C#字符串操作的性能"陷阱":为什么你的代码慢得像蜗牛?
你有没有遇到过这种情况?
写了个看似简单的日志记录功能,循环里拼接几千条数据,结果程序卡得像PPT。打开性能分析器一看——好家伙,90%的CPU时间都耗在字符串操作上。改用StringBuilder后,速度直接提升了50倍。
这不是段子。上周帮一个朋友排查生产环境的性能问题,发现他们的报表生成模块,处理5000条数据需要18秒。罪魁祸首?一个无辜的+=操作符。
今天咱们就掰开揉碎了讲讲:字符串拼接为啥这么慢?StringBuilder凭什么快?以及——什么场景该用哪个?
读完这篇,你能拿到:
✅ 字符串不可变性的底层真相(不是背概念)
✅ 3种实战场景的性能对比数据(附完整测试代码)
✅ 2个可直接复用的优化模板
✅ 避开5个常见的性能陷阱
🔍 为什么字符串操作会成为性能杀手?
不可变性:被忽视的内存杀手
很多人知道C#的string是"不可变的"(immutable),但真正理解其影响的不多。
咱们看个例子。假设你这样写:
c#string result = "Hello";
result += " World";
result += "!";
你以为的操作:在原字符串后面追加内容。
实际发生的事:
- 创建新字符串"Hello World"(分配新内存)
- 复制"Hello"的内容过去
- 追加" World"
- 原来的"Hello"变成垃圾,等待GC回收
- 再创建新字符串"Hello World!"
- 复制"Hello World"... (又是一轮循环)
三次赋值 = 创建3个字符串对象 + 2次完整内容复制
想象一下:如果循环1000次呢?每次操作都要复制之前所有的内容。这就像搬家——每次添置新家具,都要把整个房子的东西搬到更大的房子里。
真实场景的恐怖数据
我专门做了个测试(测试环境:. NET 10.0,100000次拼接操作):
c#// 方法1:直接用+拼接
var sw = Stopwatch.StartNew();
string result = "";
