬件加速渲染,性能卓越
- 丰富的绘图API,效果专业
- 跨平台支持,一套代码多端运行
- 与WinForms/WPF无缝集成
💡 系统架构设计
🏗️ 核心数据模型
首先定义管线段的数据结构,这是整个系统的基础:
c#public class PipelineSegment
{
public SKPoint StartPoint { get; set; }
public SKPoint EndPoint { get; set; }
public float CurvatureStrength { get; set; } // 弧度强度:-1到1
public Guid Id { get; set; }
}
public class PipelineStyle
{
public float PipeWidth { get; set; }
public SKColor PipeColor { get; set; }
public SKColor FlowColor { get; set; }
public float FlowSpeed { get; set; }
public PipelineType PipelineType { get; set; }
}
设计亮点:
CurvatureStrength让每个管线段都可以调整弧度,无需复杂的类型区分- 统一的样式管理,便于主题切换和批量操作
🎨 绘制引擎核心
SkiaSharp的绘制逻辑清晰简洁,性能出色:
c#private void DrawPipelineSegment(SKCanvas canvas, PipelineSegment segment, SKPaint paint)
{
if (Math.Abs(segment.CurvatureStrength) < 0.01f)
{
// 直线段 - 最优性能
canvas.DrawLine(segment.StartPoint, segment.EndPoint, paint);
}
else
{
// 弧形段 - 二次贝塞尔曲线
var controlPoint = GetCurvatureControlPoint(segment);
using (var path = new SKPath())
{
path.MoveTo(segment.StartPoint);
path.QuadTo(controlPoint, segment.EndPoint);
canvas.DrawPath(path, paint);
}
}
}