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++)
{
result += "Item" + i + ",";
}
sw.Stop();
c#// 方法2:使用StringBuilder
var sw = Stopwatch.StartNew();
var sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++)
{
sb.Append("Item").Append(i).Append(",");
}
string result = sb.ToString();
sw.Stop();
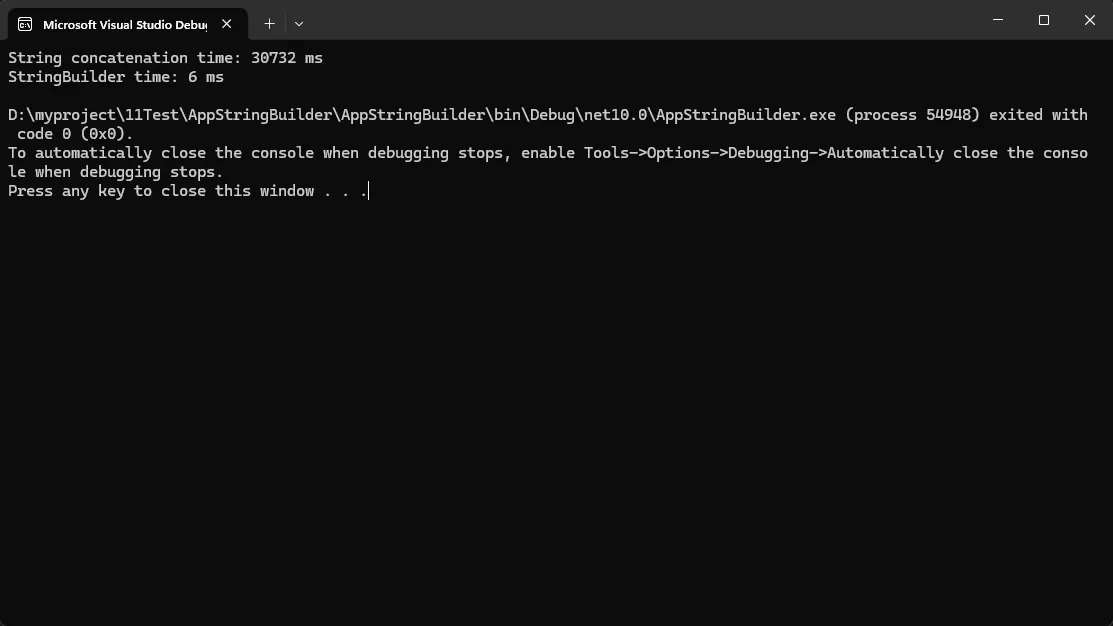 这还只是1万次,性能差距几十倍。生产环境动辄几十万条数据,差距会更夸张。
这还只是1万次,性能差距几十倍。生产环境动辄几十万条数据,差距会更夸张。
你是否在为工业监控系统的实时报警处理而头疼?传统的直接通信模式在面对大量设备报警时往往力不从心,消息丢失、处理延迟、系统耦合度高等问题层出不穷。今天,我将通过一个完整的C#工业报警系统案例,带你深入理解如何用RabbitMQ构建高可靠、高性能的消息处理架构。本文不仅提供完整可运行的代码,更重要的是分享在生产环境中的实战经验和踩坑指南。
🎯 问题分析:工业报警系统的核心挑战
传统报警系统的痛点
在传统的工业监控系统中,我们通常面临以下核心问题:
1. 消息丢失风险高
- 网络故障导致报警信息无法送达
- 系统重启时未处理的报警丢失
- 处理失败的消息无法重试
2. 系统耦合度过高
- 报警产生方与处理方直接耦合
- 新增报警处理逻辑需要修改现有系统
- 难以实现灵活的报警分发策略
3. 性能瓶颈明显
- 同步处理模式导致响应缓慢
- 无法有效处理突发大量报警
- 缺乏负载均衡机制
💡 解决方案:基于RabbitMQ的分布式报警架构
🏗️ 核心设计思路
我们采用RabbitMQ的Direct Exchange模式来构建报警系统,通过路由键实现精确的消息分发。整体架构如下:
- 生产者:各类工业设备发送报警消息
- Exchange:Direct类型,根据路由键精确分发
- 消费者:不同的报警处理服务,可按需订阅
- 路由键规则:
设备类型.车间格式,如PLC.A、Sensor.B
🎪 技术亮点
- 消息持久化:确保系统重启后消息不丢失
- 手动确认机制:只有处理成功才确认消息
- 灵活的订阅筛选:支持通配符模式订阅
- 异步处理:提升系统响应性能
🛠️ 架构设计
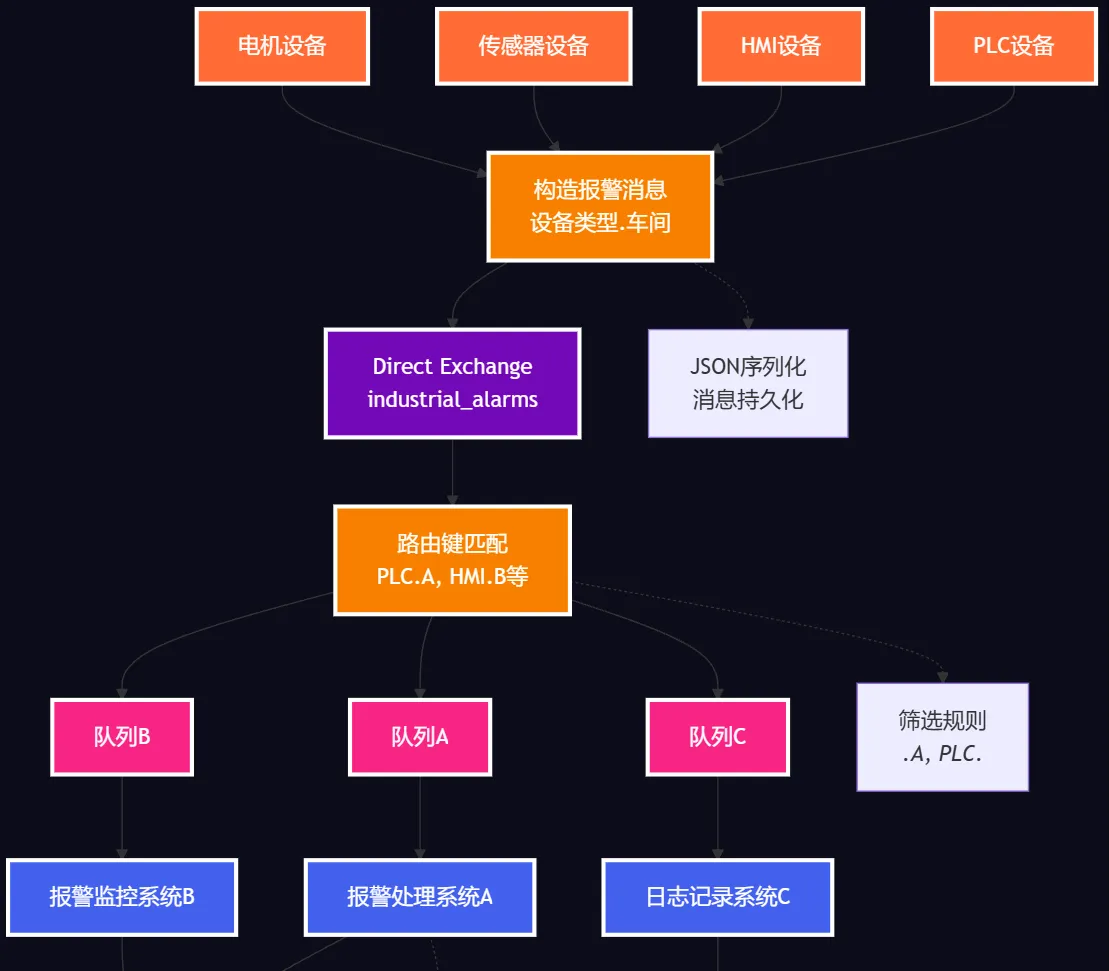
🛠️ 代码实战:完整的报警系统实现
📦 项目配置
首先,让我们看看项目的依赖配置:
xml<Project Sdk="Microsoft.NET.Sdk">
<PropertyGroup>
<OutputType>WinExe</OutputType>
<TargetFramework>net8.0-windows</TargetFramework>
<UseWindowsForms>true</UseWindowsForms>
</PropertyGroup>
<ItemGroup>
<PackageReference Include="Newtonsoft.Json" Version="13.0.4" />
<PackageReference Include="RabbitMQ.Client" Version="7.2.0" />
</ItemGroup>
</Project>
🚀 WPF依赖属性实战指南:从零开始构建自定义依赖属性
在WPF开发中,你是否遇到过这样的困扰:想要创建一个可以支持数据绑定、样式设置和动画的自定义控件,但普通属性无法满足需求?或者在开发过程中发现自定义控件的属性无法在XAML中正常绑定?
本文将彻底解决这些问题,通过3个实战案例,带你深入理解WPF依赖属性系统,掌握自定义依赖属性的核心技巧,让你的自定义控件具备原生WPF控件的强大功能。
🎯 为什么需要自定义依赖属性?
普通属性 VS 依赖属性
在WPF中,普通的.NET属性虽然能存储数据,但缺少以下关键特性:
- 数据绑定支持:无法作为绑定目标
- 样式设置:不能通过Style进行统一管理
- 动画支持:无法参与WPF动画系统
- 属性变更通知:缺少强大的变更检测机制
c#// ❌ 普通属性 - 功能有限
public class MyControl : UserControl
{
public string Title { get; set; } // 无法绑定、无法设置样式
}
// ✅ 依赖属性 - 功能完整
public class MyControl : UserControl
{
public static readonly DependencyProperty TitleProperty =
DependencyProperty.Register("Title", typeof(string), typeof(MyControl));
public string Title
{
get { return (string)GetValue(TitleProperty); }
set { SetValue(TitleProperty, value); }
}
}
🔒 C#中的SafeHandle:让你的Win32 API调用更安全更优雅
在日常的C#开发中,你是否遇到过这样的困扰:调用Win32 API时担心内存泄漏?处理文件句柄时不知道何时释放?多线程环境下句柄管理变得复杂?如果你点头了,那么今天这篇文章将彻底解决你的痛点。
SafeHandle 是.NET框架中一个被严重低估但极其重要的类,它专门用于安全地管理非托管资源句柄。通过掌握SafeHandle的正确使用方式,你将告别句柄泄漏的噩梦,让代码更加健壮和优雅。
🤔 为什么需要SafeHandle?深度剖析痛点
传统句柄管理的三大陷阱
在没有SafeHandle之前,开发者直接使用IntPtr来管理Win32句柄,这带来了诸多问题:
1. 内存泄漏风险
c#// ❌ 危险的传统做法
IntPtr fileHandle = CreateFile(...);
// 如果这里发生异常,句柄永远不会被释放
DoSomething();
CloseHandle(fileHandle);
2. 多线程竞争条件
当一个线程正在使用句柄时,另一个线程可能同时尝试释放它,导致程序崩溃。
3. 异常安全性问题
异常抛出时,传统的句柄清理代码可能不会执行。
🛡️ SafeHandle:你的句柄守护神
核心优势解析
SafeHandle通过以下机制解决了传统方案的所有问题:
- 自动资源管理:利用.NET垃圾回收器确保资源释放
- 线程安全:内置引用计数机制防止竞争条件
- 异常安全:即使发生异常也能正确清理资源
🔥 实战解决方案:5种常见场景的最佳实践
📁 方案一:安全的文件句柄管理
c#using Microsoft.Win32.SafeHandles;
namespace AppSafeFileHandle
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
SafeFileExample.ReadFileWithSafeHandle("hi.txt");
}
}
internal class SafeFileExample
{
public static void ReadFileWithSafeHandle(string filePath)
{
// 使用SafeFileHandle,自动管理文件句柄
using (var fileStream = new FileStream(filePath, FileMode.Open))
{
SafeFileHandle safeHandle = fileStream.SafeFileHandle;
// 即使发生异常,句柄也会被正确释放
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
fileStream.Read(buffer, 0, buffer.Length);
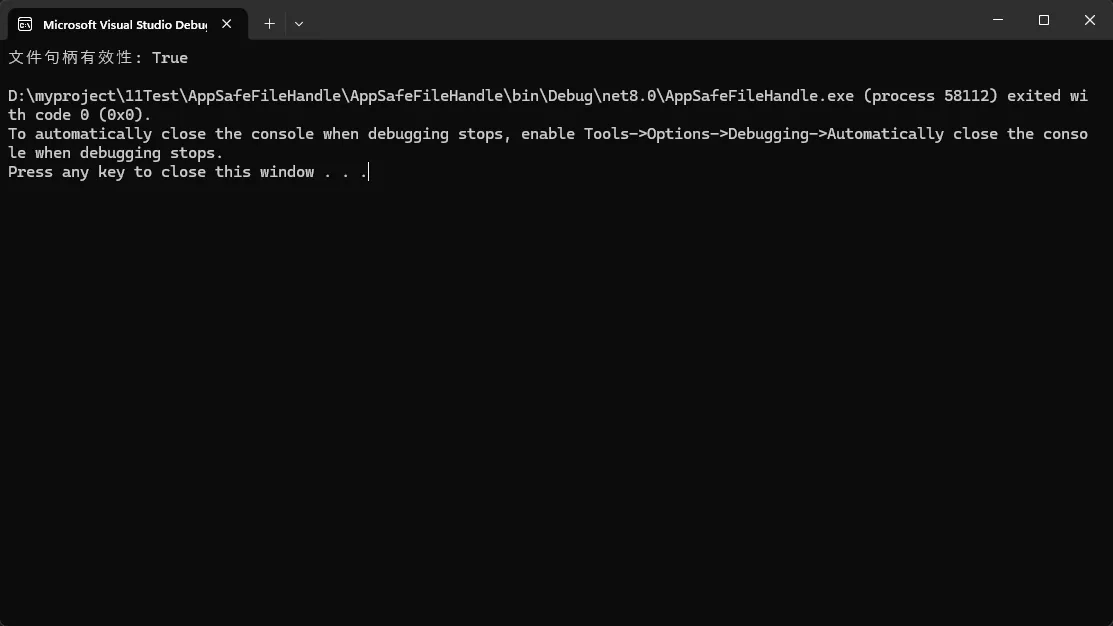
Console.WriteLine($"文件句柄有效性: {!safeHandle.IsInvalid}");
} // 自动释放资源
}
}
}
📊 Matplotlib散点图与条形图:别再画出"程序员审美"的图表了
说实话,第一次看到同事用Matplotlib画的数据图时,我差点以为是Excel 2003自动生成的——密密麻麻的散点、毫无美感的配色、挤成一团的坐标轴标签。更尴尬的是,这图还要放进给客户的分析报告里。
数据显示,超过60%的Python开发者都在用Matplotlib做可视化,但真正能把图表做得"专业又好看"的不到15%。问题不在工具,而在于大家对scatter()和bar()这些基础函数的参数体系理解不够深入。今天咱们就彻底搞懂这两类图表,顺便拯救一下程序员的审美。
看完这篇,你能掌握:
- 散点图的5种高级用法(不只是打点)
- 条形图的视觉陷阱与破解方案
- 8个参数让图表瞬间"高级感"拉满
- 一套可直接复用的配色方案模板
🎯 为什么你的图表总是"丑得有特点"
常见灾难现场
见过这样的代码吗?
pythonimport matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
matplotlib.use('TkAgg')
x = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
y = [2, 4, 6, 8, 10]
plt.scatter(x, y)
plt.show()
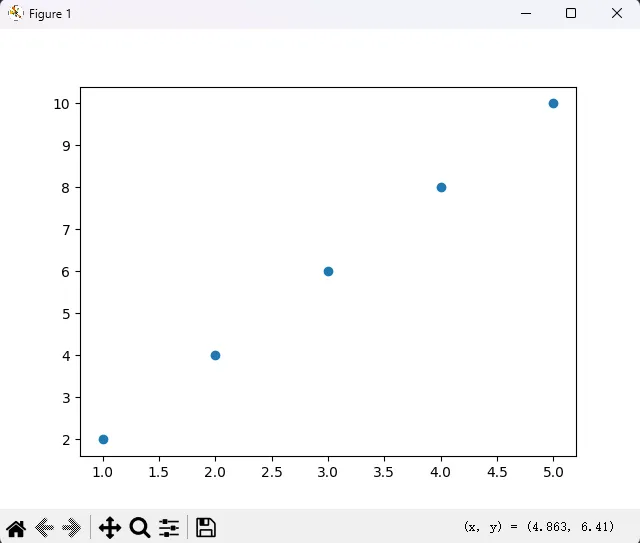 运行后——一片蓝点,孤零零地悬在白底上。没标题、没图例、坐标轴标签也不知道啥意思。这就像给客户发了份没署名、没日期、没主题的合同。
运行后——一片蓝点,孤零零地悬在白底上。没标题、没图例、坐标轴标签也不知道啥意思。这就像给客户发了份没署名、没日期、没主题的合同。
问题根源三连击:
- 参数默认值依赖症:90%的人只用前两个位置参数
- 配色随缘主义:蓝色打天下,从不考虑色盲用户
- 细节恐惧症:觉得调整间距、字体是"浪费时间"
但真相是:客户看不懂的图表=无效加班。某数据分析团队统计,优化可视化后,报告理解时间缩短40%,需求返工率降低55%。
🔍 散点图的底层逻辑:不只是plot()的兄弟
很多人误以为scatter()就是plot()加个标记点样式。错!
核心差异对照
| 维度 | plot() | scatter() |
|---|---|---|
| 数据关系 | 强调连续性 | 强调离散分布 |
| 性能 | 大数据集友好 | 点过多会卡顿 |
| 定制性 | 统一样式 | 每个点可单独配置 |
关键洞察:scatter()的真正价值在于多维信息映射——通过颜色、大小、形状同时展现3-4个数据维度。